World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (1): 16-22.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.186
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jing Yang1, Hanqi Tang1, Shihuan Shao2, Feng Xu3, Yangyang Fu4, Shengyong Xu1, Chen Li5, Yan Li1, Yang Liu1, Joseph Harold Walline6, Huadong Zhu1, Yuguo Chen3( ), Xuezhong Yu1(
), Xuezhong Yu1( ), Jun Xu1(
), Jun Xu1( )
)
Received:2023-06-11
Accepted:2023-10-16
Online:2023-12-31
Published:2024-01-01
Contact:
Yuguo Chen,Xuezhong Yu,Jun Xu
E-mail:chen919085@sdu.edu.cn;yxz@medmail.com.cn;xujunfree@126.com
Jing Yang, Hanqi Tang, Shihuan Shao, Feng Xu, Yangyang Fu, Shengyong Xu, Chen Li, Yan Li, Yang Liu, Joseph Harold Walline, Huadong Zhu, Yuguo Chen, Xuezhong Yu, Jun Xu. A novel predictor of unsustained return of spontaneous circulation in cardiac arrest patients through a combination of capnography and pulse oximetry: a multicenter observational study[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(1): 16-22.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.186
Table 1.
Baseline information of patients in the sustained ROSC group and unsustained ROSC group
| Parameters | Unsustained ROSC patients (n=32) | Sustained ROSC patients (n=48) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, female, n (%) | 7 (21.9) | 17 (35.4) | 0.195 |
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 63.0 (45.5, 77.0) | 63.5 (50.3, 73.5) | 0.848 |
| Location of cardiac arrest, n (%) | |||
| Out of hospital | 6 (18.8) | 11 (22.9) | 0.655 |
| In hospital | 26 (81.2) | 37 (77.1) | |
| Cause of cardiac arrest, n (%) | |||
| Cardiogenic | 12 (37.5) | 17 (35.4) | 0.849 |
| Hypoxemic | 9 (28.1) | 18 (37.5) | 0.385 |
| Shock | 6 (18.8) | 6 (12.5) | 0.655 |
| Stroke | 2 (6.3) | 3 (6.3) | 1.000 |
| Trauma | 3 (9.4) | 4 (8.3) | 1.000 |
| Survival rate, n (%) | |||
| 24-hour survival | 3 (9.4) | 14 (29.2) | 0.034* |
| 28-day survival | 0 (0) | 4 (8.3) | 0.249 |
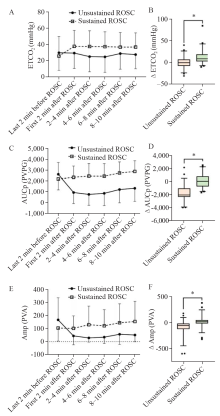
Figure 2.
Mean parameter values every two minutes from 2 min before ROSC to 10 min after ROSC, and differences of changes in parameter values between 2 min after ROSC and 2 min before ROSC in unsustained and sustained ROSC groups. A: ETCO2; B: ΔETCO2; C: AUCp; D: ΔAUCp; E: Amp; F: ΔAmp. *P<0.05. ROSC: return of spontaneous circulation; ETCO2: end-tidal carbon dioxide; AUCp: area under the curve of pulse oximetry photoplethysmogram; Amp: wave amplitude of pulse oximetry photoplethysmogram; ΔETCO2, ΔAUCp, ΔAmp: change in ETCO2, AUCp and Amp from 2 min after ROSC and 2 min before ROSC. PVPG: pulse oximeter voltage plehtysmography; PVA: pulse oximeter votage amplitude.
| 1 |
Fukuda T, Ohashi-Fukuda N, Sekiguchi H, Inokuchi R, Kukita I. Survival from pediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrest during nights and weekends: an updated Japanese registry-based study. JACC Asia. 2022; 2(4):433-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2022.01.005 |
| 2 |
Yan SJ, Chen M, Wen J, Fu WN, Song XY, Chen HJ, et al. Global research trends in cardiac arrest research: a visual analysis of the literature based on CiteSpace. World J Emerg Med. 2022; 13(4):290-6.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.071 |
| 3 |
Bartos JA, Yannopoulos D. Refractory cardiac arrest: where extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation fits. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2020; 26(6):596-602.
doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000769 pmid: 33027149 |
| 4 |
Salcido DD, Stephenson AM, Condle JP, Callaway CW, Menegazzi JJ. Incidence of rearrest after return of spontaneous circulation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2010; 14(4):413-8.
doi: 10.3109/10903127.2010.497902 pmid: 20809686 |
| 5 |
Woo JH, Cho JS, Lee CA, Kim GW, Kim YJ, Moon HJ, et al. Survival and rearrest in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients with prehospital return of spontaneous circulation: a prospective multi-regional observational study. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2021; 25(1):59-66.
doi: 10.1080/10903127.2020.1733716 |
| 6 |
Shinada K, Koami H, Matsuoka A, Sakamoto Y. Prediction of return of spontaneous circulation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with non-shockable initial rhythm using point-of-care testing: a retrospective observational study. World J Emerg Med. 2023; 14(2):89-95.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.031 pmid: 36911060 |
| 7 |
Salcido DD, Sundermann ML, Koller AC, Menegazzi JJ. Incidence and outcomes of rearrest following out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2015; 86:19-24.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2014.10.011 pmid: 25447433 |
| 8 | Lerner EB, O’Connell M, Pirrallo RG. Rearrest after prehospital resuscitation. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2011; 15(1):50-4. |
| 9 |
Salcido DD, Schmicker RH, Kime N, Buick JE, Cheskes S, Grunau B, et al. Effects of intra-resuscitation antiarrhythmic administration on rearrest occurrence and intra-resuscitation ECG characteristics in the ROC ALPS trial. Resuscitation. 2018; 129:6-12.
doi: S0300-9572(18)30239-9 pmid: 29803703 |
| 10 | Lee DK, Jung E, Jo YH, Kim J, Lee JH, Park SM, et al. The association of extreme tachycardia and sustained return of spontaneous circulation after nontraumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Emerg Med Int. 2020; 2020:5285178. |
| 11 |
Lewis LM, Stothert J, Standeven J, Chandel B, Kurtz M, Fortney J. Correlation of end-tidal CO2 to cerebral perfusion during CPR. Ann Emerg Med. 1992; 21(9):1131-4.
pmid: 1514728 |
| 12 | Garnett AR, Ornato JP, Gonzalez ER, Johnson EB. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. JAMA. 1987; 257(4):512-5. |
| 13 |
Gomersall CD, Joynt GM, Morley AP. End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337(23):1694.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM199712043372314 |
| 14 |
Kolar M, Krizmaric M, Klemen P, Grmec S. Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field: a prospective observational study. Crit Care. 2008; 12(5):R115.
doi: 10.1186/cc7009 |
| 15 |
Murphy RA, Bobrow BJ, Spaite DW, Hu C, McDannold R, Vadeboncoeur TF. Association between prehospital CPR quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2016; 20(3):369-77.
doi: 10.3109/10903127.2015.1115929 pmid: 26830353 |
| 16 |
Paiva EF, Paxton JH, O'Neil BJ. The use of end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) measurement to guide management of cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Resuscitation. 2018; 123:1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2017.12.003 |
| 17 |
Xu J, Li C, Tang HQ, Tan DY, Fu YY, Zong L, et al. Pulse oximetry waveform: a non-invasive physiological predictor for the return of spontaneous circulation in cardiac arrest patients —A multicenter, prospective observational study. Resuscitation. 2021; 169:189-97.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.09.032 |
| 18 |
Meaney PA, Bobrow BJ, Mancini ME, Christenson J, de Caen AR, Bhanji F, et al. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality: [corrected]improving cardiac resuscitation outcomes both inside and outside the hospital: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013; 128(4):417-35.
doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829d8654 pmid: 23801105 |
| 19 |
Stankovic N, Holmberg MJ, Høybye M, Granfeldt A, Andersen LW. Age and sex differences in outcomes after in-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2021; 165:58-65.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.05.017 pmid: 34098034 |
| 20 |
Jacobs I, Nadkarni V, Bahr J, Berg RA, Billi JE, Bossaert L, et al. Cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcome reports: update and simplification of the Utstein templates for resuscitation registries: a statement for healthcare professionals from a task force of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, European Resuscitation Council, Australian Resuscitation Council, New Zealand Resuscitation Council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Inter American Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Councils of Southern Africa). Circulation. 2004; 110(21):3385-97.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000147236.85306.15 pmid: 15557386 |
| 21 |
Guay J, Lortie L. An evaluation of pediatric in-hospital advanced life support interventions using the pediatric Utstein guidelines: a review of 203 cardiorespiratory arrests. Can J Anaesth. 2004; 51(4):373-8.
doi: 10.1007/BF03018242 |
| 22 |
Benhamed A, Canon V, Mercier E, Heidet M, Gossiome A, Savary D, et al. Prehospital predictors for return of spontaneous circulation in traumatic cardiac arrest. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021; 92(3):553-60.
doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000003474 pmid: 34797815 |
| 23 |
Lin YR, Wu HP, Huang CY, Chang YJ, Lin CY, Chou CC. Significant factors in predicting sustained ROSC in paediatric patients with traumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrest admitted to the emergency department. Resuscitation. 2007; 74(1):83-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2006.11.022 |
| 24 |
Bhardwaj A, Ikeda DJ, Grossestreuer AV, Sheak KR, Delfin G, Layden T, et al. Factors associated with re-arrest following initial resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2017; 111:90-5.
doi: S0300-9572(16)30584-6 pmid: 27992736 |
| 25 |
Jung YH, Jeung KW, Lee HY, Lee BK, Lee DH, Shin J, et al. Rearrest during hospitalisation in adult comatose out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients: risk factors and prognostic impact, and predictors of favourable long-term outcomes. Resuscitation. 2022; 170:150-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.11.037 |
| 26 |
Pokorná M, Necas E, Kratochvíl J, Skripský R, Andrlík M, Franek O. A sudden increase in partial pressure end-tidal carbon dioxide (P(ET)CO(2)) at the moment of return of spontaneous circulation. J Emerg Med. 2010; 38(5):614-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2009.04.064 pmid: 19570645 |
| 27 |
Gudipati CV, Weil MH, Bisera J, Deshmukh HG, Rackow EC. Expired carbon dioxide: a noninvasive monitor of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Circulation. 1988; 77(1):234-9.
pmid: 3121209 |
| 28 |
Awad AA, Stout RG, Ghobashy MAM, Rezkanna HA, Silverman DG, Shelley KH. Analysis of the ear pulse oximeter waveform. J Clin Monit Comput. 2006; 20(3):175-84.
doi: 10.1007/s10877-006-9018-z pmid: 16612551 |
| 29 |
Reisner A, Shaltis PA, McCombie D, Asada HH. Utility of the photoplethysmogram in circulatory monitoring. Anesthesiology. 2008; 108(5):950-8.
doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31816c89e1 pmid: 18431132 |
| 30 |
McGrath SP, Ryan KL, Wendelken SM, Rickards CA, Convertino VA. Pulse oximeter plethysmographic waveform changes in awake, spontaneously breathing, hypovolemic volunteers. Anesth Analg. 2011; 112(2):368-74.
doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181cb3f4a pmid: 20103539 |
| [1] | Rashed Alremeithi, Quincy K. Tran, Megan T. Quintana, Soroush Shahamatdar, Ali Pourmand. Approach to traumatic cardiac arrest in the emergency department: a narrative literature review for emergency providers [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(1): 3-9. |
| [2] | Shuang Xu, Lang Guo, Weijing Shao, Licai Liang, Tingting Shu, Yuhan Zhang, He Huang, Guangqi Guo, Qing Zhang, Peng Sun. Vagus nerve stimulation protects against cerebral injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation by inhibiting inflammation through the TLR4/NF-κB and α7nAChR/JAK2 signaling pathways [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(6): 462-470. |
| [3] | Gannan Wang, Zhe Wang, Yi Zhu, Zhongman Zhang, Wei Li, Xufeng Chen, Yong Mei. The neuro-prognostic value of the ion shift index in cardiac arrest patients following extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 354-359. |
| [4] | Guang-qi Guo, Yan-nan Ma, Shuang Xu, Hong-rong Zhang, Peng Sun. Effect of post-rewarming fever after targeted temperature management in cardiac arrest patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(3): 217-223. |
| [5] | Gan-nan Wang, Zhong-man Zhang, Wen Chen, Xiao-quan Xu, Jin-song Zhang. Timing of brain computed tomography for predicting neurological prognosis in comatose cardiac arrest survivors: a retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(5): 349-354. |
| [6] | Shi-jiao Yan, Mei Chen, Jing Wen, Wen-ning Fu, Xing-yue Song, Huan-jun Chen, Ri-xing Wang, Mei-ling Chen, Xiao-tong Han, Chuan-zhu Lyu. Global research trends in cardiac arrest research: a visual analysis of the literature based on CiteSpace [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(4): 290-296. |
| [7] | Hong-li Xiao, Lian-xing Zhao, Jun Yang, Nan Tong, Le An, Guo-xing Wang, Miao-rong Xie, Chun-sheng Li. Increasing angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) 2/ACE axes ratio alleviates early pulmonary vascular remodeling in a porcine model of acute pulmonary embolism with cardiac arrest [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(3): 208-214. |
| [8] | Chao-yu Lei, Heng-wei Qin, Xue-jie Dong, Jia-lin You, Lin Zhang. Layperson’s performance on an unconversant type of AED device: A prospective crossover simulation experimental study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(2): 98-105. |
| [9] | Ryan W. Horton, Kian R. Niknam, Viveta Lobo, Kathryn H. Pade, Drew Jones, Kenton L. Anderson. A cadaveric model for transesophageal echocardiography transducer placement training: A pilot study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(1): 18-22. |
| [10] | Ji-yang Ling, Chun-sheng Li, Yun Zhang, Xiao-li Yuan, Bo Liu, Yong Liang, Qiang Zhang. Protective effect of extracorporeal membrane pulmonary oxygenation combined with cardiopulmonary resuscitation on post-resuscitation lung injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(4): 303-308. |
| [11] | Wei-jing Shao, Ting-ting Shu, Shuang Xu, Li-cai Liang, Jehane Michael Le Grange, Yu-ran Zhou, He Huang, Yu Cai, Qing Zhang, Peng Sun. Left-sided vagus nerve stimulation improves cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcomes in rats as effectively as right-sided vagus nerve stimulation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(4): 309-316. |
| [12] | Xue-jie Dong, Lin Zhang, Yue-lin Yu, Shu-xiao Shi, Xiao-chen Yang, Xiao-qian Zhang, Shuang Tian, Helge Myklebust, Guo-hong Li, Zhi-jie Zheng. The general public’s ability to operate automated external defibrillator: A controlled simulation study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 238-245. |
| [13] | Alexei Birkun, Fatima Trunkwala, Adhish Gautam, Miriam Okoroanyanwu, Adesokan Oyewumi. Availability of basic life support courses for the general populations in India, Nigeria and the United Kingdom: An internet-based analysis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(3): 133-139. |
| [14] | Jung Wan Kim, Jin Woong Lee, Seung Ryu, Jung Soo Park, InSool Yoo, Yong Chul Cho, Hong Joon Ahn. Changes in peak inspiratory flow rate and peak airway pressure with endotracheal tube size during chest compression [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 97-101. |
| [15] | Ye-cheng Liu, Yan-meng Qi, Hui Zhang, Joseph Walline, Hua-dong Zhu. A survey of ventilation strategies during cardiopulmonary resuscitation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(4): 222-227. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
