World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (2): 144-152.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.033
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chunxue Wang1,2, Dianyin Yang1,2, Yuxin Zhu1,2, Qian Yang1,2, Tong Liu1,2, Xiandong Liu1,2, Dongyang Zhao1,2, Xiaowei Bao1,2, Tiancao Dong1,2, Li Shao3, Lunxian Tang1,2( )
)
Received:2024-08-02
Accepted:2024-12-09
Online:2025-03-19
Published:2025-03-01
Contact:
Lunxian Tang, Email: Chunxue Wang, Dianyin Yang, Yuxin Zhu, Qian Yang, Tong Liu, Xiandong Liu, Dongyang Zhao, Xiaowei Bao, Tiancao Dong, Li Shao, Lunxian Tang. Circulating circular RNAs act as potential novel biomarkers for sepsis secondary to pneumonia: a prospective cohort study[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 144-152.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.033
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the study population
| Characteristics | Patients with pneumonia-induced sepsis (n=80) | Patients with pneumonia (n=60) | Healthy control (n=40) |
|---|---|---|---|
| General characteristics Age, years, mean±SD Male, n (%) Blood laboratory examination WBC, 109/L, mean±SD Neutrophil cell count, 109/L, median (IQR) Neutrophil percentage, %, mean±SD Lymphocyte cell count, 109/L, median (IQR) Lymphocyte percentage, %, median (IQR) PLT, 109/L, mean±SD CRP, mg/L, median (IQR) SAA, mg/L, median (IQR) IL-6, pg/mL, median (IQR) PCT, ng/mL, median (IQR) Comorbidities, n (%) Hypertension Diabetes Chronic renal insufficiency | 72.11±12.13 37 (46.25) 16.10±2.99*# 9.23 (6.11, 13.18) *# 83.23 ± 6.22*# 1.05 (0.311, 2.22) *# 6.22 (3.21, 18.72) *# 166.35 ± 91.44*# 89.01 (44.08, 179.23) *# 131.00 (50.60, 273.23) *# 69.07 (21.21, 184.23) *# 7.78 (1.12, 20.11) *# 36 (45) *# 28 (35) *# 23 (28.75) *# | 70.11±9.13 25 (41.67) 10.39±2.07* 6.90 (5.88, 11.01) * 77.11±7.23* 1.44 (0.91, 3.92) * 12.60 (8.32, 20.32) * 202.55±111.32 22.18 (15.88, 64.72) * 27.11 (18.22, 84.23) * 30.12 (12.03, 88.98) * 0.61 (0.06, 1.65) * 11 (18.33) 12 (20) 7 (11.67) | 69.09±10.32 21 (52.5) 6.85±1.01 4.01 (3.11, 5.23) 62.21±8.88 2.13 (1.98, 3.01) 30.33 (25.41, 40.35) 201.43±111.32 1.13 (0.34, 2.88) 4.50 (2.22, 6.74) 8.22 (6.55, 10.18) 0.03 (0.01, 0.07) 6 (15) 9 (22.5) 5 (12.5) |
| Coronary heart disease Clinical scores, mean±SD SOFA score APACHE II score Prognosis, n (%) Survival Dead | 24 (30) *# 6.28±2.13 17.21±8.89 53 (66.25) 27 (33.75) | 9 (16) - - 60 (100) 0 (0) | 5 (12.5) - - 40 (100) 0 (0) |
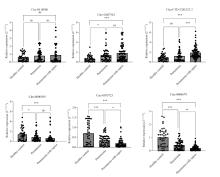
Figure 1.
Relative expression of six serum circRNAs in 40 healthy volunteers, 60 pneumonia patients and 80 pneumonia-induced sepsis patients performed using qRT-PCR. The upregulation of Circ-CTD-2281E23.2 and the downregulation of Circ-0008679 and Circ-0075723 were consistent with the RNA sequencing results. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001; ns: not significant.
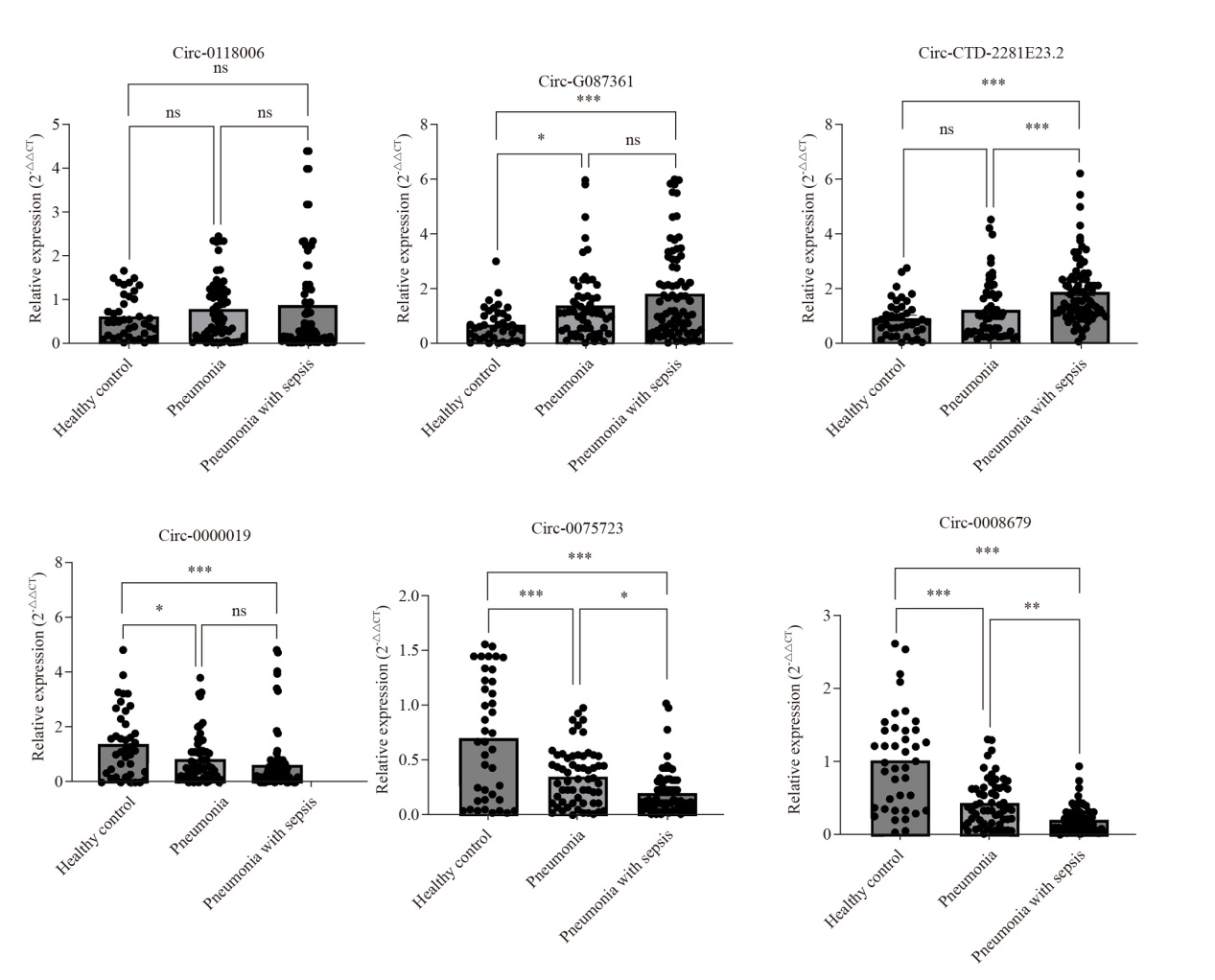
Table 2.
The correlation between Circ-CTD-2281E23.2, Circ-0075723, Circ-0008679 and inflammatory indexes and sepsis severity
| Variables | Circ-CTD-2281E23.2 | Circ-0075723 | Circ-0008679 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P-value | r | P-value | r | P-value | |||
| WBC | 0.59 | <0.001 | -0.29 | 0.010 | -0.31 | 0.010 | ||
| CRP | 0.38 | 0.010 | -0.52 | <0.001 | -0.51 | <0.001 | ||
| SAA IL-6 PCT | 0.45 0.69 0.62 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 | -0.31 -0.57 -0.68 | 0.003 0.010 0.004 | -0.42 -0.71 -0.61 | 0.002 <0.001 <0.001 | ||
| SOFA score | 0.48 | <0.001 | -0.64 | <0.001 | -0.55 | <0.001 | ||
| APACHEII score | 0.27 | 0.020 | -0.24 | 0.002 | -0.51 | 0.020 | ||
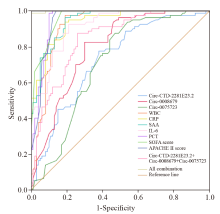
Figure 2.
The ROC curves of CircRNAs, inflammatory indexes and sepsis severity scores for diagnosis of pneumonia-induced sepsis. WBC:white blood cell; CRP: C-reaction protein; SAA: serum amyloid A; IL-6: interleukin-6; PCT: procalcitonin; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; APACHE: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation.
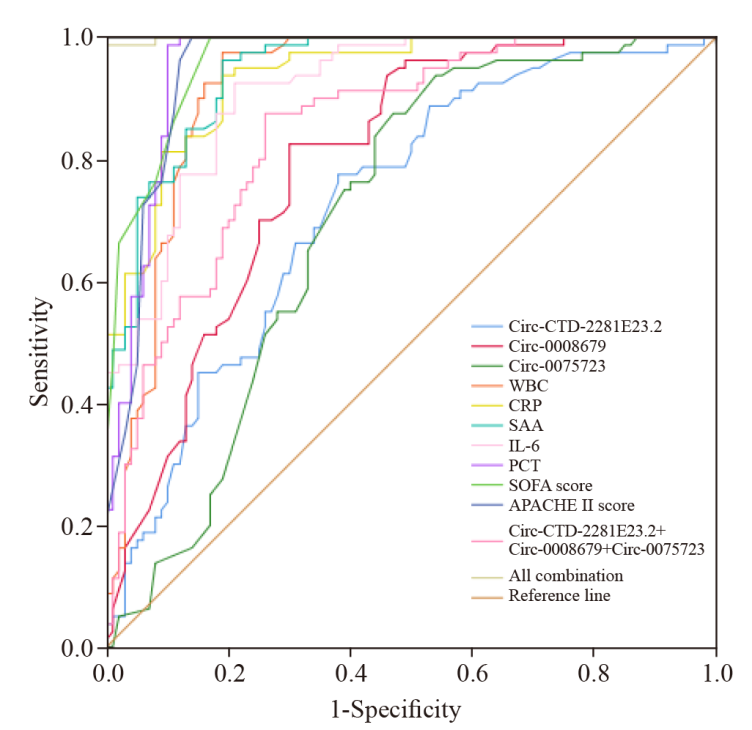
Table 3.
Diagnostic performance of CircRNAs, inflammatory indexes and sepsis severity scores in pneumonia-induced sepsis
| Variables | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cutoff |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC | 0.923 | 97.5% | 76.0% | 11.44×109/L |
| CRP | 0.936 | 97.5% | 75.0% | 22.15 mg/L |
| PCT | 0.959 | 92.5% | 93.0% | 1.805 ng/mL |
| SAA | 0.942 | 96.4% | 80.0% | 32.85 mg/L |
| IL-6 | 0.917 | 96.3% | 76.0% | 25.93 pg/mL |
| SOFA score | 0.963 | 100% | 83.0% | 2.5 |
| APACHEII score | 0.951 | 100% | 86.0% | 10 |
| Circ-CTD-2281E23.2 | 0.728 | 77.5% | 62.0% | 1.06 |
| Circ-0075723 | 0.706 | 87.5% | 53.0% | 0.4 |
| Circ-0008679 | 0.793 | 82.5% | 70.0% | 0.47 |
| CircRNAs combination | 0.846 | 86.3% | 74.0% | - |
| All combination | 0.990 | 96.0% | 95.0% | - |
Table 4.
Clinical characteristics of patients with pneumonia-induced sepsis
| Characteristics | Survivor (n=53) | Non-survivor (n=27) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| General characteristics Age, years, mean±SD Male, n (%) Blood laboratory examination, mean±SD WBC, 109/L CRP, mg/L SAA, mg/L IL-6, pg/mLD PCT, ng/mL LAC, mmol/L | 66.38±10.76 20 (37.74) 15.12±1.60 57.13±27.17 69.84±27.20 57.76±24.24 5.58±3.40 3.61±1.68 | 75.34±12.16 11 (40.74) 18.31±3.17 117.30±39.66 146.90±47.67 114.01±30.81 13.70±11.38 5.20±2.16 | 0.02 0.79 0.03 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) Hypertension Diabetes Chronic renal insufficiency Coronary heart disease Clinical scores, mean±SD SOFA score APACHEII score Outcomes Length of ICU stay, days, mean±SD Relative expression of Circ-RNAs, mean±SD Circ-CTD-2281E23.2 Circ-0075723 Circ-0008679 | 20 (37.74) 16 (30.19) 13 (24.53) 13 (24.53) 5.54±1.92 13.81±1.98 17.70±6.51 1.59±0.86 0.25±0.21 0.23±0.19 | 16 (59.26) 12 (44.44) 10 (37.04) 11 (40.74) 9.83±1.64 19.92±4.94 10.11±4.64 2.43±1.48 0.10±0.09 0.17±0.15 | 0.07 0.21 0.24 0.14 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 0.14 |
| 1 |
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315(8): 801-10.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 pmid: 26903338 |
| 2 |
Markwart R, Saito H, Harder T, Tomczyk S, Cassini A, Fleischmann-Struzek C, et al. Epidemiology and burden of sepsis acquired in hospitals and intensive care units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020; 46(8): 1536-51.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06106-2 pmid: 32591853 |
| 3 |
Esper AM, Moss M, Lewis CA, Nisbet R, Mannino DM, Martin GS. The role of infection and comorbidity: factors that influence disparities in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34(10): 2576-82.
doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000239114.50519.0E pmid: 16915108 |
| 4 |
Mayr FB, Yende S, Angus DC. Epidemiology of severe sepsis. Virulence. 2014; 5(1): 4-11.
doi: 10.4161/viru.27372 pmid: 24335434 |
| 5 | Pierrakos C, Velissaris D, Bisdorff M, Marshall JC, Vincent JL. Biomarkers of sepsis: time for a reappraisal. Crit Care. 2020; 24(1): 287. |
| 6 |
Póvoa P, Coelho L, Dal-Pizzol F, Ferrer R, Huttner A, Conway Morris A, et al. How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: guide to clinicians. Intensive Care Med. 2023; 49(2): 142-53.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06956-y pmid: 36592205 |
| 7 | Enguix A, Rey C, Concha A, Medina A, Coto D, Diéguez MA. Comparison of procalcitonin with C-reactive protein and serum amyloid for the early diagnosis of bacterial sepsis in critically ill neonates and children. Intensive Care Med. 2001; 27(1): 211-5. |
| 8 | Barichello T, Generoso JS, Singer M, Dal-Pizzol F. Biomarkers for sepsis: more than just fever and leukocytosis-a narrative review. Crit Care. 2022; 26(1): 14. |
| 9 | Du LZ. Early diagnosis and management of neonatal sepsis: a perspective. World J Pediatr. 2024; 20(4):303-6. |
| 10 | Zhou WY, Cai ZR, Liu J, Wang DS, Ju HQ, Xu RH. Circular RNA: metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol Cancer. 2020; 19(1): 172. |
| 11 | Xiao L, Ma XX, Luo J, Chung HK, Kwon MS, Yu TX, et al. Circular RNA CircHIPK 3 promotes homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium by reducing microRNA 29b function. Gastroenterology. 2021; 164(4): 1303-17.e3. |
| 12 |
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019; 20(11): 675-91.
doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7 pmid: 31395983 |
| 13 | Patop IL, Wüst S, Kadener S. Past, present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J. 2019; 38(16): e100836. |
| 14 | Zhang F, Jiang JJ, Qian H, Yan YM, Xu WR. Exosomal circRNA: emerging insights into cancer progression and clinical application potential. J Hematol Oncol. 2023; 16(1): 67. |
| 15 |
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol. 2017; 14(8): 1035-45.
doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1271524 pmid: 27982727 |
| 16 |
Danckwardt S, Trégouët DA, Castoldi E. Post-transcriptional control of haemostatic genes: mechanisms and emerging therapeutic concepts in thrombo-inflammatory disorders. Cardiovasc Res. 2023; 119(8): 1624-40.
doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad046 pmid: 36943786 |
| 17 | Jiao L, Liu Y, Yu XY, Pan X, Zhang Y, Tu J, et al. Ribosome biogenesis in disease: new players and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023; 8(1): 15. |
| 18 | Bhat AA, Gupta G, Goyal A, Thapa R, Almalki WH, Kazmi I, et al. Unwinding circular RNA’s role in inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024; 397(5): 2567-88. |
| 19 |
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang JJ. CircRNA hsa_circ_0005105 upregulates NAMPT expression and promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation by sponging miR-26a. Cell Biol Int. 2017; 41(12): 1283-9.
doi: 10.1002/cbin.10761 pmid: 28276108 |
| 20 |
Bao XW, Zhang QQ, Liu N, Zhuang SG, Li Z, Meng QS, et al. Characteristics of circular RNA expression of pulmonary macrophages in mice with sepsis-induced acute lung injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2019; 23(10): 7111-5.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14577 pmid: 31411002 |
| 21 | Zhao DY, Wang CX, Liu XD, Liu N, Zhuang SG, Zhang QQ, et al. CircN4bp1 facilitates sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome through mediating macrophage polarization via the miR-138-5p/EZH2 axis. Mediators Inflamm. 2021; 2021:7858746. |
| 22 | Di Raimondo D, Pirera E, Rizzo G, Simonetta I, Musiari G, Tuttolomondo A. Non-coding RNA networks as potential novel biomarker and therapeutic target for sepsis and sepsis-related multi-organ failure. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12(6): 1355. |
| 23 | Yang DY, Zhao DY, Ji JL, Wang CX, Liu N, Bao XW, et al. CircRNA_0075723 protects against pneumonia-induced sepsis through inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis by sponging miR-155-5p and regulating SHIP1 expression. Front Immunol. 2023; 14: 1095457. |
| 24 |
Laura E, Andrew R, Waleed A, Massimo A, Craig M C, Craig F, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021; 47(11):1181-47.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y pmid: 34599691 |
| 25 |
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 2021; 49(11): e1063-e1143.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005337 pmid: 34605781 |
| 26 |
Wacker C, Prkno A, Brunkhorst FM, Schlattmann P. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013; 13(5): 426-35.
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70323-7 pmid: 23375419 |
| 27 | Liu CX, Li X, Nan F, Jiang S, Gao X, Guo SK, et al. Structure and degradation of circular RNAs regulate PKR activation in innate immunity. Cell. 2019; 177(4): 865-80.e21. |
| 28 | Zhang Z, Gao W, Long QQ, Zhang J, Huang W, Xiao F. Circular RNA circFADS2 regulates inflammation response as a microRNA-1207-5p sponge in human atrial fibrillation. Molecular Biology Reports. 2020; 47(9):6785-93. |
| 29 |
Yang L, Fu JR, Zhou YF. Circular RNAs and their emerging roles in immune regulation. Front Immunol. 2018; 9: 2977.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02977 pmid: 30619334 |
| 30 | Milad A, Ali Z, Ebrahim M, Amir RA, Gautam S, Wang LZ, et al. Non-coding RNA-based regulation of inflammation. Semin Immunol. 2022; 59:101606. |
| 31 |
Peng XJ, Li HL, Zhang WB, Zhang DS. Discovery and verification of mmu_Circ_26986/hsa_Circ_0072463 as a potential biomarker and intervention target for sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024; 81(1): 154.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05079-x pmid: 38538857 |
| 32 | Wei BH, Yu L. Circular RNA PRKCI and microRNA-545 relate to sepsis risk, disease severity and 28-day mortality. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2020; 80(8): 659-66. |
| [1] | Peili Chen, Yan Ge, Huiqiu Sheng, Wenwu Sun, Jiahui Wang, Li Ma, Enqiang Mao. The role of early changes in routine coagulation tests in predicting the occurrence and prognosis of sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 136-143. |
| [2] | Qiang Sun, Haoze Cao, Xuesong Bai, Xin Han, Wanlu You, Zhongquan Sun, Yixin Zhang, Xiaochang Wu, Feng Fang, Fan Wu, Lianyue Yang, Sheng Yan, Yuan Ding, Weilin Wang. Adult split liver transplantation to treat liver cancer: a single-center retrospective study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(1): 57-62. |
| [3] | Tianpeng Hu, Yan Li, Shengtao Yan, Lichao Sun, Rui Lian, Jieqiong Yu, Jie Chen, Xiaoyu Liu, Guoqiang Zhang. Application of myxovirus resistance protein A in the etiological diagnosis of infections in adults [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(1): 35-42. |
| [4] | Qingliu Zheng, Changyun Liu, Lingying Le, Qiqi Wu, Zhihong Xu, Jiyan Lin, Qiuyun Chen. ICU-acquired weakness in critically ill patients at risk of malnutrition: risk factors, biomarkers, and early enteral nutrition impact [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(1): 51-56. |
| [5] | Cheng Chi, Hao Gong, Kai Yang, Peng Peng, Xiaoxia Zhang. Early peripheral perfusion index predicts 28-day outcome in patients with septic shock [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(5): 372-378. |
| [6] | Subi Abudurexiti, Shihai Xu, Zhangping Sun, Yi Jiang, Ping Gong. Glucose metabolic reprogramming-related parameters for the prediction of 28-day neurological prognosis and all-cause mortality in patients after cardiac arrest: a prospective single-center observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(3): 197-203. |
| [7] | Jiale Yang, Fanghe Gong, Xuezhi Shi, Fanfan Wang, Jing Qian, Lulu Wan, Yi Chen, Huaisheng Chen, Huasheng Tong. A nomogram based on lymphocyte percentage for predicting hospital mortality in exertional heatstroke patients: a 13-year retrospective study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(6): 434-441. |
| [8] | Tian Yan, Ziyin Chen, Shengdong Zou, Zefan Wang, Quan Du, Wenhua Yu, Wei Hu, Yongke Zheng, Keyi Wang, Xiaoqiao Dong, Shuangyong Dong. A prospective cohort study on serum A20 as a prognostic biomarker of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 360-366. |
| [9] | Yue Li, Yong-peng Xie, Xiao-min Li, Tao Lu. Effects of early standardized enteral nutrition on preventing acute muscle loss in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with mechanical ventilation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(3): 193-197. |
| [10] | Xiao-guang Zhu, Jia-mei Jiang, Yong-xia Li, Jing Gao, Wei Wu, Qi-ming Feng. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in patients with acute pancreatitis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(1): 44-48. |
| [11] | Gan-nan Wang, Zhong-man Zhang, Wen Chen, Xiao-quan Xu, Jin-song Zhang. Timing of brain computed tomography for predicting neurological prognosis in comatose cardiac arrest survivors: a retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 349-354. |
| [12] | Fei Shao, Xian Shi, Shu-hua Huo, Qing-yu Liu, Ji-xue Shi, Jian Kang, Ping Gong, Sheng-tao Yan, Guo-xing Wang, Li-jie Qin, Fei Wang, Ke Feng, Feng-ying Chen, Yong-jie Yin, Tao Ma, Yan Li, Yang Wu, Hao Cui, Chang-xiao Yu, Song Yang, Wei Gan, Sai Wang, Liu-ye-zi Du, Ming-chen Zhao, Zi-ren Tang, Shen Zhao. Development and evaluation of a predictive nomogram for survival in heat stroke patients: a retrospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 355-360. |
| [13] | Li Li, Li-ying Lin, Yuan-qiang Lu. Analysis of imaging characteristics of blunt traumatic aortic dissection: an 8-year experience [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 361-366. |
| [14] | Jehad A. Rababah, Mohammed M. Al-Hammouri, Esra’a AlNsour. Effectiveness of an educational program on improving healthcare providers’ knowledge of acute stroke: A randomized block design study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(2): 93-98. |
| [15] | Yu-ming Wang, Yan-jun Zheng, Ying Chen, Yun-chuan Huang, Wei-wei Chen, Ran Ji, Li-li Xu, Zhi-tao Yang, Hui-qiu Sheng, Hong-ping Qu, En-qiang Mao, Er-zhen Chen. Effects of fluid balance on prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients secondary to sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 216-222. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
