World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (5): 386-392.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.077
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Saifeng Chen1,2, Xuewei Hao1, Guo Chen2, Guorong Liu2, Xiaoyan Yuan2( ), Peiling Shen2(
), Peiling Shen2( ), Dongfeng Guo1,2(
), Dongfeng Guo1,2( )
)
Received:2023-01-06
Accepted:2023-05-20
Online:2023-10-30
Published:2023-09-01
Contact:
Dongfeng Guo, Email: Saifeng Chen, Xuewei Hao, Guo Chen, Guorong Liu, Xiaoyan Yuan, Peiling Shen, Dongfeng Guo. Effects of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor on sepsis-associated acute kidney injury[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 386-392.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.077
Figure 1.
Expression of MANF in the kidney and serum of mice. A: Western blotting analysis of MANF in protein extracts from the kidney tissue of the S-AKI mice at different time; B: Western blotting analysis of MANF levels in protein extracts from the kidney tissue among different groups at 48 h; C: MANF in the serum at different time detected by the MANF ELISA kit. MANF: mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor; S-AKI: sepsis-associated acute kidney injury; n.s.: no significance. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
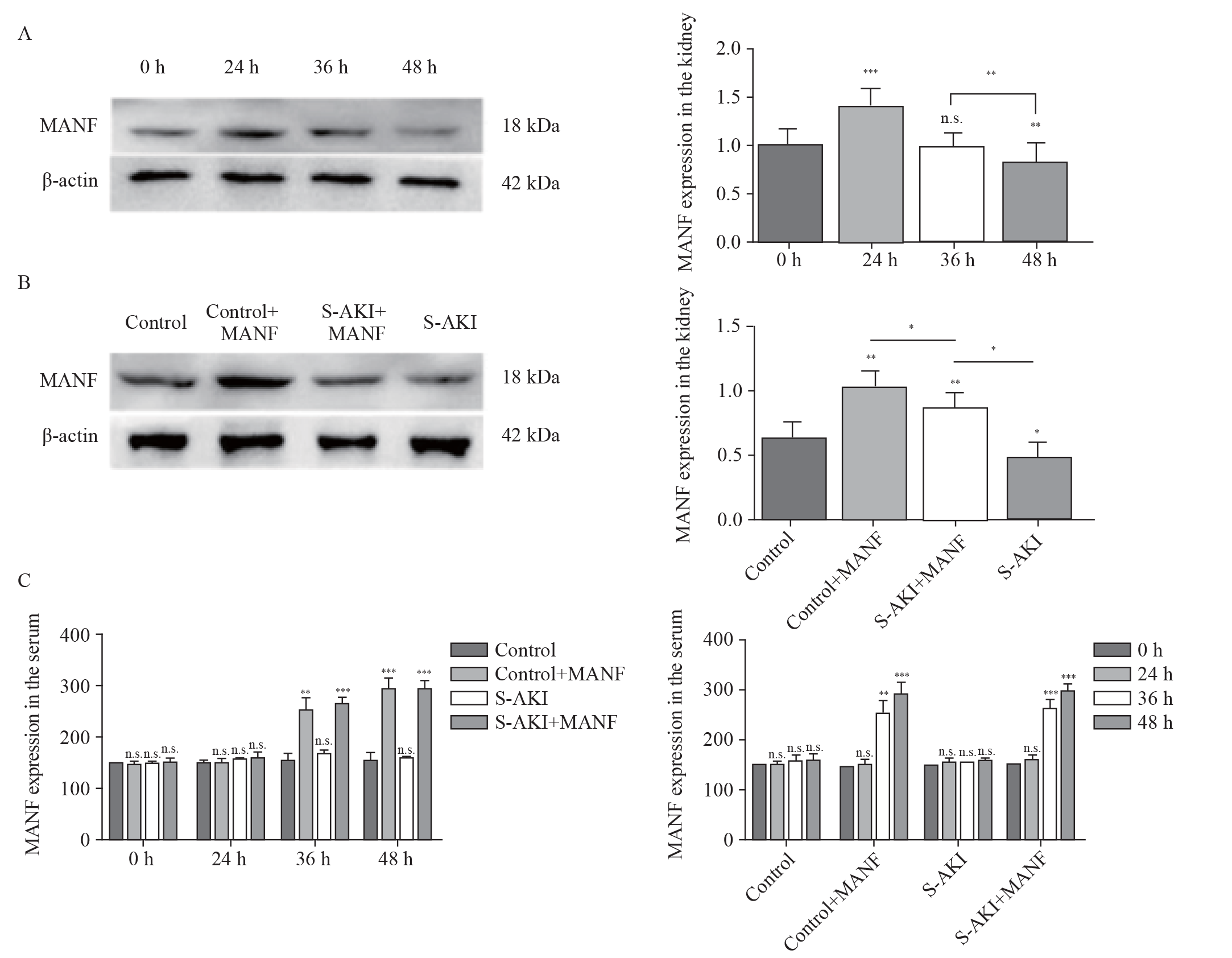

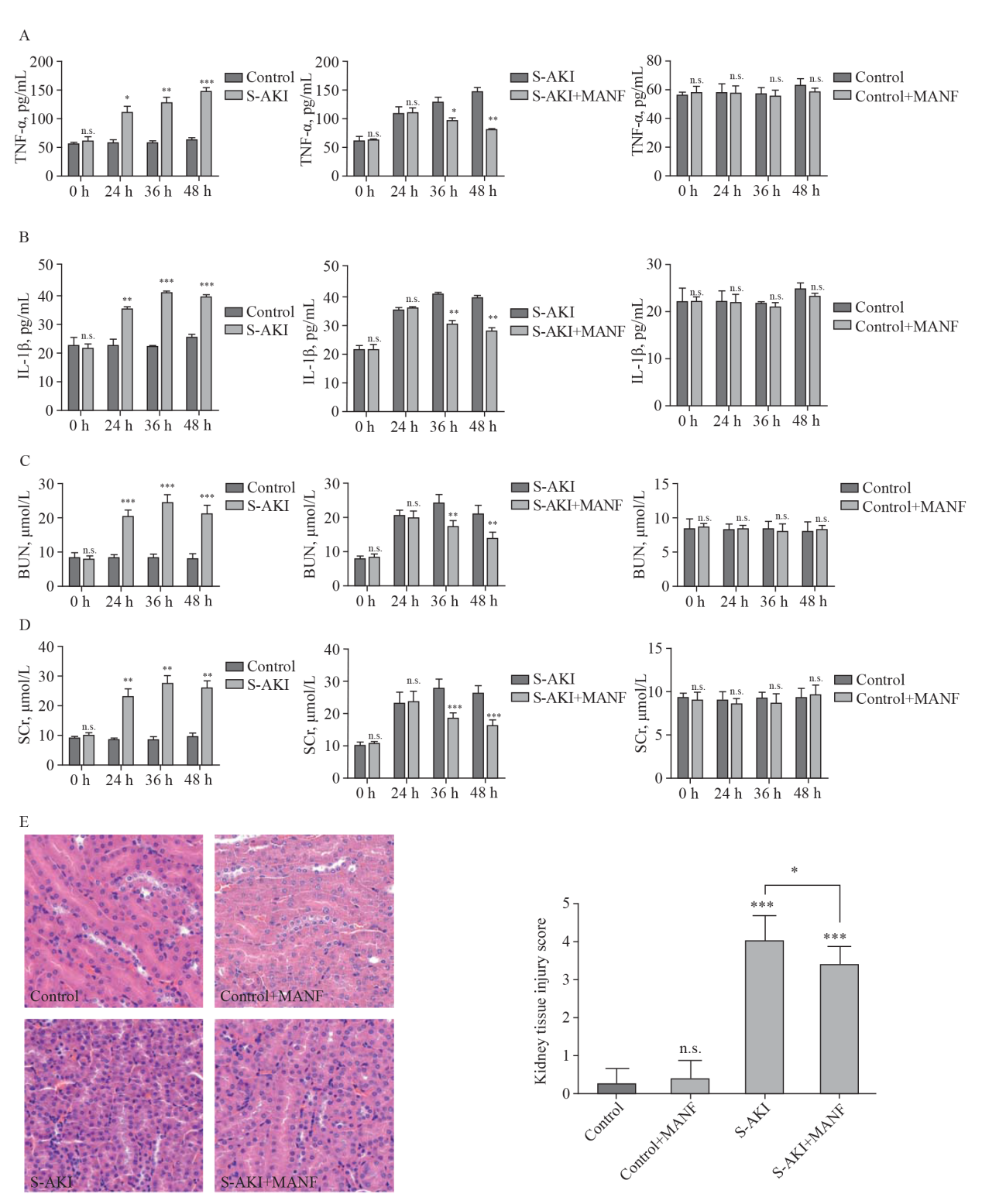
Figure 2.
Changes of pro-inflammatory cytokines,BUN, SCr, and histological findings among different groups. A: changes of TNF-α; B: changes of IL-1β; C: changes of BUN; D: changes of SCr; E: histological findings of the kidney tissue detected by hematoxylin-eosin staining (H&E, ×40) staining. TNF-α: necrosis factor-α; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; MANF: mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor; S-AKI: sepsis-associated acute kidney injury; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; SCr: serum creatinine. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001
| 1 | Yu SY, Ge ZZ, Xiang J, Gao YX, Lu X, Walline JH, et al. Is rosuvastatin protective against sepsis-associated encephalopathy? A secondary analysis of the SAILS trial. World J Emerg Med. 2022; 13(5):367-72. |
| 2 |
Kopec G, Collin M, Das A. Application of Kaiser Sepsis Calculator in culture-positive infants with early onset sepsis. World J Pediatr. 2021; 17(4):429-33.
doi: 10.1007/s12519-021-00446-9 |
| 3 |
Prachanukool T, Sanguanwit P, Yuksen KSC, Vichiensanth P. Initial venous lactate levels as a predictor of mortality in severe sepsis: a single-center retrospective cohort study. World J Emerg Med. 2022; 13(5):396-9.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.078 pmid: 36119767 |
| 4 |
Montomoli J, Donati A, Ince C. Acute kidney injury and fluid resuscitation in septic patients: are we protecting the kidney? Nephron. 2019; 143(3):170-3.
doi: 10.1159/000501748 |
| 5 |
Goriki Y, Tanaka A, Nishihira K, Kuriyama N, Shibata Y, Node K. A novel prediction model of acute kidney injury based on combined blood variables in STEMI. JACC Asia. 2021; 1(3):372-81.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2021.07.013 pmid: 36341223 |
| 6 |
Zhang D, Lu H, Hou W, Bai Y, Wu X. Effect of miR-132-3p on sepsis-induced acute kidney injury in mice via regulating HAVCR1/KIM-1. Am J Transl Res. 2021; 13(7):7794-803.
pmid: 34377256 |
| 7 |
Kothari NR, Gipson GT, Kidd JM. From surviving sepsis to surviving sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: focusing on risk stratification of acute kidney injury/acute kidney disease after sepsis. Kidney Med. 2021; 3(4):475-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2021.06.002 |
| 8 |
Chen HG, Han HZ, Li Y, Yu YH, Xie KL. Hydrogen alleviated organ injury and dysfunction in sepsis: the role of cross-talk between autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress: experimental research. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020; 78:106049.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106049 |
| 9 |
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A. Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2006; 7(9):880-5.
doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400779 pmid: 16953201 |
| 10 |
Huang M, Cai S, Su J. The pathogenesis of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(21):5376.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20215376 |
| 11 |
Niu Y, Chen Y, Sun P, Wang Y, Luo J, Ding Y, et al. Intragastric and atomized administration of canagliflozin inhibit inflammatory cytokine storm in lipopolysaccharide-treated sepsis in mice: a potential COVID-19 treatment. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021; 96:107773.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107773 |
| 12 |
Lindahl M, Saarma M, Lindholm P. Unconventional neurotrophic factors CDNF and MANF: structure, physiological functions and therapeutic potential. Neurobiol Dis. 2017; 97:90-102.
doi: S0969-9961(16)30171-1 pmid: 27425895 |
| 13 |
Kim Y, Lee H, Manson SR, Lindahl M, Evans B, Miner JH, et al. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor as a urine biomarker for endoplasmic reticulum stress-related kidney diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016; 27(10):2974-82.
pmid: 26940092 |
| 14 |
Wang Y, Wen W, Li H, Clementino M, Xu H, Xu M, et al. MANF is neuroprotective against ethanol-induced neurodegeneration through ameliorating ER stress. Neurobiol Dis. 2021; 148:105216.
doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105216 |
| 15 |
Xu S, Di Z, He Y, Wang R, Ma Y, Sun R, et al. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) protects against Aβ toxicity via attenuating Aβ-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Neuroinflammation. 2019; 16(1):35.
doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1429-0 |
| 16 |
Danilova T, Galli E, Pakarinen E, Palm E, Lindholm P, Saarma M, et al. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) is highly expressed in mouse tissues with metabolic function. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019; 10:765.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00765 |
| 17 |
Danilova T, Lindahl M. Emerging roles for mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) in pancreatic beta cells and diabetes. Front Physiol. 2018; 9:1457.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01457 pmid: 30386256 |
| 18 |
Wang P, Yang Y, Pang G, Zhang C, Wei C, Tao X, et al. Hepatocyte-derived MANF is protective for rifampicin-induced cholestatic hepatic injury via inhibiting ATF4-CHOP signal activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021; 162:283-97.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.10.028 |
| 19 |
Wu H, Li H, Wen W, Wang Y, Xu H, Xu M, et al. MANF protects pancreatic acinar cells against alcohol-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and cellular injury. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021; 28(10):883-92.
doi: 10.1002/jhbp.928 pmid: 33644980 |
| 20 |
Glembotski CC, Thuerauf DJ, Huang CQ, Vekich JA, Gottlieb RA, Doroudgar S. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor protects the heart from ischemic damage and is selectively secreted upon sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium depletion. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287(31):25893-904.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.356345 pmid: 22637475 |
| 21 |
Ma S, Evans RG, Iguchi N, Tare M, Parkington HC, Bellomo R, et al. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: a disease of the microcirculation. Microcirculation. 2019; 26(2):e12483.
doi: 10.1111/micc.2019.26.issue-2 |
| 22 |
Fu J, Nchambi KM, Wu H, Luo X, An X, Liu D. Liraglutide protects pancreatic β cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress by upregulating MANF to promote autophagy turnover. Life Sci. 2020; 252:117648.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117648 |
| 23 | Li L, Peng X, Guo L, Zhao Y, Cheng Q. Sepsis causes heart injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020; 13(5):964-71. |
| 24 |
Gao FJ, Zhang SH, Li TT, Wu JH, Wu Q. Expression and distribution of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor in the retina and optic nerve. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017; 10:686.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00686 |
| 25 |
Yang Y, Wang P, Zhang C, Huang F, Pang G, Wei C, et al. Hepatocyte-derived MANF alleviates hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury via regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in mice. Liver Int. 2021; 41(3):623-39.
doi: 10.1111/liv.14697 pmid: 33064897 |
| 26 |
Brochard L, Abroug F, Brenner M, Broccard AF, Danner RL, Ferrer M, et al. An Official ATS/ERS/ESICM/SCCM/SRLF Statement: prevention and management of acute renal failure in the ICU patients: an international consensus conference in intensive care medicine. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 181(10):1128-55.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.200711-1664ST |
| 27 |
Liu H, Wang L, Weng X, Chen H, Du Y, Diao C, et al. Inhibition of Brd4 alleviates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress by blocking FoxO4-mediated oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2019; 24:101195.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101195 |
| 28 |
Li WY, Li W, Leng Y, Xiong YH, Xia ZY. Ferroptosis is involved in diabetes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress. DNA Cell Biol. 2020; 39(2):210-25.
doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.5097 pmid: 31809190 |
| 29 |
Hadley G, Neuhaus AA, Couch Y, Beard DJ, Adriaanse BA, Vekrellis K, et al. The role of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response following cerebral ischemia. Int J Stroke. 2018; 13(4):379-90.
doi: 10.1177/1747493017724584 pmid: 28776456 |
| 30 |
Trychta KA, Bäck S, Henderson MJ, Harvey BK. KDEL receptors are differentially regulated to maintain the ER proteome under calcium deficiency. Cell Rep. 2018; 25(7):1829-40.e6.
doi: S2211-1247(18)31644-9 pmid: 30428351 |
| 31 |
Allen TM, Hansen CB, Guo LS. Subcutaneous administration of liposomes: a comparison with the intravenous and intraperitoneal routes of injection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993; 1150(1):9-16.
pmid: 8334142 |
| 32 |
Wang X, Li W, Zhou Q, Li J, Wang X, Zhang J, et al. MANF promotes diabetic corneal epithelial wound healing and nerve regeneration by attenuating hyperglycemia-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. Diabetes. 2020; 69(6):1264-78.
doi: 10.2337/db19-0835 pmid: 32312869 |
| 33 | Zhang J, Tong W, Sun H, Jiang M, Shen Y, Liu Y, et al. Nrf2-mediated neuroprotection by MANF against 6-OHDA-induced cell damage via PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway. Exp Gerontol. 2017; 100:77-86. |
| 34 |
Lewington AJP, Cerdá J, Mehta RL. Raising awareness of acute kidney injury: a global perspective of a silent killer. Kidney Int. 2013; 84(3):457-67.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.153 pmid: 23636171 |
| 35 |
Bucaloiu ID, Lester Kirchner H, Norfolk ER, Hartle JE II, Perkins RM. Increased risk of death and de novo chronic kidney disease following reversible acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012; 81(5):477-85.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.405 pmid: 22157656 |
| 36 |
Kramann R, Tanaka M, Humphreys BD. Fluorescence microangiography for quantitative assessment of peritubular capillary changes after AKI in mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014; 25(9):1924-31.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013101121 pmid: 24652794 |
| 37 |
Sato Y, Yanagita M. Immune cells and inflammation in AKI to CKD progression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018; 315(6): F1501-F1512.
doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00195.2018 |
| 38 |
Sharfuddin AA, Molitoris BA. Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011; 7(4):189-200.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.16 pmid: 21364518 |
| [1] | Yi-wen Fan, Shao-wei Jiang, Jia-meng Chen, Hui-qi Wang, Dan Liu, Shu-ming Pan, Cheng-jin Gao. A pulmonary source of infection in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury leads to a worse outcome and poor recovery of kidney function [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(1): 18-26. |
| [2] | Zhi-wei Liu, Hai-ying Wang, Lan Guan, Bin Zhao. Regulatory effects of hydrogen sulfide on alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with acute lung injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 67-73. |
| [3] | Yan-jun Qin, Xin-liang Zhang, Yue-qing Yu, Xiao-hua Bian, Shi-min Dong. Cardioprotective effect of erythropoietin on sepsis-induced myocardial injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(3): 215-223. |
| [4] | Lu-yi Liu, Yong-jian Zhu, Xiao-li Li, Ya-feng Liang, Zuo-peng Liang, Yong-hong Xia. Blood hemoperfusion with resin adsorption combined continuous veno-venous hemofiltration for patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(1): 44-48. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
