World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (3): 190-196.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.041
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huixin Zhao, Yiming Dong, Sijia Wang, Jiayuan Shen, Zhenju Song( ), Mingming Xue(
), Mingming Xue( ), Mian Shao(
), Mian Shao( )
)
Received:2023-10-29
Accepted:2024-02-20
Online:2024-05-15
Published:2024-05-01
Contact:
Mian Shao, Email: Huixin Zhao, Yiming Dong, Sijia Wang, Jiayuan Shen, Zhenju Song, Mingming Xue, Mian Shao. Comparison between sepsis-induced coagulopathy and sepsis-associated coagulopathy criteria in identifying sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(3): 190-196.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.041
Table 1.
The scoring system of the ISTH overt-DIC and SIC criteria
| Items | Point | Overt-DIC | SIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platelet, ×109/L | 0 | >100 | ≥150 |
| 1 | 50-100 | ≥100, < 150 | |
| 2 | <50 | <100 | |
| Prolonged PT/INR, s | 0 | <3 | ≤1.2 |
| 1 | 3-6 | >1.2, ≤ 1.4 | |
| 2 | >6 | >1.4 | |
| Fibrinogen, g/mL | 0 | ≥100 | - |
| 1 | <100 | - | |
| D-dimer a | 0 | Normal | - |
| 2 | Moderate increase | - | |
| 3 | Severe increase | - | |
| SOFA score b | 0 | - | 0 |
| 1 | - | 1 | |
| 2 | - | ≥2 | |
| Diagnosis | ≥5 points | ≥4 points c |
Table 2.
The scoring system of sepsis-associated coagulopathy (SAC)
| INR | PLT (×109/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥150 | 100-149 | 80-99 | <80 | |
| <1.2 | No SAC | No SAC | No SAC | No SAC |
| ≥1.2, <1.4 | No SAC | Mild SAC | Moderate SAC | Moderate SAC |
| ≥1.4, <1.6 | No SAC | Moderate SAC | Moderate SAC | Moderate SAC |
| ≥1.6 | No SAC | Moderate SAC | Moderate SAC | Severe SAC |
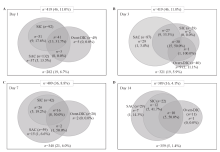
Figure 1.
Distribution and mortality of patients according to the overt-DIC, SIC and SAC criteria. The numbers represent the number of cases in each category. The numbers in parentheses are the non-survivors and mortality rate. DIC: disseminated intravascular coagulation; SIC: sepsis-induced coagulopathy; SAC: sepsis-associated coagulopathy.
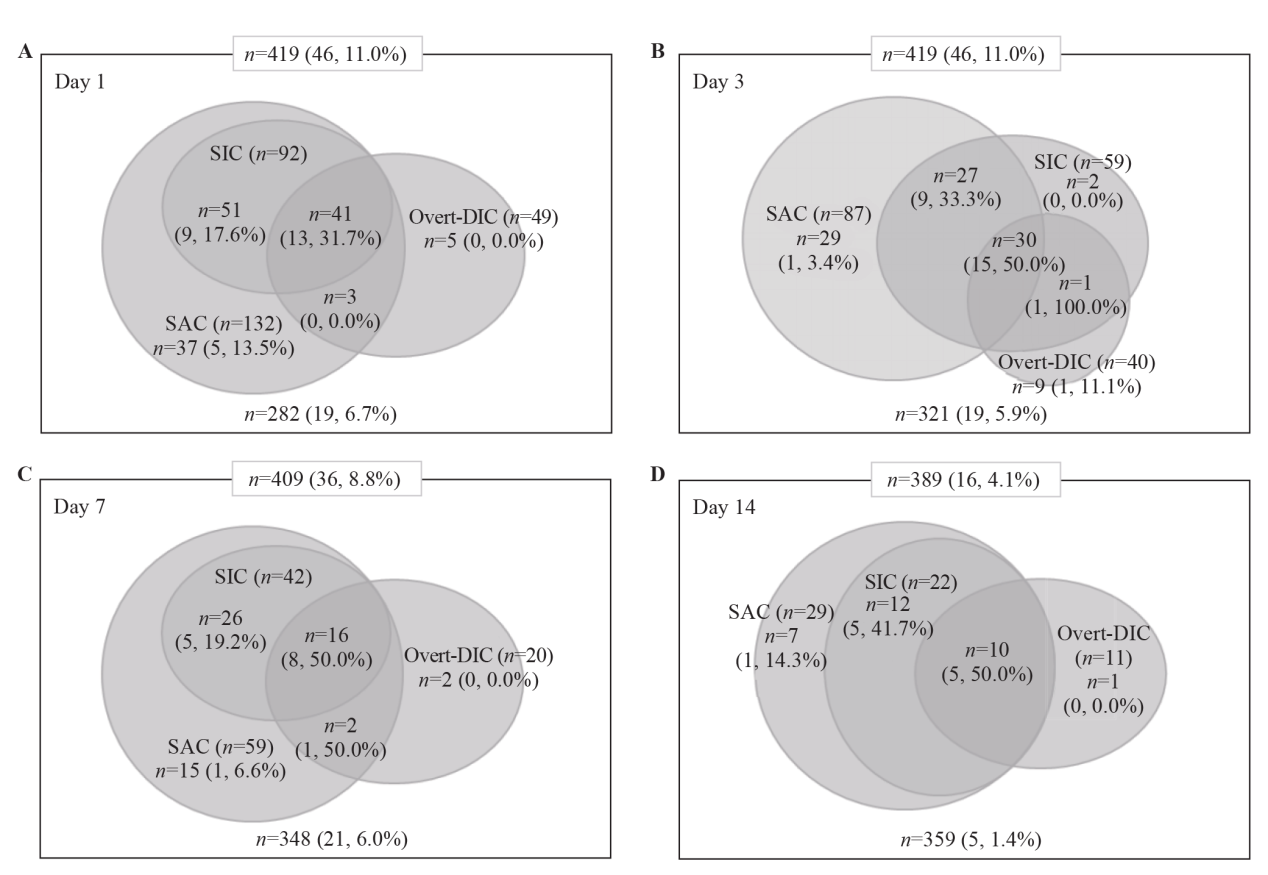
Table 3.
Comparison of SIC and SAC criteria for detecting overt-DIC in sepsis patients
| Time | SIC | SAC | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | |||
| Prevalence, % | 22.0 (92/419) | 31.5 (132/419) | <0.001 |
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.85 (0.81-0.88) | 0.83 (0.79-0.87) | 0.307 |
| Sensitivity, % | 83.67 | 89.80 | 0.250 |
| Specificity, % | 86.22 | 76.22 | <0.001 |
| PPV, % | 44.6 | 33.3 | 0.088 |
| NPV, % | 97.6 | 98.3 | 0.545 |
| Day 3 | |||
| Prevalence, % | 14.1 (59/419) | 20.8 (87/419) | <0.001 |
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.84 (0.80-0.87) | 0.81 (0.77-0.85) | 0.097 |
| Sensitivity, % | 75.00 | 77.50 | 1.000 |
| Specificity, % | 92.16 | 84.86 | <0.001 |
| PPV, % | 50.8 | 35.6 | 0.067 |
| NPV, % | 97.2 | 97.2 | 0.957 |
| Day 7 | |||
| Prevalence, % | 10.3 (42/409) | 14.4 (59/409) | <0.001 |
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.86 (0.82-0.90) | 0.89 (0.85-0.92) | 0.422 |
| Sensitivity, % | 80.00 | 90.00 | 0.500 |
| Specificity, % | 92.40 | 88.18 | <0.001 |
| PPV, % | 38.1 | 30.5 | 0.426 |
| NPV, % | 98.7 | 99.4 | 0.725 |
| Day 14 | |||
| Prevalence, % | 5.7 (22/389) | 7.5 (29/389) | 0.016 |
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.93 (0.89-0.96) | 0.91 (0.87-0.95) | 0.007 |
| Sensitivity, % | 90.91 | 90.91 | 1.000 |
| Specificity, % | 94.69 | 91.59 | 0.016 |
| PPV, % | 45.5 | 34.5 | 0.128 |
| NPV, % | 99.5 | 99.5 | 0.539 |
Table 4.
Comparison of SIC and SAC criteria for detecting pre-DIC in sepsis patients
| Criteria | AUC | 95% CI | Cut-off value | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIC criteria | 0.62* | 0.57-0.66 | - | 44.00% | 79.44% | 12.0% | 95.7% |
| SAC criteria | 0.61* | 0.56-0.67 | - | 52.00% | 69.80% | 9.8% | 95.8% |
| SIC score on day 1 | 0.69* | 0.65-0.74 | >3 | 72.00% | 62.94% | 11.0% | 97.3% |
| SAC rating | 0.61* | 0.57-0.66 | > 0 | 52.00% | 69.80% | 9.8% | 95.8% |
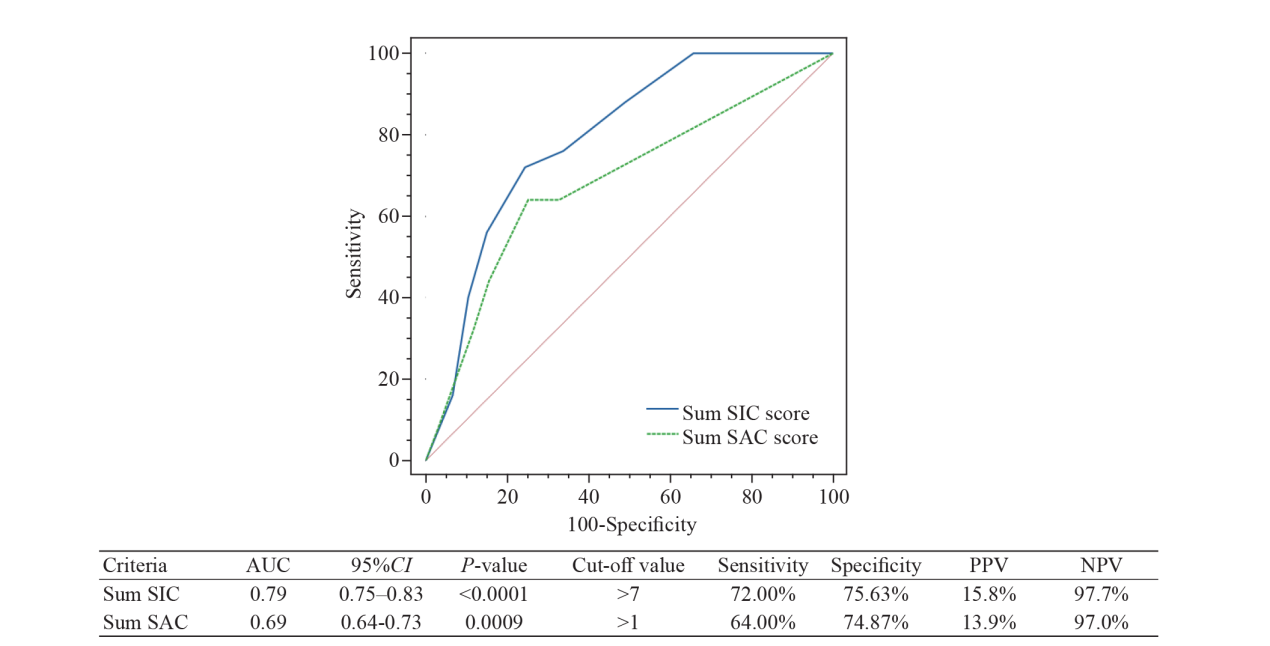
Figure 2.
ROC curve of cumulative SIC and SAC scores on days 1 and 3 for the detection of pre-DIC. ROC curve: receiver operating characteristic curve; SIC: sepsis-induced coagulopathy; SAC: sepsis-associated coagulopathy; DIC: disseminated intravascular coagulation; AUC: area under the curve; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; PPV: positive predictive value; NPV: negative predictive value.
| 1 |
Wang J, Weng L, Xu J, Du B. Blood gas analysis as a surrogate for microhemodynamic monitoring in sepsis. World J Emerg Med. 2023; 14(6):421-7.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.093 pmid: 37969221 |
| 2 |
Sljivancanin Jakovljevic T, Martic J, Jacimovic J, Nikolic N, Milasin J, Mitrović TL. Association between innate immunity gene polymorphisms and neonatal sepsis development: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Pediatr. 2022; 18(10):654-70.
doi: 10.1007/s12519-022-00569-7 pmid: 35666457 |
| 3 |
Levi M, van der Poll T. Coagulation and sepsis. Thromb Res. 2017; 149:38-44.
doi: S0049-3848(16)30619-3 pmid: 27886531 |
| 4 |
Gando S, Levi M, Toh CH. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016; 2:16037.
doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.37 pmid: 27250996 |
| 5 |
Saito S, Uchino S, Hayakawa M, Yamakawa K, Kudo D, Iizuka Y, et al. Epidemiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation in sepsis and validation of scoring systems. J Crit Care. 2019; 50:23-30.
doi: S0883-9441(18)30679-8 pmid: 30471557 |
| 6 | Iba T, Umemura Y, Watanabe E, Wada T, Hayashida K, Kushimoto S, et al. Diagnosis of sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation and coagulopathy. Acute Med Surg. 2019; 6(3):223-32. |
| 7 | Egi M, Ogura H, Yatabe T, Atagi K, Inoue S, Iba T, et al. The Japanese clinical practice guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2020 (J-SSCG 2020). Acute Med Surg. 2021; 8(1):e659. |
| 8 |
Wada H, Matsumoto T, Yamashita Y. Diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) according to four DIC guidelines. J Intensive Care. 2014; 2(1):15.
doi: 10.1186/2052-0492-2-15 pmid: 25520831 |
| 9 | Taylor FB Jr, Toh CH, Hoots WK, Wada H, Levi M, Scientific Subcommittee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH). Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 2001; 86(5):1327-30. |
| 10 | Jackson Chornenki NL, Dwivedi DJ, Kwong AC, Zamir N, Fox-Robichaud AE, Liaw PC, et al. Identification of hemostatic markers that define the pre-DIC state: a multi-center observational study. J Thromb Haemost. 2020; 18(10):2524-31. |
| 11 | Ding RY, Wang Z, Lin Y, Liu BY, Zhang ZD, Ma XC. Comparison of a new criteria for sepsis-induced coagulopathy and International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis disseminated intravascular coagulation score in critically ill patients with sepsis 3.0: a retrospective study. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2018; 29(6):551-8. |
| 12 | Iba T, Nisio MD, Levy JH, Kitamura N, Thachil J. New criteria for sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) following the revised sepsis definition: a retrospective analysis of a nationwide survey. BMJ Open. 2017; 7(9):e017046. |
| 13 |
Lyons PG, Micek ST, Hampton N, Kollef MH. Sepsis-associated coagulopathy severity predicts hospital mortality. Crit Care Med. 2018; 46(5):736-42.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002997 pmid: 29373360 |
| 14 |
Iba T, Levy JH, Yamakawa K, Thachil J, Warkentin TE, Levi M, et al. Proposal of a two-step process for the diagnosis of sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2019; 17(8):1265-8.
doi: 10.1111/jth.14482 pmid: 31099127 |
| 15 |
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315(8):801-10.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 pmid: 26903338 |
| 16 |
Bakhtiari K, Meijers JCM, de Jonge E, Levi M. Prospective validation of the International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Crit Care Med. 2004; 32(12):2416-21.
doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000147769.07699.e3 pmid: 15599145 |
| 17 |
Wada H, Minamikawa K, Wakita Y, Nakase T, Kaneko T, Ohiwa M, et al. Hemostatic study before onset of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Hematol. 1993; 43(3):190-4.
doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830430306 pmid: 8352234 |
| 18 | Peng JC, Nie F, Li YJ, Xu QY, Xing SP, Li W, et al. Favorable outcomes of anticoagulation with unfractioned heparin in sepsis-induced coagulopathy: a retrospective analysis of MIMIC-III database. Front Med. 2022; 8:773339. |
| 19 | Yamakawa K, Yoshimura J, Ito T, Hayakawa M, Hamasaki T, Fujimi S. External validation of the two newly proposed criteria for assessing coagulopathy in sepsis. Thromb Haemost. 2019; 119(2):203-12. |
| 20 |
Iba T, Levy JH, Warkentin TE, Thachil J, van der Poll T, Levi M, et al. Diagnosis and management of sepsis-induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2019; 17(11):1989-94.
doi: 10.1111/jth.14578 pmid: 31410983 |
| 21 |
Iba T, Arakawa M, Di Nisio M, Gando S, Anan H, Sato K, et al. Newly proposed sepsis-induced coagulopathy precedes international society on thrombosis and haemostasis overt-disseminated intravascular coagulation and predicts high mortality. J Intensive Care Med. 2020; 35(7):643-9.
doi: 10.1177/0885066618773679 pmid: 29720054 |
| 22 |
Helms J, Severac F, Merdji H, Clere-Jehl R, François B, Mercier E, et al. Performances of disseminated intravascular coagulation scoring systems in septic shock patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2020; 10(1):92.
doi: 10.1186/s13613-020-00704-5 pmid: 32651674 |
| 23 |
Okamoto K, Wada H, Hatada T, Uchiyama T, Kawasugi K, Mayumi T, et al. Frequency and hemostatic abnormalities in pre-DIC patients. Thromb Res. 2010; 126(1):74-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2010.03.017 pmid: 20452653 |
| 24 |
Liao DY, Zhou F, Luo LL, Xu M, Wang HB, Xia JH, et al. Haematological characteristics and risk factors in the classification and prognosis evaluation of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2020; 7(9):e671-e678.
doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30217-9 pmid: 32659214 |
| 25 | Papageorgiou C, Jourdi G, Adjambri E, Walborn A, Patel P, Fareed J, et al. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: an update on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic strategies. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018; 24(9_suppl):8S-28S. |
| [1] | A-ling Tang, Yan Li, Li-chao Sun, Xiao-yu Liu, Nan Gao, Sheng-tao Yan, Guo-qiang Zhang. Xuebijing improves intestinal microcirculation dysfunction in septic rats by regulating the VEGF-A/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(3): 206-213. |
| [2] | Qing Zhao, Jinfu Ma, Jianguo Xiao, Zhe Feng, Hui Liu. Data driven analysis reveals prognostic genes and immunological targets in human sepsis-associated acute kidney injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(2): 91-97. |
| [3] | Weichao Ding, Wei Zhang, Juan Chen, Mengmeng Wang, Yi Ren, Jing Feng, Xiaoqin Han, Xiaohang Ji, Shinan Nie, Zhaorui Sun. Protective mechanism of quercetin in alleviating sepsis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(2): 111-120. |
| [4] | Wei Zhou, Maiying Fan, Xiang Li, Fang Yu, En Zhou, Xiaotong Han. Molecular mechanism of Xuebijing in treating pyogenic liver abscess complicated with sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(1): 35-40. |
| [5] | Jingyi Wang, Li Weng, Jun Xu, Bin Du. Blood gas analysis as a surrogate for microhemodynamic monitoring in sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(6): 421-427. |
| [6] | Saifeng Chen, Xuewei Hao, Guo Chen, Guorong Liu, Xiaoyan Yuan, Peiling Shen, Dongfeng Guo. Effects of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor on sepsis-associated acute kidney injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 386-392. |
| [7] | Mubing Qin, Yanxia Gao, Shigong Guo, Xin Lu, Qian Zhao, Zengzheng Ge, Huadong Zhu, Yi Li. Establishment and evaluation of animal models of sepsis-associated encephalopathy [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 349-353. |
| [8] | Meng-meng An, Chen-xi Liu, Ping Gong. Effects of continuous renal replacement therapy on inflammation-related anemia, iron metabolism and prognosis in sepsis patients with acute kidney injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(3): 186-192. |
| [9] | Jue-xian Wei, Hui-lin Jiang, Xiao-hui Chen. Endothelial cell metabolism in sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(1): 10-16. |
| [10] | Hui Liu, Jie Hu, Jian-guo Xiao, Hong-jun Kang, Fei-hu Zhou. The procalcitonin-to-cortisol ratio is a potential prognostic predictor in sepsis with abdominal source: a retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(6): 441-447. |
| [11] | Ralph Bou Chebl, Nadim Kattouf, Mohamad Assaf, Saadeddine Haidar, Gilbert Abou Dagher, Sarah Abdul Nabi, Rana Bachir, Mazen El Sayed. Comparing the demographic data and outcomes of septic shock patients presenting to teaching or non-teaching metropolitan hospitals in the United States [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(6): 433-440. |
| [12] | Shi-yuan Yu, Zeng-zheng Ge, Jun Xiang, Yan-xia Gao, Xin Lu, Joseph Harold Walline, Mu-bing Qin, Hua-dong Zhu, Yi Li. Is rosuvastatin protective against sepsis-associated encephalopathy? A secondary analysis of the SAILS trial [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 367-372. |
| [13] | A-ling Tang, Mei-jia Shen, Guo-qiang Zhang. Intestinal microcirculation dysfunction in sepsis: pathophysiology, clinical monitoring, and therapeutic interventions [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 343-348. |
| [14] | Xiao-kang Dai, Zhen-xing Ding, Yuan-yuan Tan, Hua-rui Bao, Dong-yao Wang, Hong Zhang. Neutrophils inhibit CD8+ T cells immune response by arginase-1 signaling in patients with sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(4): 266-273. |
| [15] | Xuan Fu, Xue Lin, Samuel Seery, Li-na Zhao, Hua-dong Zhu, Jun Xu, Xue-zhong Yu. Speckle-tracking echocardiography for detecting myocardial dysfunction in sepsis and septic shock patients: A single emergency department study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(3): 175-181. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
