World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (5): 372-378.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.081
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Cheng Chi1, Hao Gong2, Kai Yang2, Peng Peng2( ), Xiaoxia Zhang2(
), Xiaoxia Zhang2( )
)
Received:2024-04-20
Online:2024-09-09
Published:2024-09-01
Contact:
Xiaoxia Zhang, Email: 394068616@qq.com; Peng Peng, Email: pengpeng4949@126.com
Cheng Chi, Hao Gong, Kai Yang, Peng Peng, Xiaoxia Zhang. Early peripheral perfusion index predicts 28-day outcome in patients with septic shock[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(5): 372-378.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.081
Table 1.
The demographic and baseline clinical characteristics of patients with septic shock
| Variables | Survival group (n=84) | Death group (n=116) | χ2/Z/t | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 56.79±18.32 | 65.60±15.08 | -3.727 | <0.001 |
| Male | 48 (57.14) | 76 (65.51) | 1.450 | 0.228 |
| Underlying disease | ||||
| Diabetes | 25 (29.76) | 32 (27.59) | 0.113 | 0.737 |
| Hypertension | 48 (57.14) | 62 (53.45) | 0.408 | 0.523 |
| CHD | 21 (25.00) | 32 (27.59) | 0.167 | 0.683 |
| Tumor | 4 (4.76) | 3 (2.59) | 0.191 | 0.662 |
| CKD | 18 (21.43) | 12 (10.34) | 4.694 | 0.030 |
| Immunological diseases | 0 (0) | 12 (10.34) | 9.244 | 0.002 |
| Onset time, h | 8 (2, 22) | 7 (5, 20) | -0.088 | 0.930 |
| Vital signs | ||||
| T, °C | 37.54±1.80 | 37.50±1.42 | 0.181 | 0.856 |
| HR, beats/min | 135 (108, 153) | 120 (66, 148) | -1.640 | 0.101 |
| MAP, mmHg | 61 (53, 65) | 63 (55, 66) | -0.829 | 0.407 |
| Respiratory rate, breaths/min | 25 (20, 33) | 22 (18, 33) | -0.881 | 0.378 |
| Etiology | 0.987 | 0.964 | ||
| Lung infection | 59 (70.23 ) | 81 (69.82) | ||
| Abdominal infection | 18 (21.43) | 26 (22.41) | ||
| Intracranial infection | 4 (4.76) | 4 (3.45) | ||
| Catheter-related infection | 2 (2.38) | 2 (1.72) | ||
| Skin and soft tissue infection | 1 (1.19) | 3 (2.59) | ||
| Clinical score | ||||
| GCS score | 15 (5, 15) | 3 (3, 3) | -9.749 | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 6 (4, 8) | 12 (10, 14) | -10.351 | <0.001 |
| APACHE II score | 19 (16, 24) | 37 (32, 40) | -11.525 | <0.001 |
| Blood testing | ||||
| Oxygenation index | 179 (91, 264) | 189 (96, 280) | -0.728 | 0.467 |
| WBC, ×109/L | 11.20 (7.94, 16.36) | 11.20 (7.94, 16.59) | -0.124 | 0.901 |
| Hb, g/L | 112.89±40.43 | 108.97±39.43 | 0.684 | 0.495 |
| PLT, ×109/L | 165 (125, 244) | 166 (127, 236) | -0.288 | 0.773 |
| Total bilirubin, μmol/L | 16 (10, 27) | 16 (11, 27) | -0.067 | 0.947 |
| CRE, μmol/L | 100 (65, 26) | 99 (69, 25) | -0.203 | 0.839 |
| IL-6, pg/mL | 104.5 (30.9, 1878.2) | 102.5 (38.6, 1507.0) | -0.188 | 0.851 |
| PCT, ng/mL | 1.47 (0.26, 11.75) | 1.00 (0.19, 9.26) | -0.594 | 0.552 |
| ALT, U/L | 20.12 (14.00, 40.00) | 33.50 (21.00, 71.00) | -3.066 | 0.002 |
| AST, U/L | 27.70 (22.90, 39.61) | 49.83 (32.25, 142.12) | -6.148 | <0.001 |
| PT, s | 13.10 (11.60, 15.50) | 14.90 (12.70, 21.30) | -3.772 | <0.001 |
| APTT, s | 27.90 (26.10, 31.30) | 31.20 (28.80, 36.50) | -5.089 | <0.001 |
| D-dimer, nmoml/L | 1,076 (471.00, 3,427.00) | 1,159 (262.75, 5,588.00) | -0.498 | 0.619 |
| 0-h Lac, mmol/L | 2.30 (2.00, 4.40) | 4.15 (3.03, 6.40) | -6.279 | <0.001 |
| 6-h Lac, mmol/L | 1.50 (1.20, 2.30) | 4.15 (2.70, 7.25) | -7.946 | <0.001 |
| 12-h Lac, mmol/L | 1.20 (1.00, 1.98) | 2.95 (2.20, 6.20) | -7.835 | <0.001 |
| 0-h PPI | 0.84 (0.60, 1.74) | 0.44 (0.27, 0.82) | -4.996 | <0.001 |
| 6-h PPI | 1.92 (0.87, 2.62) | 0.76 (0.42, 1.35) | -7.289 | <0.001 |
| 12-h PPI | 3.24 (2.22, 4.08) | 0.92 (0.46, 1.53) | -10.727 | <0.001 |
| 0-6 h Lac clearance rate, % | 38.10 (18.44, 54.37) | 15.84 (-34.00, 38.62) | -4.926 | <0.001 |
| 0-12 h Lac clearance rate, % | 91.29 (62.96, 142.86) | 40.37 (-27.12, 118.59) | -4.450 | <0.001 |
| 0-6 h PPI change rate, % | 61.80 (10.06, 305.48) | 36.84 (11.91, 128.67) | -1.715 | 0.086 |
| 0-12 h PPI change rate, % | 226.82 (95.12, 605.11) | 51.91 (5.52, 193.66) | -5.988 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | ||||
| Fluid volume, mL/d | 3,298.26±1,850.21 | 4,955.48±2,059.30 | -5.859 | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 21 (25.00) | 91 (78.40) | 56.485 | <0.001 |
| Vasoactive drugs | ||||
| NE | 25 (29.76) | 89 (76.72) | 43.839 | <0.001 |
| Dose of NE, mg/d | 50 (50, 100) | 100 (100, 200) | -7.774 | <0.001 |
| Dopamine | 22 (26.19) | 78 (67.24) | 32.841 | <0.001 |
| Dose of dopamine, mg/d | 125 (88, 150) | 100 (50, 150) | -1.281 | 0.200 |
| Dobutamine | 1 (1.19) | 10 (8.62) | 3.844 | 0.051 |
| Antibiotic | ||||
| Combination of two drugs | 9 (10.71) | 5 (4.31) | 3.069 | 0.080 |
| Carbapenem | 32 (38.10) | 66 (56.90) | 6.892 | 0.009 |
| Quinolone | 5 (5.95) | 12 (10.34) | 1.209 | 0.272 |
| Cephalosporin | 29 (34.52) | 26 (22.41) | 3.584 | 0.058 |
| Others | 9 (10.71) | 7 (6.03) | 2.879 | 0.092 |
Table 2.
Univariate Cox regression analysis of risk factors of 28-day mortality in septic shock patients
| Variables | β | SE | Wald | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.017 | 0.006 | 9.485 | 1.017 | 1.006-1.029 | 0.002 |
| GCS score | -0.256 | 0.038 | 45.820 | 0.774 | 0.718-0.833 | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 0.248 | 0.025 | 94.654 | 1.281 | 1.219-1.347 | <0.001 |
| APACHE II score | 0.106 | 0.010 | 107.473 | 1.112 | 1.090-1.134 | <0.001 |
| CKD | -0.605 | 0.305 | 3.930 | 1.246 | 0.800-1.993 | 0.057 |
| ALT | 0.003 | 0.002 | 2.665 | 1.003 | 0.999-1.007 | 0.103 |
| AST | 0.001 | 0.001 | 3.669 | 1.001 | 1.000-1.003 | 0.054 |
| PT | 0.035 | 0.008 | 20.327 | 1.035 | 1.020-1.035 | <0.001 |
| APTT | 0.010 | 0.015 | 45.168 | 1.015 | 1.074-1.138 | <0.001 |
| Fluid volume, mL/d | 0.000 | 0.000 | 36.106 | 1.000 | 1.000-1.000 | <0.001 |
| Dose of NE, mg/d | 0.007 | 0.001 | 65.880 | 1.007 | 1.005-1.009 | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 1.611 | 0.232 | 48.405 | 5.007 | 3.180-7.882 | <0.001 |
| 0-h Lac | 0.082 | 0.023 | 12.436 | 1.085 | 1.037-1.136 | <0.001 |
| 6-h Lac | 0.125 | 0.020 | 40.194 | 1.113 | 1.090-1.178 | <0.001 |
| 12-h Lac | 0.160 | 0.021 | 60.350 | 1.174 | 1.127-1.222 | <0.001 |
| 0-h PPI | -0.903 | 0.184 | 24.103 | 0.405 | 0.282-0.581 | <0.001 |
| 6-h PPI | -0.921 | 0.139 | 44.193 | 0.398 | 0.303-0.522 | <0.001 |
| 12-h PPI | -1.237 | 0.126 | 96.614 | 0.290 | 0.227-0.371 | <0.001 |
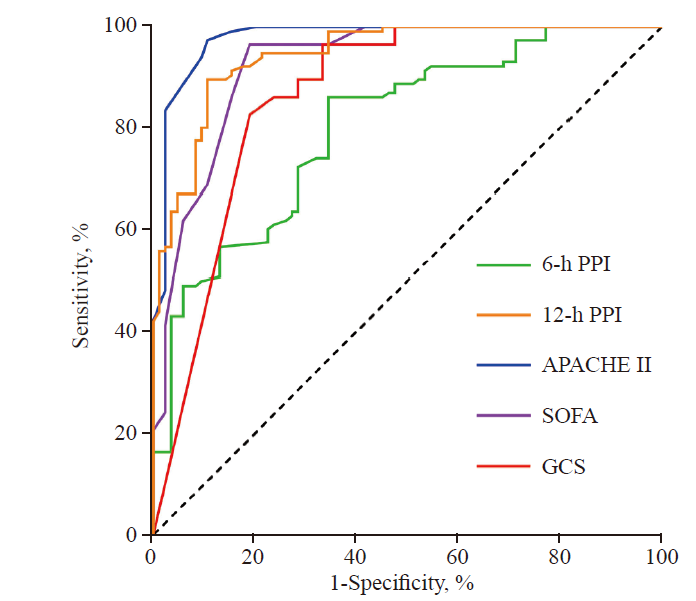
Figure 1.
The ROC curve of 6-h PPI, 12-h PPI, along with GCS, SOFA and APACHE II scores for predicting the 28-day prognosis in patients with septic shock. GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; APACHE II: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; PPI: peripheral perfusion index.
| 1 | Chebl RB, Kattouf N, Assaf M, Haidar S, Dagher GA, Nabi SA, et al. Comparing the demographic data and outcomes of septic shock patients presenting to teaching or non-teaching metropolitan hospitals in the United States. World J Emerg Med. 2022 ;13(6):433-40. |
| 2 | Sahu P, Raj Stanly EA, Simon Lewis LE, Prabhu K, Rao M, Kunhikatta V. Prediction modelling in the early detection of neonatal sepsis. World J Pediatr. 2022 ;18(3):160-75. |
| 3 | Merdji H, Levy B, Jung C, Ince C, Siegemund M, Meziani F. Microcirculatory dysfunction in cardiogenic shock. Ann Intensive Care. 2023 ;13(1):38. |
| 4 | Lawler PR, van Diepen S. Toward a broader characterization of macro- and microcirculatory uncoupling in cardiogenic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 ;206(10):1192-3. |
| 5 | Elshal MM, Hasanin AM, Mostafa M, Gamal RM. Plethysmographic peripheral perfusion index: could it be a new vital sign? Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:651909. |
| 6 | Coutrot M, Dudoignon E, Joachim J, Gayat E, Vallée F, Dépret F. Perfusion index: physical principles, physiological meanings and clinical implications in anaesthesia and critical care. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2021 ;40(6):100964. |
| 7 | Fu X, Lin X, Seery S, Zhao LN, Zhu HD, Xu J, et al. Speckle-tracking echocardiography for detecting myocardial dysfunction in sepsis and septic shock patients: a single emergency department study. World J Emerg Med. 2022 ;13(3):175-81. |
| 8 | Bauer M, Gerlach H, Vogelmann T, Preissing F, Stiefel J, Adam D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia between 2009 and 2019: results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2020 ;24(1):239. |
| 9 | Liu YC, Yao Y, Yu MM, Gao YL, Qi AL, Jiang TY, et al. Frequency and mortality of sepsis and septic shock in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2022 ;22(1):564. |
| 10 | Foster DM, Kellum JA. Endotoxic septic shock: diagnosis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 ;24(22):16185. |
| 11 | Gavelli F, Castello LM, Avanzi GC. Management of sepsis and septic shock in the emergency department. Intern Emerg Med. 2021 ;16(6):1649-61. |
| 12 | Zampieri FG, Bagshaw SM, Semler MW. Fluid therapy for critically ill adults with sepsis: a review. JAMA. 2023 ;329(22):1967-80. |
| 13 | He HW, Liu WL, Zhou X, Long Y, Liu DW. Effect of mean arterial pressure change by norepinephrine on peripheral perfusion index in septic shock patients after early resuscitation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 ;133(18):2146-52. |
| 14 | de Backer D, Ricottilli F, Ospina-Tascón GA. Septic shock: a microcirculation disease. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021 ;34(2):85-91. |
| 15 | Duranteau J, de Backer D, Donadello K, Shapiro NI, Hutchings SD, Rovas A, et al. The future of intensive care: the study of the microcirculation will help to guide our therapies. Crit Care. 2023 ;27(1):190. |
| 16 | Merdji H, Bataille V, Curtiaud A, Bonello L, Roubille F, Levy B, et al. Mottling as a prognosis marker in cardiogenic shock. Ann Intensive Care. 2023 ;13(1):80. |
| 17 | Merdji H, Curtiaud A, Aheto A, Studer A, Harjola VP, Monnier A, et al. Performance of early capillary refill time measurement on outcomes in cardiogenic shock: an observational, prospective multicentric study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 ;206(10):1230-8. |
| 18 | Janotka M, Ostadal P. Biochemical markers for clinical monitoring of tissue perfusion. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 ;476(3):1313-26. |
| 19 | Hariri G, Joffre J, Leblanc G, Bonsey M, Lavillegrand JR, Urbina T, et al. Narrative review: clinical assessment of peripheral tissue perfusion in septic shock. Ann Intensive Care. 2019 ;9(1):37. |
| 20 | Lima AP, Beelen P, Bakker J. Use of a peripheral perfusion index derived from the pulse oximetry signal as a noninvasive indicator of perfusion. Crit Care Med. 2002 ;30(6):1210-3. |
| 21 | Rasmussen PS, Aasvang EK, Olsen RM, Haahr-Raunkjaer C, Elvekjaer M, Sørensen HBD, et al. Continuous peripheral perfusion index in patients admitted to hospital wards - An observational study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2021 ;65(2):257-65. |
| 22 | Agerskov M, Thusholdt ANW, Holm-Sørensen H, Wiberg S, Meyhoff CS, Højlund J, et al. Association of the intraoperative peripheral perfusion index with postoperative morbidity and mortality in acute surgical patients: a retrospective observational multicentre cohort study. Br J Anaesth. 2021 ;127(3):396-404. |
| [1] | Subi Abudurexiti, Shihai Xu, Zhangping Sun, Yi Jiang, Ping Gong. Glucose metabolic reprogramming-related parameters for the prediction of 28-day neurological prognosis and all-cause mortality in patients after cardiac arrest: a prospective single-center observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(3): 197-203. |
| [2] | Jiale Yang, Fanghe Gong, Xuezhi Shi, Fanfan Wang, Jing Qian, Lulu Wan, Yi Chen, Huaisheng Chen, Huasheng Tong. A nomogram based on lymphocyte percentage for predicting hospital mortality in exertional heatstroke patients: a 13-year retrospective study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(6): 434-441. |
| [3] | Yue Li, Yong-peng Xie, Xiao-min Li, Tao Lu. Effects of early standardized enteral nutrition on preventing acute muscle loss in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with mechanical ventilation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(3): 193-197. |
| [4] | Xiao-guang Zhu, Jia-mei Jiang, Yong-xia Li, Jing Gao, Wei Wu, Qi-ming Feng. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in patients with acute pancreatitis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(1): 44-48. |
| [5] | Ralph Bou Chebl, Nadim Kattouf, Mohamad Assaf, Saadeddine Haidar, Gilbert Abou Dagher, Sarah Abdul Nabi, Rana Bachir, Mazen El Sayed. Comparing the demographic data and outcomes of septic shock patients presenting to teaching or non-teaching metropolitan hospitals in the United States [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(6): 433-440. |
| [6] | Gan-nan Wang, Zhong-man Zhang, Wen Chen, Xiao-quan Xu, Jin-song Zhang. Timing of brain computed tomography for predicting neurological prognosis in comatose cardiac arrest survivors: a retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 349-354. |
| [7] | Fei Shao, Xian Shi, Shu-hua Huo, Qing-yu Liu, Ji-xue Shi, Jian Kang, Ping Gong, Sheng-tao Yan, Guo-xing Wang, Li-jie Qin, Fei Wang, Ke Feng, Feng-ying Chen, Yong-jie Yin, Tao Ma, Yan Li, Yang Wu, Hao Cui, Chang-xiao Yu, Song Yang, Wei Gan, Sai Wang, Liu-ye-zi Du, Ming-chen Zhao, Zi-ren Tang, Shen Zhao. Development and evaluation of a predictive nomogram for survival in heat stroke patients: a retrospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 355-360. |
| [8] | Xuan Fu, Xue Lin, Samuel Seery, Li-na Zhao, Hua-dong Zhu, Jun Xu, Xue-zhong Yu. Speckle-tracking echocardiography for detecting myocardial dysfunction in sepsis and septic shock patients: A single emergency department study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(3): 175-181. |
| [9] | Ren-qi Yao, Chao Ren, Di Ren, Jin-xiu Li, Ying Li, Xue-yan Liu, Lei Huang, Yong Liu, Mian Peng, Yong-wen Feng, Yong-ming Yao. Development of septic shock and prognostic assessment in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease outside Wuhan, China [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(4): 293-298. |
| [10] | Xin Lu, Wei Han, Yan-xia Gao, Shi-gong Guo, Shi-yuan Yu, Xue-zhong Yu, Hua-dong Zhu, Yi Li. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids in immunocompetent patients with septic shock [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(2): 124-130. |
| [11] | Yu-ming Wang, Yan-jun Zheng, Ying Chen, Yun-chuan Huang, Wei-wei Chen, Ran Ji, Li-li Xu, Zhi-tao Yang, Hui-qiu Sheng, Hong-ping Qu, En-qiang Mao, Er-zhen Chen. Effects of fluid balance on prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients secondary to sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 216-222. |
| [12] | Wen-peng Yin, Jia-bao Li, Xiao-fang Zheng, Le An, Huan Shao, Chun-sheng Li. Effect of neutrophil CD64 for diagnosing sepsis in emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 79-86. |
| [13] | Shahin Shadnia, Nasim Zaman, Hossein Hassanian-Moghaddam, Hamed Shafaroodi, Mina Padandar, Mohammad Hasan Rezaeizadeh. Prognostic value of cortisol and thyroid function tests in poisoned patients admitted to toxicology ICU [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(1): 51-55. |
| [14] | Yan Ma, Xiang-you Yu, Yi Wang. Dose-related effects of dexmedetomidine on immunomodulation and mortality to septic shock in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(1): 56-63. |
| [15] | Liang-shan Peng, Juan Li, Gao-sheng Zhou, Lie-hua Deng, Hua-guo Yao. Relationships between genetic polymorphisms of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 and septic shock in a Chinese Han population [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(2): 123-130. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
