World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (5): 373-378.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.086
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chao Liu, Zhao-rui Sun, Meng-meng Wang, Zhi-zhou Yang, Wei Zhang, Yi Ren, Xiao-qin Han, Rui Liu, Quan Li, Shi-nan Nie( )
)
Received:2021-12-29
Accepted:2022-05-20
Online:2022-08-23
Published:2022-09-01
Contact:
Shi-nan Nie
E-mail:shn_nie@sina.com
Chao Liu, Zhao-rui Sun, Meng-meng Wang, Zhi-zhou Yang, Wei Zhang, Yi Ren, Xiao-qin Han, Rui Liu, Quan Li, Shi-nan Nie. Arctigenin attenuates paraquat-induced human lung epithelial A549 cell injury by suppressing ROS/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases-mediated apoptosis[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 373-378.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.086

Figure 1.
Arctigenin ameliorated paraquat (PQ)-induced A549 cell injury. A: PQ inhibited the viability of A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner, reflected by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (n=3, *P<0.05 vs. control); B: no dramatic effect of arctigenin was observed on the cell viability of A549 cells under control conditions, indicated by CCK-8 assay (n=3); C: the bar graph indicated arctigenin ameliorated PQ-induced A549 cell injury in a dose-dependent manner, determined by CCK-8 assay (n=3, *P<0.05 vs. PQ); D: representative light microscopy images indicated arctigenin ameliorated PQ-induced A549 cell injury, as reflected by more shrunken cells (scale bar=50 μm).
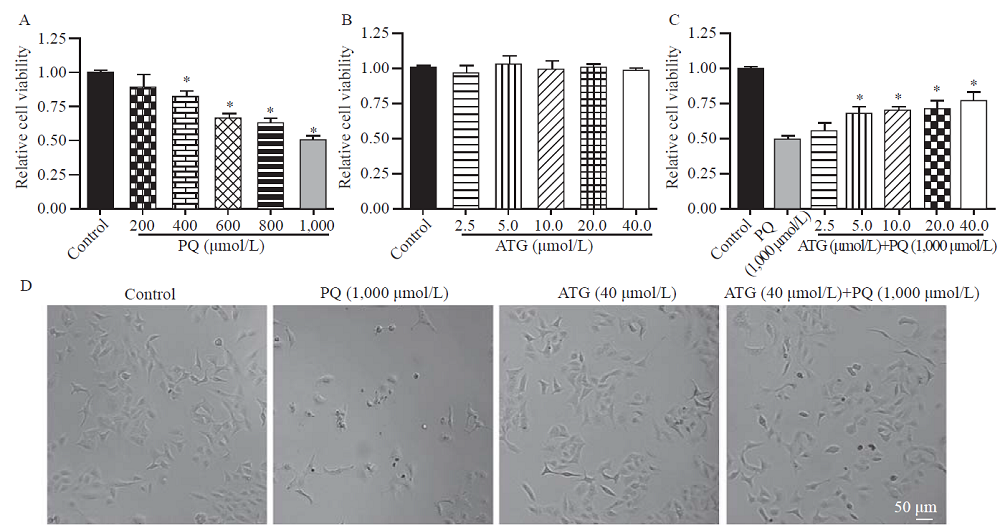
Figure 2.
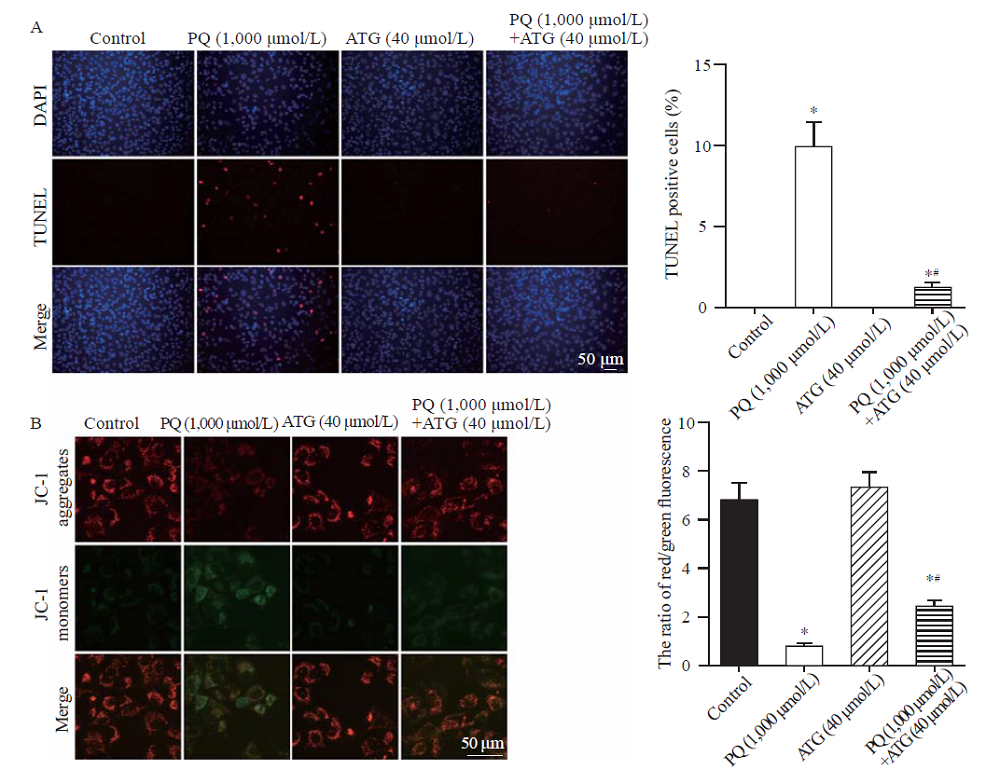
Arctigenin alleviated paraquat (PQ)-induced A549 cell apoptosis. A: representative images and statistical results of TUNEL staining showing arctigenin reduced A549 cell apoptosis induced by PQ (n=5, *P<0.05 vs. control; #P<0.05 vs. PQ; scale bar=50 μm). B: representative pictures and statistical results indicating arctigenin alleviated PQ-induced mitochondrial membrane potential loss in A549 cells. JC-1 exhibited potential-dependent accumulation in healthy mitochondria where it formed J aggregates (red) while it remained as monomer (green) upon mitochondrial depolarization. The ratio of red/green fluorescence of JC-1 dramatically decreased in PQ-treated A549 cells, which was relieved by arctigenin co-administration (n=5, *P<0.05 vs. control; #P<0.05 vs. PQ; scale bar=50 μm).
| 1 |
Xu LJ, Xu J, Wang Z. Molecular mechanisms of paraquat-induced acute lung injury: a current review. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2014; 37(2): 130-4.
doi: 10.3109/01480545.2013.834361 |
| 2 |
Jiang YF, Kang J, Huang PP, Yao JX, Wang ZH, Jiang L, et al. Evaluation of gastric lavage efficiency and utility using a rapid quantitative method in a swine paraquat poisoning model. World J Emerg Med. 2020; 11(3): 174-81.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2020.03.008 |
| 3 |
Yi JH, Zhang ZC, Zhang MB, He X, Lin HR, Huang HW, et al. Role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the pulmonary fibrosis induced by paraquat in rats. World J Emerg Med. 2021; 12(3): 214-20.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.03.009 |
| 4 |
Suntres ZE. Role of antioxidants in paraquat toxicity. Toxicology. 2002; 180(1): 65-77.
doi: 10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00382-7 |
| 5 | Sun B, He Y. Paraquat poisoning mechanism and its clinical treatment progress. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017; 29(11): 1043-46. |
| 6 |
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA, Sánchez-Navarro A, Remião F, Bastos ML, Carvalho F. Paraquat poisonings: mechanisms of lung toxicity, clinical features, and treatment. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008; 38(1): 13-71.
pmid: 18161502 |
| 7 |
Nemery B, Smith LL, Aldridge WN. Putrescine and 5-hydroxytryptamine accumulation in rat lung slices: cellular localization and responses to cell-specific lung injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987; 91(1): 107-20.
doi: 10.1016/0041-008X(87)90198-0 |
| 8 |
Hu X, Shen H, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhao M. Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 alleviates paraquat-induced acute lung injury in mice. Life Sci. 2019; 218: 38-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.12.028 |
| 9 |
Zhang ZD, Yang YJ, Liu XW, Qin Z, Li SH, Li JY. Aspirin eugenol ester ameliorates paraquat-induced oxidative damage through ROS/p38-MAPK-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Toxicology. 2021; 453: 152721.
doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152721 |
| 10 |
Horie M, Tabei Y. Role of oxidative stress in nanoparticles toxicity. Free Radic Res. 2021; 55(4): 331-42.
doi: 10.1080/10715762.2020.1859108 |
| 11 |
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A, Levi-Schaffer F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis. 2000; 5(5): 415-8.
doi: 10.1023/a:1009616228304 pmid: 11256882 |
| 12 |
Choi KC, Auersperg N, Leung PC. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in normal and (pre)neoplastic ovarian surface epithelium. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003; 1: 71.
doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-1-71 |
| 13 | Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang DG, Pae HO. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: how can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal Transduct. 2011; 2011: 792639. |
| 14 | Zhang Z, Nian Q, Chen G, Cui S, Han Y, Zhang J. Klotho alleviates lung injury caused by paraquat via suppressing ROS/P38 MAPK-Regulated inflammatory responses and apoptosis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020: 1854206. |
| 15 |
Gao Q, Yang M, Zuo Z. Overview of the anti-inflammatory effects, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacies of arctigenin and arctiin from Arctium lappa L. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018; 39(5): 787-801.
doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.32 |
| 16 |
Yang J, Yin HS, Cao YJ, Jiang ZA, Li YJ, Song MC, et al. Arctigenin attenuates ischemia/reperfusion induced ventricular arrhythmias by decreasing oxidative stress in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 49(2): 728-42.
doi: 10.1159/000493038 |
| 17 |
He Y, Fan Q, Cai T, Huang W, Xie X, Wen Y, et al. Molecular mechanisms of the action of Arctigenin in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 108: 403-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.158 |
| 18 |
Gao F, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Wang M, Zhou Z, Zhang W, et al. Arctigenin suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway in PQ-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 11: 584098
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.584098 |
| 19 |
Shi X, Sun H, Zhou D, Xi H, Shan L. Arctigenin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Inflammation. 2015; 38(2): 623-31.
doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9969-z |
| 20 |
Zhang WZ, Jiang ZK, He BX, Liu XB. Arctigenin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary oxidative stress and inflammation in a mouse model via suppression of MAPK, HO-1, and iNOS signaling. Inflammation. 2015; 38(4): 1406-14.
doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0115-3 |
| 21 |
Liu C, Hu YH, Han Y, Wang YB, Zhang Y, Zhang XQ, et al. MG53 protects against contrast-induced acute kidney injury by reducing cell membrane damage and apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020; 41(11): 1457-64.
doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0420-8 |
| 22 |
Liu C, Chen K, Wang H, Zhang Y, Duan X, Xue Y, et al. Gastrin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by a PI3K/Akt/bad-mediated anti-apoptosis signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 11: 540479.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.540479 |
| 23 | Dong G, Huang X, Jiang S, Ni L, Chen S. Simvastatin mitigates apoptosis and transforming growth factor-beta upregulation in stretch-induced endothelial cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019; 2019: 6026051. |
| 24 |
Liu C, Li X, Fu J, Chen K, Liao Q, Wang J, et al. Increased AT1 receptor expression mediates vasoconstriction leading to hypertension in Snx1-/- mice. Hypertens Res. 2021; 44(8): 906-17.
doi: 10.1038/s41440-021-00661-x |
| 25 |
Chen YW, Yang YT, Hung DZ, Su CC, Chen KL. Paraquat induces lung alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis via Nrf-2-regulated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress. Arch Toxicol. 2012; 86(10): 1547-58.
doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0873-8 pmid: 22678742 |
| 26 |
Ali S, Jain SK, Abdulla M, Athar M. Paraquat induced DNA damage by reactive oxygen species. IUBMB Life 1996; 39(1): 63-7.
doi: 10.1080/15216549600201061 |
| 27 |
Fukushima T, Tanaka K, Lim H, Moriyama M. Mechanism of cytotoxicity of paraquat. Environ Health Prev Med. 2002; 7(3): 89-94.
doi: 10.1265/ehpm.2002.89 |
| 28 | Bandyopadhyay U, Das D, Banerjee R. Reactive oxygen species: oxidative damage and pathogenesis. Curr Sci. 1999; 77: 658-66. |
| 29 |
Carmody RJ, Cotter TG. Signalling apoptosis: a radical approach. Redox Rep. 2001; 6(2): 77-90.
doi: 10.1179/135100001101536085 pmid: 11450987 |
| 30 |
Kaminska B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy—from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005; 1754(1-2): 253-62.
pmid: 16198162 |
| 31 |
Hyam SR, Lee IA, Gu W, Kim KA, Jeong JJ, Jang SE, et al. Arctigenin ameliorates inflammation in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway and polarizing M1 macrophages to M2-like macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013; 708(1-3): 21-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.014 |
| 32 |
Lu Z, Chang L, Zhou H, Liu X, Li Y, Mi T, et al. Arctigenin attenuates tumor metastasis through inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via suppressing GSK3β-dependent Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Front Pharmacol. 2019; 10: 937
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00937 |
| 33 |
Zhu Z, Yan J, Jiang W, Yao XG, Chen J, Chen L, et al. Arctigenin effectively ameliorates memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease model mice targeting both β-amyloid production and clearance. J Neurosci. 2013; 33(32): 13138-49.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4790-12.2013 |
| 34 | Rose MS, Smith LL, Wyatt I. Evidence for energy-dependent accumulation of paraquat into rat lung. Nature. 1974; 252(5481): 314-5. |
| 35 | Baba Y, Shigemi Z, Hara N, Moriguchi M, Ikeda M, Watanabe T, et al. Arctigenin induces the apoptosis of primary effusion lymphoma cells under conditions of glucose deprivation. Int J Oncol. 2018; 52(2): 505-17. |
| 36 |
Liu CY, Zhou Y, Chen T, Lei JC, Jiang XJ. AMPK/SIRT1 pathway is involved in arctigenin-mediated protective effects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 11: 616813.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.616813 |
| 37 |
Song J, Li N, Xia Y, Gao Z, Zou SF, Kong L, et al. Arctigenin treatment protects against brain damage through an anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic mechanism after needle insertion. Front Pharmacol. 2016; 7: 182.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00182 pmid: 27445818 |
| 38 | D’Autréaux B, Toledano MB. ROS as signalling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 8(10): 813-24. |
| 39 |
Blanco-Ayala T, Andérica-Romero AC, Pedraza-Chaverri J. New insights into antioxidant strategies against paraquat toxicity. Free Radic Res. 2014; 48(6): 623-40.
doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.899694 |
| [1] | Xiao-fang Guo, Shuang-shuang Gu, Jun Wang, Hao Sun, Yu-juan Zhang, Peng-fei Yu, Jin-song Zhang, Lei Jiang. Protective effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal treatment of hippocampal neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(1): 46-53. |
| [2] | Jian-hua Yi, Zhao-cai Zhang, Mei-bian Zhang, Xin He, Hao-ran Lin, Hai-wen Huang, Hai-bin Dai, Yu-wen Huang. Role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the pulmonary fibrosis induced by paraquat in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(3): 214-220. |
| [3] | Yun-fei Jiang, Jian Kang, Pei-pei Huang, Jia-xi Yao, Zhong-he Wang, Lei Jiang, Jun Wang, Li Qiao, Bao-li Zhu, Hao Sun, Jin-song Zhang. Evaluation of gastric lavage efficiency and utility using a rapid quantitative method in a swine paraquat poisoning model [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(3): 174-181. |
| [4] | Jia-jun Xu, Jian-tao Zhen, Li Tang, Qing-ming Lin. Intravenous injection of Xuebijing attenuates acute kidney injury in rats with paraquat intoxication [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(1): 61-64. |
| [5] | Hui Fu, Qiao-sheng Wang, Qiong Luo, Si Tan, Hua Su, Shi-lin Tang, Zheng-liang Zhao, Li-ping Huang. Simvastatin inhibits apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by sepsis through upregulating the expression of Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(4): 291-297. |
| [6] | Jian Lu, Yi Shen, Hui-yin Qian, Li-jun Liu, Bao-chun Zhou, Yan Xiao, Jin-ning Mao, Guo-yin An, Ming-zhong Rui, Tao Wang, Chang-lai Zhu. Effects of mild hypothermia on the ROS and expression of caspase-3 mRNA and LC3 of hippocampus nerve cells in rats after cardiopulmonary resuscitation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(4): 298-305. |
| [7] | Guo-ming Zhang, Yu Wang, Tian-de Li, Xiao-yan Li, Shao-ping Su, Yuan-yuan Sun, Xiu-hua Liu. Post-conditioning with gradually increased reperfusion provides better cardioprotection in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 128-134. |
| [8] | Pei-ren Shan, Wei-wei Xu, Zhou-qing Huang, Jun Pu, Wei-jian Huang. Protective role of retinoid X receptor in H9c2 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 122-127. |
| [9] | Shou-peng Li, Ji-yuan Han, Peng Sun, Guo-yan Wu, Xiang-yan Bai. Effect of SP-A/B in lipoic acid on acute paraquat poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(1): 57-62. |
| [10] | Yan-jun Qin, Xin-liang Zhang, Yue-qing Yu, Xiao-hua Bian, Shi-min Dong. Cardioprotective effect of erythropoietin on sepsis-induced myocardial injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(3): 215-223. |
| [11] | Xiao-xiao Meng, Rui-lan Wang, Shan Gao, Hui Xie, Jiu-ting Tan, Yong-bin Qian. Effect of ulinastatin on paraquat-induced-oxidative stress in human type II alveolar epithelial cells [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(2): 133-137. |
| [12] | Qiang Su, Lang Li, Yang-chun Liu, You Zhou, Wei-ming Wen. Effect of metoprolol on myocardial apoptosis after coronary microembolization in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(2): 138-143. |
| [13] | Yin-song Jiang, Yu-ying Ma, Zhan-qing Wang, Guang-jun Li. Therapeutic effects of smecta or smectite powder on rats with paraquat toxication [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(2): 144-150. |
| [14] | Zhi-jian Zhang, Li-bo Peng, Ya-juan Luo, Cong-yang Zhou. Prospective experimental studies on the renal protective effect of ulinastatin after paraquat poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(4): 299-304. |
| [15] | Ying-zhen Wang, Shi-wen Wang, You-cheng Zhang, Zhi-jiang Sun. Protective effect of exogenous IGF-I on the intestinal mucosal barrier in rats with severe acute pancreatitis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(3): 213-220. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
