World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (1): 35-42.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.011
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tianpeng Hu1, Yan Li1, Shengtao Yan1, Lichao Sun1, Rui Lian1, Jieqiong Yu1, Jie Chen1,2, Xiaoyu Liu1,2, Guoqiang Zhang1( )
)
Received:2024-06-16
Accepted:2024-11-25
Online:2025-01-23
Published:2025-01-01
Contact:
Guoqiang Zhang
E-mail:zhangchong2003@vip.sina.com
Tianpeng Hu, Yan Li, Shengtao Yan, Lichao Sun, Rui Lian, Jieqiong Yu, Jie Chen, Xiaoyu Liu, Guoqiang Zhang. Application of myxovirus resistance protein A in the etiological diagnosis of infections in adults[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(1): 35-42.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.011
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients
| Parameters | All patients (n=121) | Viral infection (n=45) | Bacterial infection (n=30) | Co-infection (n=46) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| Males, n (%) | 73 (60.3) | 26 (57.8) | 16 (53.3) | 31 (67.4) | 0.433 |
| Females, n (%) | 48 (39.7) | 19 (42.2) | 14 (46.7) | 15 (32.6) | |
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 70.0 (59.5-77.0) | 72.0 (54.5-77.0) | 68.0 (59.5-77.0) | 71.0 (60.0-79.3) | 0.894 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |||||
| Hypertension | 63 (52.1) | 25 (55.6) | 19 (63.3) | 19 (41.3) | 0.150 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 44 (36.4) | 15 (33.3) | 7 (23.3) | 22 (47.8) | 0.083 |
| Coronary disease | 25 (20.7) | 10 (22.2) | 2 (6.7) | 13 (28.3) | 0.070 |
| Stroke | 22 (18.2) | 6 (13.3) | 11 (36.7) | 5 (10.9) | 0.010 |
| Cancer | 13 (10.7) | 1 (2.2) | 4 (13.3) | 8 (17.4) | 0.044 |
| Respiratory system diseases | 19 (15.7) | 5 (11.1) | 5 (16.7) | 9 (19.6) | 0.569 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 6 (5.0) | 2 (4.4) | 1 (3.3) | 3 (6.5) | 1.000 |
| Rheumatism | 7 (5.8) | 1 (2.2) | 3 (10.0) | 3 (6.5) | 0.379 |
| Hemopathy | 3 (2.5) | 3 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.063 |
| Others | 24 (19.8) | 7 (15.6) | 6 (20.0) | 11 (23.9) | 0.651 |
| Sites of infection, n (%) | |||||
| Lower respiratory tract infection | 108 (89.3) | 45 (100.0) | 22 (73.3) | 41 (89.1) | <0.001 |
| Gastrointestinal infection | 4 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (10.0) | 1 (2.2) | 0.083 |
| Urinary tract infection | 2 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (2.2) | 0.715 |
| Multisite infection | 7 (5.8) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (13.3) | 3 (6.5) | 0.039 |
| MxA, ng/mL, median (IQR) | 28.9 (13.0-111.4) | 82.3 (24.5-182.9) | 16.4 (10.8-26.5) | 28.5 (10.2-106.8) | <0.001 |
| WBC, ×109/L, median (IQR) | 10.4 (7.5-13.6) | 10.0 (5.9-12.5) | 11.1 (7.2-18.0) | 10.4 (7.9-13.9) | 0.477 |
| CRP, mg/L, median (IQR) | 66.9 (21.7-126.4) | 34.8 (10.8-95.1) | 83.5 (40.1-123.8) | 83.7 (22.9-160.0) | 0.021 |
| PCT, ng/mL, median (IQR) | 0.4 (0.2-2.9) | 0.2 (0.2-0.6) | 0.5 (0.3-4.2) | 0.8 (0.2-4.0) | 0.001 |
| APACHE Ⅱ score, median (IQR) | 16.0 (12.0-21.0) | 13.0 (11.0-16.5) | 15.0 (12.0-23.0) | 18.5 (13.0-26.0) | 0.001 |
| SOFA score, median (IQR) | 6.0 (4.0-10.0) | 5.0 (4.0-8.0) | 6.0 (4.0-9.3) | 7.0 (5.8-11.2) | 0.002 |
| Mortality, in hospital), n (%) | 19 (15.7) | 3 (6.7) | 5 (16.7) | 11 (23.9) | 0.070 |

Figure 2.
The expression of MxA in the blood distinguishes between viral, bacterial, and viral-bacterial co-infections. A: the expression levels of MxA in viral (n=45), bacterial (n=30), and viral-bacterial co-infections (n=46) patients. The horizontal bars indicate the medians and interquartile ranges. P-values were calculated with the Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn's multiple comparisons test. B: ROC analysis of MxA for the differentiation of patients with viral and bacterial infections. C: ROC analysis of MxA for the differentiation of patients with viral and viral-bacterial co-infections. D: ROC analysis of MxA levels for the differentiation of patients with bacterial and viral-bacterial co-infections. MxA: myxovirus resistance protein A; ROC: receiver operating characteristic.
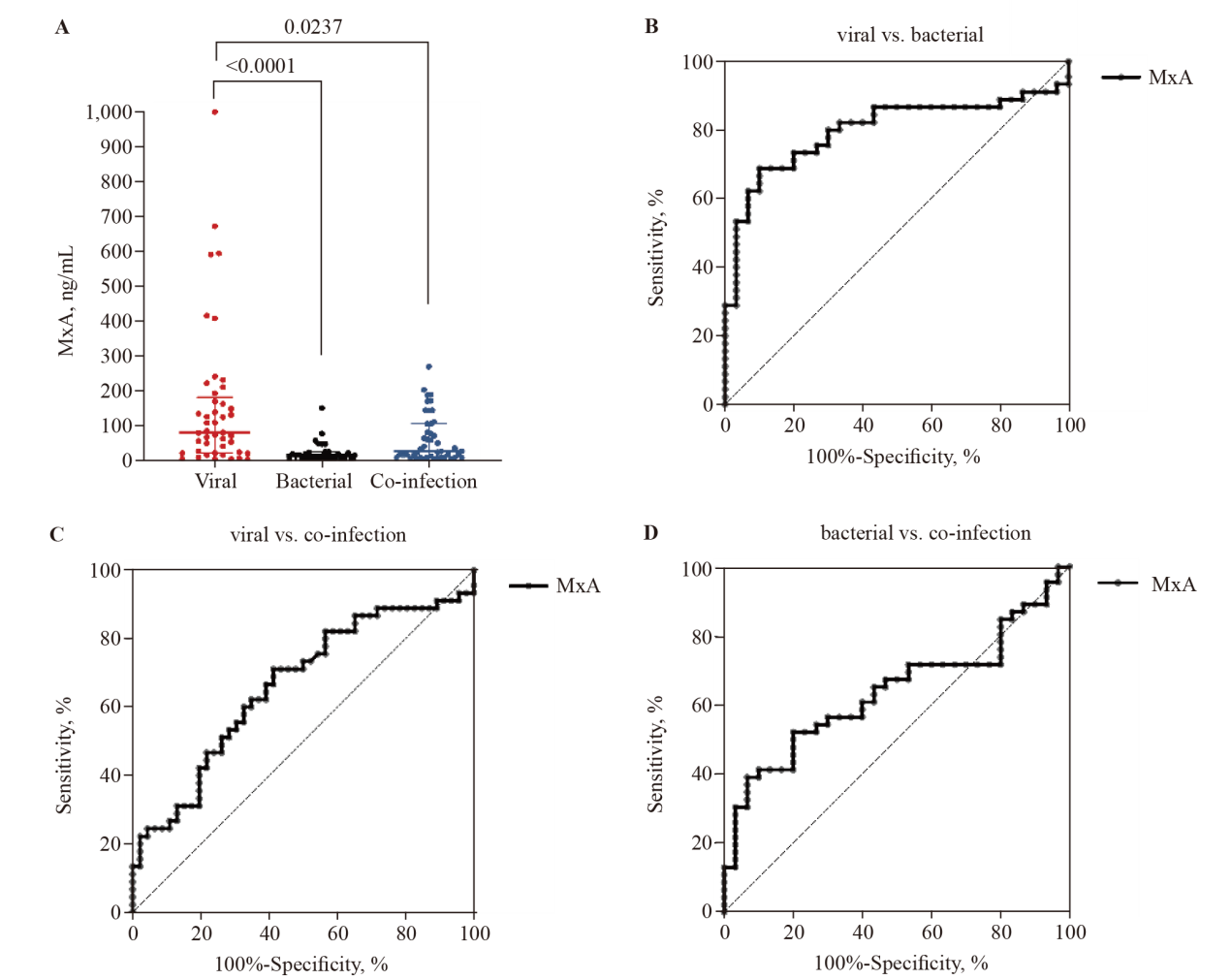

Figure 3.
MxA combined with CRP or PCT can reliably distinguish between viral, bacterial, and viral-bacterial co-infections. A, B: MxA/CRP and MxA/PCT ratios in viral (n=45), bacterial (n=30), and viral-bacterial co-infections (n=46). The horizontal bars represent the medians and interquartile ranges. P-values were calculated with the Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn's multiple comparisons test. C: ROC analysis of MxA/CRP and MxA/PCT for the differentiation of patients with viral and bacterial infections. D: ROC analysis of CRP, PCT, and MxA levels; the combination of MxA and CRP levels; the combination of MxA and PCT levels; and the combination of MxA and CRP levels and PCT levels to distinguish patients with viral and bacterial infections. AUC: area under the curve; MxA: myxovirus resistance protein A; ROC: receiver operating characteristic; CRP: C-reactive protein; PCT: procalcitonin.
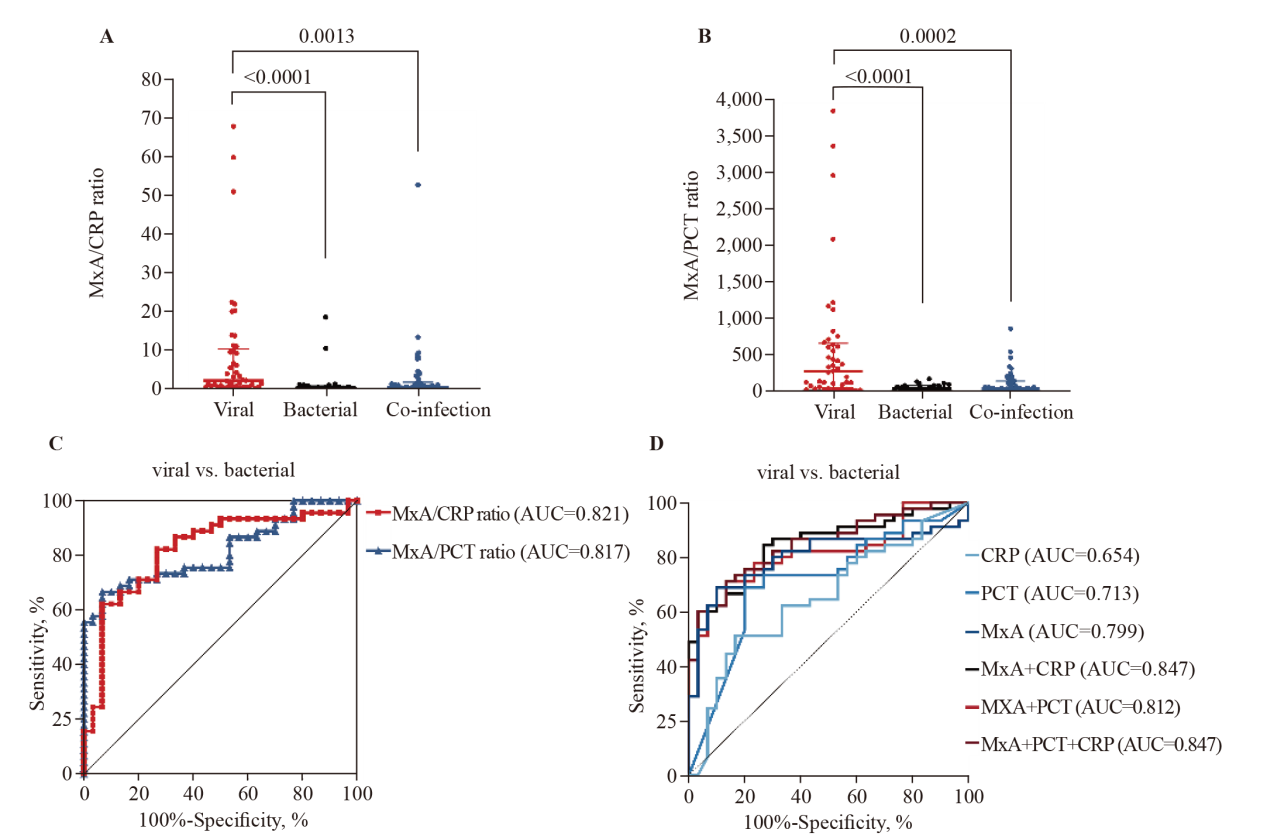

Figure 4.
Expression of MxA in patients infected with different types of viruses. The bars indicate the median, and the horizontal bars represent the interquartile ranges. SARS-CoV-2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; IAV: influenza A virus; IBV: influenza B virus; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; HCMV: human cytomegalovirus; RSV: respiratory syncytial virus; MxA: myxovirus resistance protein A.

| 1 |
Collaborators AR. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022; 399(10325):629-55.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0 pmid: 35065702 |
| 2 | World Bank Group. Drug-resistant infections: a threat to our economic future 2017. Available at https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/health/publication/drug-resistant-infections-a-threat-to-our-economic-future |
| 3 | Gao S, von der Malsburg A, Paeschke S, Behlke J, Haller O, Kochs G, et al. Structural basis of oligomerization in the stalk region of dynamin-like MxA. Nature. 2010; 465(7297): 502-6. |
| 4 |
Haller O, Stertz S, Kochs G. The Mx GTPase family of interferon-induced antiviral proteins. Microbes Infect. 2007; 9(14-15):1636-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2007.09.010 pmid: 18062906 |
| 5 |
Sadler AJ, Williams BR, Williams BR. Interferon-inducible antiviral effectors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008; 8(7): 559-68.
doi: 10.1038/nri2314 pmid: 18575461 |
| 6 |
Zav’yalov VP, Hämäläinen-Laanaya H, Korpela TK, Wahlroos T. Interferon-inducible myxovirus resistance proteins: potential biomarkers for differentiating viral from bacterial infections. Clin Chem. 2019; 65(6): 739-50.
doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2018.292391 pmid: 30593466 |
| 7 | Wang YZ, Zhou JG, Lu YM, Hu H, Xiao FF, Ge T, et al. Altered gut microbiota composition in children and their caregivers infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. World J Pediatr. 2023; 19(5):478-88. |
| 8 | Saheb Sharif-Askari N, Saheb Sharif-Askari F, Hafezi S, Kalaji Z, Temsah M, Almuhsen S, et al. Airways tissue expression of type I interferons and their stimulated genes is higher in children than adults. Heliyon. 2022; 8(11):e11724. |
| 9 | Cohen CA, Li APY, Hachim A, Hui DSC, Kwan MYW, Tsang OTY, et al. SARS-CoV-2 specific T-cell responses are lower in children and increase with age and time after infection. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):4678. |
| 10 |
Lam RPK, Dai Z, Lau EHY, Ip CYT, Chan HC, Zhao L, et al. Comparing 11 early warning scores and three shock indices in early sepsis prediction in the emergency department. World J Emerg Med. 2024; 15(4):273-82.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.052 pmid: 39050223 |
| 11 | Engelmann I, Dubos F, Lobert PE, Houssin C, Degas V, Sardet A, et al. Diagnosis of viral infections using myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA). Pediatrics. 2015; 135(4):e985-93. |
| 12 | Metz M, Gualdoni GA, Winkler HM, Warenits AM, Stöckl J, Burgmann H, et al. MxA for differentiating viral and bacterial infections in adults: a prospective, exploratory study. Infection. 2023; 51(5): 1329-37. |
| 13 | Self WH, Rosen J, Sharp SC, Filbin MR, Hou PC, Parekh AD, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of FebriDx: a rapid test to detect immune responses to viral and bacterial upper respiratory infections. J Clin Med. 2017; 6(10): 94. |
| 14 | Brendish NJ, Davis C, Chapman ME, Borca F, Waddington D, Hill C, et al. Emergency department point-of-care antiviral host response testing is accurate during periods of multiple respiratory virus co-circulation. J Infect. 2024; 88(1): 41-7. |
| 15 | Shapiro NI, Filbin MR, Hou PC, Kurz MC, Han JH, Aufderheide TP, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a bacterial and viral biomarker point-of-care test in the outpatient setting. JAMA Netw Open. 2022; 5(10): e2234588. |
| 16 | Tong-Minh K, Daenen K, Endeman H, Ramakers C, Gommers D, van Gorp E, et al. Performance of the FebriDx rapid point-of-care test for differentiating bacterial and viral respiratory tract infections in patients with a suspected respiratory tract infection in the emergency department. J Clin Med. 2023; 13(1): 163. |
| 17 | Shapiro NI, Self WH, Rosen J, Sharp SC, Filbin MR, Hou PC, et al. A prospective, multi-centre US clinical trial to determine accuracy of FebriDx point-of-care testing for acute upper respiratory infections with and without a confirmed fever. Ann Med. 2018; 50(5): 420-9. |
| 18 | Piri R, Yahya M, Ivaska L, Toivonen L, Lempainen J, Nuolivirta K, et al. Myxovirus resistance protein A as a marker of viral cause of illness in children hospitalized with an acute infection. Microbiol Spectr. 2022; 10(1): e0203121. |
| 19 |
Toivonen L, Schuez-Havupalo L, Rulli M, Ilonen J, Pelkonen J, Melen K, et al. Blood MxA protein as a marker for respiratory virus infections in young children. J Clin Virol. 2015; 62: 8-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2014.11.018 pmid: 25542463 |
| 20 | Piri R, Ivaska L, Yahya M, Toivonen L, Lempainen J, Kataja J, et al. Prevalence of respiratory viruses and antiviral MxA responses in children with febrile urinary tract infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020; 39(7):1239-44. |
| 21 |
Iliopoulou K, Koufargyris P, Doulou S, Tasouli E, Katopodis S, Chachali SP, et al. Developing a tool for differentiation between bacterial and viral respiratory infections using myxovirus resistance protein A and C-reactive protein. Infect Dis Ther. 2024; 13(1): 105-19.
doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00901-2 pmid: 38112973 |
| 22 |
Ronni T, Melén K, Malygin A, Julkunen I. Control of IFN-inducible MxA gene expression in human cells. J Immunol. 1993; 150(5):1715-26.
pmid: 7679692 |
| 23 |
Horisberger MA. Interferon-induced human protein MxA is a GTPase which binds transiently to cellular proteins. J Virol. 1992; 66(8): 4705-9.
pmid: 1629950 |
| 24 |
Sambursky R, Shapiro N. Evaluation of a combined MxA and CRP point-of-care immunoassay to identify viral and/or bacterial immune response in patients with acute febrile respiratory infection. Eur Clin Respir J. 2015; 2:28245.
doi: 10.3402/ecrj.v2.28245 pmid: 26672961 |
| 25 | Yoshimasu T, Manabe A, Ebihara Y, Tanaka R, Ooi J, Iseki T, et al. MxA expression in patients with viral infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003; 32(3):313-6. |
| 26 |
Manabe A, Yoshimasu T, Ebihara Y, Yagasaki H, Wada M, Ishikawa K, et al. Viral infections in juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia: prevalence and clinical implications. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2004; 26(10):636-41.
pmid: 15454834 |
| 27 | Rhedin S, Eklundh A, Ryd-Rinder M, Peltola V, Waris M, Gantelius J, et al. Myxovirus resistance protein A for discriminating between viral and bacterial lower respiratory tract infections in children - The TREND study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022; 28(9):1251-7. |
| 28 |
Lagi F, Trevisan S, Piccica M, Graziani L, Basile G, Mencarini J, et al. Use of the FebriDx point-of-care test for the exclusion of SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis in a population with acute respiratory infection during the second (COVID-19) wave in Italy. Int J Infect Dis. 2021; 108:231-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.065 pmid: 33901656 |
| 29 |
Mitchell PS, Emerman M, Malik HS. An evolutionary perspective on the broad antiviral specificity of MxA. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013; 16(4):493-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.04.005 pmid: 23725670 |
| 30 |
Netherton CL, Simpson J, Haller O, Wileman TE, Takamatsu HH, Monaghan P, et al. Inhibition of a large double-stranded DNA virus by MxA protein. J Virol. 2009; 83(5): 2310-20.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00781-08 pmid: 19109387 |
| 31 |
Johnston SC, Lin KL, Connor JH, Ruthel G, Goff A, Hensley LE. In vitro inhibition of monkeypox virus production and spread by Interferon-β. Virol J. 2012; 9:5.
doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-5 pmid: 22225589 |
| 32 | Lorenzo MM, Sanchez-Puig JM, Blasco R. Vaccinia virus and Cowpox virus are not susceptible to the interferon-induced antiviral protein MxA. PLoS One. 2017; 12(7):e0181459. |
| [1] | Peili Chen, Yan Ge, Huiqiu Sheng, Wenwu Sun, Jiahui Wang, Li Ma, Enqiang Mao. The role of early changes in routine coagulation tests in predicting the occurrence and prognosis of sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 136-143. |
| [2] | Chunxue Wang, Dianyin Yang, Yuxin Zhu, Qian Yang, Tong Liu, Xiandong Liu, Dongyang Zhao, Xiaowei Bao, Tiancao Dong, Li Shao, Lunxian Tang. Circulating circular RNAs act as potential novel biomarkers for sepsis secondary to pneumonia: a prospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 144-152. |
| [3] | Qingliu Zheng, Changyun Liu, Lingying Le, Qiqi Wu, Zhihong Xu, Jiyan Lin, Qiuyun Chen. ICU-acquired weakness in critically ill patients at risk of malnutrition: risk factors, biomarkers, and early enteral nutrition impact [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(1): 51-56. |
| [4] | Li Zhong, Feifei Shuai, Conglin Wang, Lipeng Han, Zhifeng Liu, Ming Wu. Serum procalcitonin levels are associated with rhabdomyolysis following exertional heatstroke: an over 10-year intensive care survey [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(1): 23-27. |
| [5] | Cansu Durak, Ebru Guney Sahin, Yasar Yusuf Can, Alican Sarisaltik, Kubra Boydag Guvenc. The value of prognostic markers for pediatric trauma patients [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(6): 448-453. |
| [6] | Tian Yan, Ziyin Chen, Shengdong Zou, Zefan Wang, Quan Du, Wenhua Yu, Wei Hu, Yongke Zheng, Keyi Wang, Xiaoqiao Dong, Shuangyong Dong. A prospective cohort study on serum A20 as a prognostic biomarker of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 360-366. |
| [7] | Cai-fang Xu, Ming-chao Huo, Jin-hui Huang, Chun-feng Liu, Wei Xu. Early changes in white blood cell, C-reactive protein and procalcitonin levels in children with severe multiple trauma [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(6): 448-452. |
| [8] | Hui Liu, Jie Hu, Jian-guo Xiao, Hong-jun Kang, Fei-hu Zhou. The procalcitonin-to-cortisol ratio is a potential prognostic predictor in sepsis with abdominal source: a retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(6): 441-447. |
| [9] | Li-wei Duan, Jin-long Qu, Jian Wan, Yong-hua Xu, Yi Shan, Li-xue Wu, Jin-hao Zheng, Wei-wei Jiang, Qi-tong Chen, Yan Zhu, Jian Zhou, Wen-bo Yu, Lei Pei, Xi Song, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Effects of viral infection and microbial diversity on patients with sepsis: A retrospective study based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(1): 29-35. |
| [10] | Wen-peng Yin, Jia-bao Li, Xiao-fang Zheng, Le An, Huan Shao, Chun-sheng Li. Effect of neutrophil CD64 for diagnosing sepsis in emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 79-86. |
| [11] | Wan-qin Xie, Lin Zhou, Yong Chen, Bin Ni. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of congenital heart defects [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2016, 7(2): 85-89. |
| [12] | Jing Li, Huan Ye, Li Zhao. B-type natriuretic peptide in predicting the severity of community-acquired pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(2): 131-136. |
| [13] | Kun Chen, Qiu-xiang Zhou, Hong-wei Shan, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Prognostic value of CD4+CD25+ Tregs as a valuable biomarker for patients with sepsis in ICU [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 40-43. |
| [14] | Li-ming Li, Wen-bo Cai, Qin Ye, Jian-min Liu, Xin Li, Xiao-xing Liao. Comparison of plasma microRNA-1 and cardiac troponin T in early diagnosis of patients with acute myocardial infarction [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(3): 182-186. |
| [15] | Yan Chen, Wei Yang, Gan-nan Wang, Jun Li, Xiao-rong Li, Jian Zhang, Wei Yuan, Dao-wu Wang, Jin-song Zhang, Ke-jiang Cao. Circulating microRNAs, novel biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction: a systemic review [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(4): 257-260. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
