World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (1): 10-17.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.001
• Review Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Azzah S Alharbi1,2( ), Raghad Hassan Sanyi3, Esam I Azhar2,4
), Raghad Hassan Sanyi3, Esam I Azhar2,4
Received:2024-05-29
Accepted:2024-10-20
Online:2025-01-23
Published:2025-01-01
Contact:
Azzah S Alharbi
E-mail:asalharbi3@kau.edu.sa
Azzah S Alharbi, Raghad Hassan Sanyi, Esam I Azhar. Bacteria and host: what does this mean for sepsis bottleneck?[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(1): 10-17.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.001
Table 1.
Spectrum of bacteria causing sepsis in different patient groups
| Patient group | Bacteria | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Neonates | ||
| Early onset (within the first 72 h) | Coagulase-negative staphylococci | [ |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | [ | |
| Group B Streptococcus | [ | |
| Escherichia coli | [ | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | [ | |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | [ | |
| Late onset (after 72 h) | Coagulase-negative staphylococci, gram-negative bacilli, Enterobacteriaceae, and both methicillin- sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | [ |
| Children | Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas, and Meningococcus | [ |
| Haemophilus influenza | [ | |
| Proteus mirabilis | [ | |
| Adults | Escherichia coli | [ |
| Staphylococcus aureus | [ | |
| Pseudomonas spp, Acinetobacter spp, Enterobacter spp | [ | |
| Immunocompromised adults | Community acquired gram-negative bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus, gram-positive cocci (group A-β hemolytic Streptococcus that produces pyrogenic exotoxin) | [ |
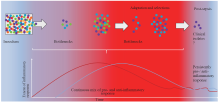
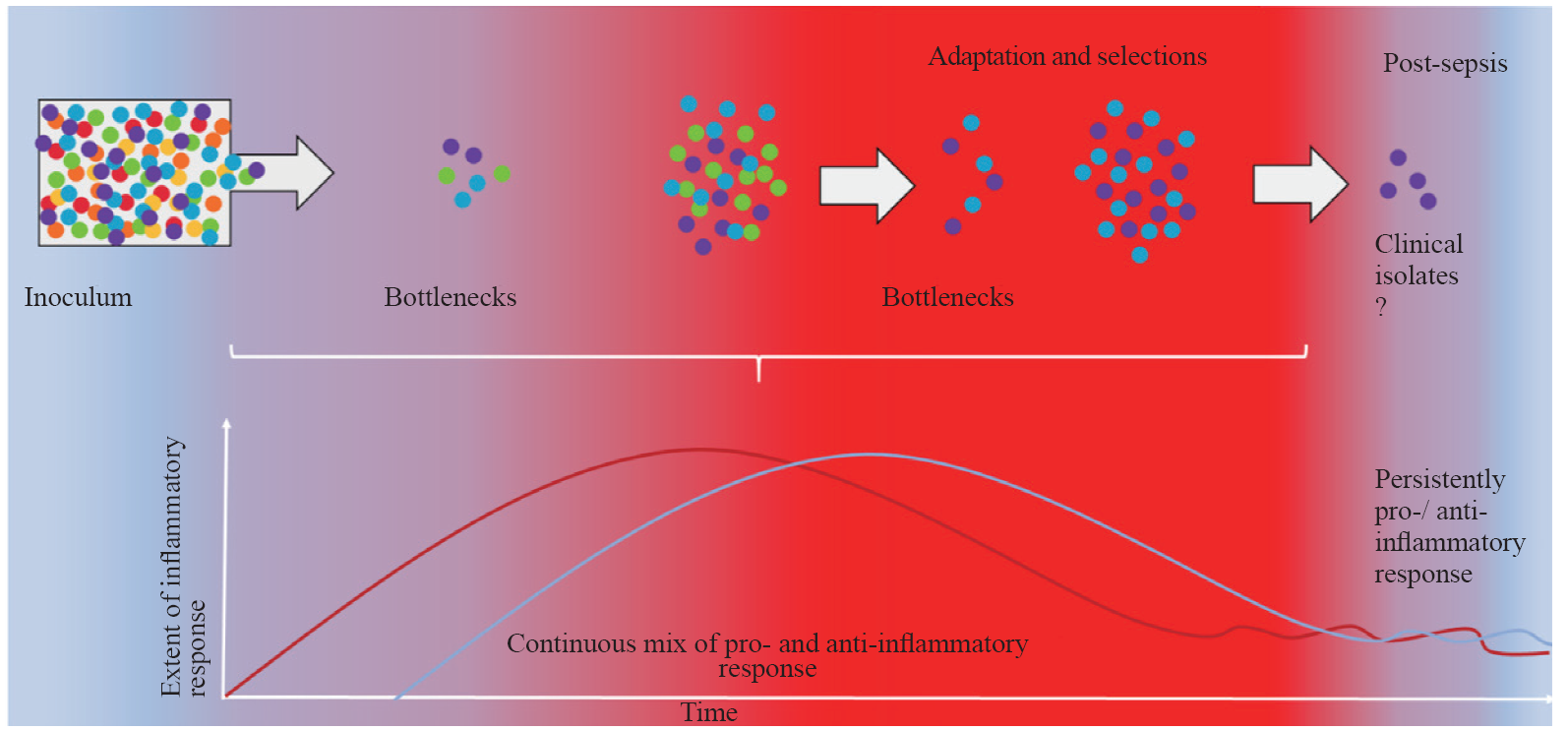
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of parallel dynamics of selective pressures experienced by pathogens, which produce so-called bottlenecks, and the quality of the systemic inflammatory response. Recent experimental evidence has led to the development of a new sepsis model, challenging the traditional sepsis inflammatory concept in which an initial hyper-inflammatory response is followed by an immunosuppressive phase. This new sepsis model suggests the existence of a mixed inflammatory (heterogeneous) response in the initial phase of septicaemia.[69] The scale of the inflammatory response in sepsis can create a hostile environment for pathogens, applying strong selection pressure on the bacterial population (inoculum). This pressure may continuously result in a “bottleneck” effect, reducing the overall diversity of the bacterial population by allowing only specific clones with traits that enable them to survive immune assault to persist and proliferate. These surviving clones often possess adaptations, such as increased virulence factors or resistance to host defenses, which provide them with a survival advantage against immune system attack. Each pathogen is depicted as a colored sphere, with different colors representing distinct markers. The pro-inflammatory response is represented by the red line and red gradient, whereas the anti-inflammatory response is represented by the blue line and blue gradient.
| 1 | Wei JX, Jiang HL, Chen XH. Endothelial cell metabolism in sepsis. World J Emerg Med. 2023; 14(1):10-6. |
| 2 |
Wang W, Liu CF. Sepsis heterogeneity. World J Pediatr. 2023; 19(10):919-27.
doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00689-8 pmid: 36735197 |
| 3 | Shankar-Hari M, Ambler M, Mahalingasivam V, Jones A, Rowan K, Rubenfeld GD. Evidence for a causal link between sepsis and long-term mortality: a systematic review of epidemiologic studies. Crit Care. 2016; 20: 101. |
| 4 |
Sweeney TE, Liesenfeld O, May L. Diagnosis of bacterial sepsis: why are tests for bacteremia not sufficient? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2019; 19(11): 959-62.
doi: 10.1080/14737159.2019.1660644 pmid: 31446810 |
| 5 | Hammond NE, Kumar A, Kaur P, Tirupakuzhi Vijayaraghavan BK, Ghosh A, Grattan S, et al. Estimates of sepsis prevalence and outcomes in adult patients in the ICU in India: a cross-sectional study. Chest. 2022; 161(6):1543-54. |
| 6 | Wiersinga WJ, van der Poll T. Immunopathophysiology of human sepsis. EBioMedicine. 2022; 86: 104363. |
| 7 |
Genga K, Russell J. Update of sepsis in the intensive care unit. J Innate Immun. 2017; 9: 441-55.
doi: 10.1159/000477419 pmid: 28697503 |
| 8 |
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. Lancet. 2020; 395(10219): 200-11.
doi: S0140-6736(19)32989-7 pmid: 31954465 |
| 9 |
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021; 47(11):1181-247.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y pmid: 34599691 |
| 10 |
Nedeva C, Menassa J, Puthalakath H. Sepsis: inflammation is a necessary evil. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019; 7: 108.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00108 pmid: 31281814 |
| 11 | Shen XF, Cao K, Jiang JP, Guan WX, Du JF. Neutrophil dysregulation during sepsis: an overview and update. J Cellular Molecular Medi. 2017; 21(9): 1687-97. |
| 12 |
Taeb AM, Hooper MH, Marik PE. Sepsis: current definition, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017; 32(3):296-308.
doi: 10.1177/0884533617695243 pmid: 28537517 |
| 13 | Raymond SL, Holden DC, Mira JC, Stortz JA, Loftus TJ, Mohr AM, et al. Microbial recognition and danger signals in sepsis and trauma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017; 1863(10 Pt B):2564-73. |
| 14 | Patrício P, Paiva J, Borrego L. Immune response in bacterial and Candida sepsis. Eur J Microbiol & Immunol. 2019; 9: 105-13. |
| 15 | Kim MJ, Choi EJ, Choi EJ. Evolving paradigms in sepsis management: a narrative review. Cells. 2024; 13(14): 1172. |
| 16 |
Brady J, Horie S, Laffey JG. Role of the adaptive immune response in sepsis. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020; 8(suppl 1): 20.
doi: 10.1186/s40635-020-00309-z pmid: 33336293 |
| 17 | Chen J, Wei HM. Immune intervention in sepsis. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12: 718089. |
| 18 |
Guo Y, Patil NK, Luan LM, Bohannon JK, Sherwood ER. The biology of natural killer cells during sepsis. Immunology. 2018; 153(2): 190-202.
doi: 10.1111/imm.12854 pmid: 29064085 |
| 19 |
Kumar V. Dendritic cells in sepsis: Potential immunoregulatory cells with therapeutic potential. Mol Immunol. 2018; 101: 615-26.
doi: S0161-5890(18)30534-0 pmid: 30007546 |
| 20 | Ma CY, Liu HR, Yang S, Li H, Liao XL, Kang Y. The emerging roles and therapeutic potential of B cells in sepsis. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13: 1034667. |
| 21 |
Delano MJ, Ward PA. The immune system's role in sepsis progression, resolution, and long-term outcome. Immunol Rev. 2016; 274(1):330-53.
doi: 10.1111/imr.12499 pmid: 27782333 |
| 22 | Monneret G, Venet F. Sepsis-induced immune alterations monitoring by flow cytometry as a promising tool for individualized therapy. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2016; 90(4): 376-86. |
| 23 |
Boomer JS, To K, Chang KC, Takasu O, Osborne DF, Walton AH, et al. Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis and multiple organ failure. JAMA. 2011; 306(23):2594-605.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.1829 pmid: 22187279 |
| 24 | Torres LK, Pickkers P, van der Poll T. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Annu Rev Physiol. 2022; 84: 157-81. |
| 25 |
van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP, Netea MG. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017; 17: 407-20.
doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.36 pmid: 28436424 |
| 26 | Sinha M, Jupe J, Mack H, Coleman TP, Lawrence SM, Fraley SI. Emerging technologies for molecular diagnosis of sepsis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018; 31(2): e00089-17. |
| 27 | Wilson ML. Development of new methods for detecting bloodstream pathogens. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020; 26(3): 319-24. |
| 28 | Iroh Tam PY, Bendel CM. Diagnostics for neonatal sepsis: current approaches and future directions. Pediatr Res. 2017; 82(4): 574-83. |
| 29 | Eubank TA, Long SW, Perez KK. Role of rapid diagnostics in diagnosis and management of patients with sepsis. J Infect Dis. 2020 ;222(Suppl 2):S103-S109. |
| 30 |
Hayder Hamad M, Eidan Hadi M, Ajam IK. Comparison between polymerase chain reaction and blood culture for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Arch Razi Inst. 2023; 78(1): 221-6.
doi: 10.22092/ARI.2022.358608.2259 pmid: 37312696 |
| 31 |
Wang J, Weng L, Xu J, Du B. Blood gas analysis as a surrogate for microhemodynamic monitoring in sepsis. World J Emerg Med. 2023; 14(6):421-7.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.093 pmid: 37969221 |
| 32 | Kosmeri C, Giapros V, Serbis A, Baltogianni M. Application of advanced molecular methods to study early-onset neonatal sepsis. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25(4): 2258. |
| 33 | Cendejas-Bueno E, Romero-Gómez MP, Mingorance J. The challenge of molecular diagnosis of bloodstream infections. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019; 35(4): 65. |
| 34 | Pammi M, Flores A, Leeflang M, Versalovic J. Molecular assays in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2011 ;128(4): e973-e85. |
| 35 | Pammi M, Flores A, Versalovic J, Leeflang MM. Molecular assays for the diagnosis of sepsis in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 2(2): CD011926. |
| 36 | Grondman I, Pirvu A, Riza A, Ioana M, Netea MG. Biomarkers of inflammation and the etiology of sepsis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020; 48(1): 1-14. |
| 37 | Gunsolus IL, Sweeney TE, Liesenfeld O, Ledeboer NA. Diagnosing and managing sepsis by probing the host response to infection: advances, opportunities, and challenges. J Clin Microbiol. 2019; 57(7): e00425-19. |
| 38 | Barichello T, Generoso JS, Singer M, Dal-Pizzol F. Biomarkers for sepsis: more than just fever and leukocytosis-a narrative review. Crit Care. 2022; 26(1):14. |
| 39 | Pierrakos C, Velissaris D, Bisdorff M, Marshall JC, Vincent JL. Biomarkers of sepsis: time for a reappraisal. Crit Care. 2020; 24(1):287. |
| 40 | Leite GGF, Ferreira BL, Tashima AK, Nishiduka ES, Cunha-Neto E, Brunialti MKC, et al. Combined transcriptome and proteome leukocyte’s profiling reveals up-regulated module of genes/proteins related to low density neutrophils and impaired transcription and translation processes in clinical sepsis. Front Immunol. 2021; 12: 744799. |
| 41 | Tsakiroglou M, Evans A, Pirmohamed M. Leveraging transcriptomics for precision diagnosis: lessons learned from cancer and sepsis. Front Genet. 2023; 14: 1100352. |
| 42 |
Kim H, Hur M, Moon HW, Yun YM, Di Somma S; Network GREAT. Multi-marker approach using procalcitonin, presepsin, galectin-3, and soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 for the prediction of mortality in sepsis. Ann Intensive Care. 2017; 7(1): 27.
doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0252-y pmid: 28271449 |
| 43 |
Gilfillan M, Bhandari V. Biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis: clinical practice guidelines. Early Hum Dev. 2017; 105: 25-33.
doi: S0378-3782(16)30564-3 pmid: 28131458 |
| 44 |
Kingsley SMK, Bhat BV. Role of microRNAs in sepsis. Inflamm Res. 2017; 66(7): 553-69.
doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1031-9 pmid: 28258291 |
| 45 |
Bhattacharjee P, Edelson DP, Churpek MM. Identifying patients with sepsis on the hospital wards. Chest. 2017; 151(4): 898-907.
doi: S0012-3692(16)50385-7 pmid: 27374948 |
| 46 |
Reinhart K, Daniels R, Kissoon N, O'Brien J, Machado FR, Jimenez E, et al. The burden of sepsis-a call to action in support of World Sepsis Day 2013. J Crit Care. 2013; 28(4):526-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.04.012 pmid: 23747158 |
| 47 |
Maslove DM, Wong HR. Gene expression profiling in sepsis: timing, tissue, and translational considerations. Trends Mol Med. 2014; 20(4): 204-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2014.01.006 pmid: 24548661 |
| 48 | Burnham KL, Davenport EE, Radhakrishnan J, Humburg P, Gordon AC, Hutton P, et al. Shared and distinct aspects of the sepsis transcriptomic response to fecal peritonitis and pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017; 196(3):328-39. |
| 49 | Bhat B, Dhas B, Ashmi H. Sepsis genomics: stepping forward toward sepsis prevention? Int J Adv Med Health Res. 2014; 1(1): 8. |
| 50 | Abel S, Abel zur Wiesch P, Davis BM, Waldor MK. Analysis of bottlenecks in experimental models of infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015; 11(6): e1004823. |
| 51 |
Mahrt N, Tietze A, Künzel S, Franzenburg S, Barbosa C, Jansen G, et al. Bottleneck size and selection level reproducibly impact evolution of antibiotic resistance. Nat Ecol Evol. 2021; 5(9): 1233-42.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-021-01511-2 pmid: 34312522 |
| 52 | Kono M, Zafar MA, Zuniga M, Roche AM, Hamaguchi S, Weiser JN. Single cell bottlenecks in the pathogenesis of Streptococcus pneumoniae. PLoS Pathog. 2016; 12(10): e1005887. |
| 53 |
Didelot X, Walker AS, Peto TE, Crook DW, Wilson DJ. Within-host evolution of bacterial pathogens. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016; 14(3): 150-62.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.13 pmid: 26806595 |
| 54 | Gerlini A, Colomba L, Furi L, Braccini T, Manso AS, Pammolli A, et al. The role of host and microbial factors in the pathogenesis of pneumococcal bacteraemia arising from a single bacterial cell bottleneck. PLoS Pathog. 2014; 10(3): e1004026. |
| 55 | Hullahalli K, Waldor MK. Pathogen clonal expansion underlies multiorgan dissemination and organ-specific outcomes during murine systemic infection. Elife. 2021; 10: e70910. |
| 56 |
Pidwill GR, Pyrah JF, Sutton JAF, Best A, Renshaw SA, Foster SJ. Clonal population expansion of Staphylococcus aureus occurs due to escape from a finite number of intraphagocyte niches. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1): 1188.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27928-2 pmid: 36681703 |
| 57 | Alharbi AS, Thomas RC, Ali M, Thompson JP, Stover CM. Factors in homo and heterotypic aggregate formation in sepsis. Available at https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:115147541 |
| 58 |
Bandyopadhyay T, Kumar A, Saili A, Randhawa VS. Distribution, antimicrobial resistance and predictors of mortality in neonatal sepsis. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2018; 11(2):145-53.
doi: 10.3233/NPM-1765 pmid: 29991144 |
| 59 | Emr BM, Alcamo AM, Carcillo JA, Aneja RK, Mollen KP. Pediatric sepsis update: how are children different? Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2018; 19(2):176-83. |
| 60 | Prusakowski MK, Chen AP. Pediatric sepsis. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2017; 35(1): 123-38. |
| 61 | Narayanan N, Williams RL, Turner PC, Paul SP. Early-onset neonatal sepsis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 8. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2020; 81(1):1-2. |
| 62 |
Shane AL, Sánchez PJ, Stoll BJ. Neonatal sepsis. Lancet. 2017; 390(10104):1770-80.
doi: S0140-6736(17)31002-4 pmid: 28434651 |
| 63 |
Agyeman PKA, Schlapbach LJ, Giannoni E, Stocker M, Posfay-Barbe KM, Heininger U, et al. Epidemiology of blood culture-proven bacterial sepsis in children in Switzerland: a population-based cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2017; 1(2): 124-33.
doi: S2352-4642(17)30010-X pmid: 30169202 |
| 64 | Prout AJ, Talisa VB, Carcillo JA, Decker BK, Yende S. Bacterial and fungal etiology of sepsis in children in the United States: reconsidering empiric therapy. Crit Care Med. 2020 ;48(3): e192-e199. |
| 65 | Ruth A, McCracken CE, Fortenberry JD, Hall M, Simon HK, Hebbar KB. Pediatric severe sepsis: current trends and outcomes from the Pediatric Health Information Systems database. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014; 15(9):828-38. |
| 66 | Rowe T, Araujo KL, van Ness PH, Pisani MA, Juthani-Mehta M. Outcomes of older adults with sepsis at admission to an intensive care unit. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016; 3(1): ofw010. |
| 67 |
Tsegaye EA, Teklu DS, Bonger ZT, Negeri AA, Bedada TL, Bitew A. Bacterial and fungal profile, drug resistance pattern and associated factors of isolates recovered from blood samples of patients referred to Ethiopian Public Health Institute: cross-sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2021; 21(1):1201.
doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06896-w pmid: 34844570 |
| 68 | Spoto S, Valeriani E, Costantino S. Nosography of systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in internal medicine patients. Ital J Med. 2015; 9(3): 243. |
| 69 |
Denstaedt SJ, Singer BH, Standiford TJ. Sepsis and nosocomial infection: patient characteristics, mechanisms, and modulation. Front Immunol. 2018; 9:2446.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02446 pmid: 30459764 |
| [1] | Peili Chen, Yan Ge, Huiqiu Sheng, Wenwu Sun, Jiahui Wang, Li Ma, Enqiang Mao. The role of early changes in routine coagulation tests in predicting the occurrence and prognosis of sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 136-143. |
| [2] | Chunxue Wang, Dianyin Yang, Yuxin Zhu, Qian Yang, Tong Liu, Xiandong Liu, Dongyang Zhao, Xiaowei Bao, Tiancao Dong, Li Shao, Lunxian Tang. Circulating circular RNAs act as potential novel biomarkers for sepsis secondary to pneumonia: a prospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 144-152. |
| [3] | Chao Gong, Shengyong Xu, Youlong Pan, Shigong Guo, Joseph Harold Walline, Xue Wang, Xin Lu, Shiyuan Yu, Mubing Qin, Huadong Zhu, Yanxia Gao, Yi Li. Effects of probiotic treatment on the prognosis of patients with sepsis: a systematic review [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(1): 18-27. |
| [4] | Jingyuan Xie, Jiandong Gao, Mutian Yang, Ting Zhang, Yecheng Liu, Yutong Chen, Zetong Liu, Qimin Mei, Zhimao Li, Huadong Zhu, Ji Wu. Prediction of sepsis within 24 hours at the triage stage in emergency departments using machine learning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(5): 379-385. |
| [5] | Juexian Wei, Hengzong Mo, Yuting Zhang, Wenmin Deng, Siqing Zheng, Haifeng Mao, Yang Ji, Huilin Jiang, Yongcheng Zhu. Evolutionary trend analysis and knowledge structure mapping of endothelial dysfunction in sepsis: a bibliometrics study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(5): 386-396. |
| [6] | Rex Pui Kin Lam, Zonglin Dai, Eric Ho Yin Lau, Carrie Yuen Ting Ip, Ho Ching Chan, Lingyun Zhao, Tat Chi Tsang, Matthew Sik Hon Tsui, Timothy Hudson Rainer. Comparing 11 early warning scores and three shock indices in early sepsis prediction in the emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(4): 273-282. |
| [7] | Huixin Zhao, Yiming Dong, Sijia Wang, Jiayuan Shen, Zhenju Song, Mingming Xue, Mian Shao. Comparison between sepsis-induced coagulopathy and sepsis-associated coagulopathy criteria in identifying sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(3): 190-196. |
| [8] | A-ling Tang, Yan Li, Li-chao Sun, Xiao-yu Liu, Nan Gao, Sheng-tao Yan, Guo-qiang Zhang. Xuebijing improves intestinal microcirculation dysfunction in septic rats by regulating the VEGF-A/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(3): 206-213. |
| [9] | Qing Zhao, Jinfu Ma, Jianguo Xiao, Zhe Feng, Hui Liu. Data driven analysis reveals prognostic genes and immunological targets in human sepsis-associated acute kidney injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(2): 91-97. |
| [10] | Weichao Ding, Wei Zhang, Juan Chen, Mengmeng Wang, Yi Ren, Jing Feng, Xiaoqin Han, Xiaohang Ji, Shinan Nie, Zhaorui Sun. Protective mechanism of quercetin in alleviating sepsis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(2): 111-120. |
| [11] | Wei Zhou, Maiying Fan, Xiang Li, Fang Yu, En Zhou, Xiaotong Han. Molecular mechanism of Xuebijing in treating pyogenic liver abscess complicated with sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(1): 35-40. |
| [12] | Jingyi Wang, Li Weng, Jun Xu, Bin Du. Blood gas analysis as a surrogate for microhemodynamic monitoring in sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(6): 421-427. |
| [13] | Shuang Xu, Lang Guo, Weijing Shao, Licai Liang, Tingting Shu, Yuhan Zhang, He Huang, Guangqi Guo, Qing Zhang, Peng Sun. Vagus nerve stimulation protects against cerebral injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation by inhibiting inflammation through the TLR4/NF-κB and α7nAChR/JAK2 signaling pathways [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(6): 462-470. |
| [14] | Saifeng Chen, Xuewei Hao, Guo Chen, Guorong Liu, Xiaoyan Yuan, Peiling Shen, Dongfeng Guo. Effects of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor on sepsis-associated acute kidney injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 386-392. |
| [15] | Mubing Qin, Yanxia Gao, Shigong Guo, Xin Lu, Qian Zhao, Zengzheng Ge, Huadong Zhu, Yi Li. Establishment and evaluation of animal models of sepsis-associated encephalopathy [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 349-353. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
