World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (4): 280-286.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.067
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xinlei Wang, Yao Sun, Xiaoyu Ni, Shu Zhang( )
)
Received:2022-11-25
Accepted:2023-03-28
Online:2023-06-30
Published:2023-07-01
Contact:
Shu Zhang
E-mail:164754630@qq.com
Xinlei Wang, Yao Sun, Xiaoyu Ni, Shu Zhang. Development and validation of an emergency bloodstream infection score for predicting in-hospital mortality in patients with community-acquired bloodstream infections[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(4): 280-286.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.067
Table 1.
Comparison of baseline data between the modeling and validation groups
| Variables | Modeling group (n=440) | Validation group (n=107) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 57.13±18.63 | 54.25±17.81 | 0.149 |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 270 (61.40) | 65 (60.70) | 0.907 |
| Vital signs | |||
| Temperature, °C | 38.53±1.18 | 38.39±1.38 | 0.338 |
| Heart rate, beats/min | 115.85±23.39 | 116.52±29.17 | 0.826 |
| Respiratory rate, breaths/min | 25 (21-30) | 24 (20-30) | 0.852 |
| Systolic pressure, mmHg | 94.51±16.70 | 93.86±20.46 | 0.761 |
| Diastolic pressure, mmHg | 56.51±13.34 | 56.30±15.59 | 0.899 |
| Oxygen saturation, % | 95 (93-97) | 96 (93-98) | 0.263 |
| Highest blood sugar, mmol/L | 8.88 (6.77-14.06) | 8.33 (6.70-12.50) | 0.306 |
| Laboratory results | |||
| White blood cell, 109/L | 11.56 (7.06-16.26) | 10.61 (6.20-14.89) | 0.264 |
| Lymphocyte, 109/L | 0.66 (0.37-1.07) | 0.56 (0.33-1.06) | 0.275 |
| Neutrophile granulocyte, 109/L | 10.57±6.75 | 9.39±6.05 | 0.098 |
| Direct bilirubin, µmol/L | 9.10 (5.10-21.08) | 10.50 (5.70-32.7) | 0.148 |
| AST, U/L | 41.50 (22.00-93.75) | 49.00 (25.00-109.00) | 0.163 |
| Albumin, g/L | 32.97±7.10 | 33.80±7.36 | 0.233 |
| Globulin, g/L | 32.34±7.52 | 32.19±8.44 | 0.861 |
| Urea nitrogen, mmol/L | 6.79 (4.71-10.84) | 6.40 (4.60-10.30) | 0.503 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 90.5 (67.0-131.0) | 88 (67-125) | 0.700 |
| Cystatin-C, mg/L | 1.16 (0.90-1.69) | 1.07 (0.89-1.60) | 0.311 |
| Creatine kinase, U/L | 70.50 (40.00-197.75) | 76.00 (45.00-279.00) | 0.382 |
| Lactic dehydrogenase, U/L | 243.00 (194.00-329.75) | 250.00 (191.00-343.00) | 0.689 |
| β-HBA, mmol/L | 0.25 (0.12-0.63) | 0.23 (0.13-0.47) | 0.450 |
| INR | 1.18 (1.07-1.32) | 1.24 (1.08-1.43) | 0.028 |
| D-dimer, mg/L | 4.61 (2.23-9.40) | 7.26 (1.89-9.86) | 0.394 |
| PCT, µg/L | 12.44 (1.81-48.05) | 11.14 (1.30-31.69) | 0.345 |
| Infection source, n (%) | |||
| Lower respiratory tract | 101 (22.95) | 26 (24.30) | 0.768 |
| Abdominal and gastrointestinal tract | 161 (36.59) | 47 (43.93) | 0.161 |
| Other | 178 (45.45) | 34 (31.78) | 0.099 |
| In-hospital mortality, n (%) | 54 (12.27) | 18 (16.82) | 0.212 |
Table 2.
Variables weighting for Emergency Bloodstream Infection Score
| Variables | OR (95% CI ) | P-value | Regression coefficient | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onset time, d | 0.037 | |||
| ≤1 | 1.000 | 0 | ||
| (1,5] | 2.675 (1.026-6.977) | 0.044 | 0.984 | 3 |
| (5,10] | 1.434 (0.477-4.309) | 0.521 | 0.360 | 1 |
| >10 | 3.909 (1.406-10.869) | 0.009 | 1.363 | 4 |
| Respiratory rate, breaths/min | <0.001 | |||
| (0,23] | 1.000 | 0 | ||
| (23,25] | 1.646 (0.424-6.399) | 0.472 | 0.498 | 1 |
| (25,30] | 3.373 (1.178-9.655) | 0.024 | 1.216 | 3 |
| >30 | 8.383 (3.066-22.924) | <0.001 | 2.126 | 6 |
| Altered mental status | 5.866 (2.842-12.108) | <0.001 | 1.769 | 5 |
| Lower respiratory tract infection | 4.035 (1.972-8.259) | <0.001 | 1.395 | 4 |
Table 3.
Comparison of EBS and other models in predicting the in-hospital mortality of patients with CABSIs
| Models | AUC | 95% CI | P-value | P-value vs. EBS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBS | 0.853 | 0.769-0.937 | <0.001 | |
| EBS+CCI | 0.869 | 0.786-0.951 | <0.001 | 0.601 |
| EBS+MJCC | 0.871 | 0.796-0.947 | <0.001 | 0.066 |
| SOFA | 0.848 | 0.759-0.937 | <0.001 | 0.841 |
| qSOFA | 0.779 | 0.670-0.888 | <0.001 | 0.099 |
| PBS | 0.782 | 0.688-0.876 | <0.001 | 0.225 |
| MEDS | 0.790 | 0.689-0.892 | <0.001 | 0.605 |
| CCI | 0.667 | 0.528-0.806 | 0.026 | 0.019 |
| MJCC | 0.687 | 0.538-0.835 | 0.013 | 0.059 |
Table 4.
Cutoff value, sensitivity and specificity of each model
| Models | Cutoff | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| EBS | 9.5 | 0.722 | 0.820 |
| EBS+CCI | 10.5 | 0.889 | 0.730 |
| EBS+MJCC | 8.5 | 0.889 | 0.674 |
| SOFA | 7.5 | 0.857 | 0.848 |
| qSOFA | 1.5 | 0.786 | 0.519 |
| PBS | 1.5 | 0.893 | 0.456 |
| MEDS | 9.5 | 0.786 | 0.620 |
| CCI | 3.5 | 0.389 | 0.876 |
| MJCC | 1.5 | 0.556 | 0.225 |
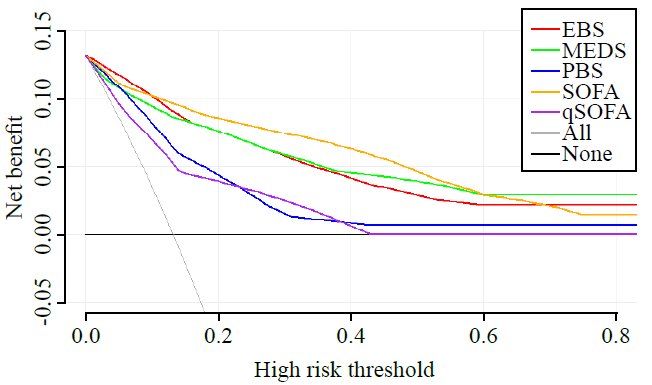
Figure 1.
Decision curve analysis for predicting in-hospital mortality in CABSIs for the EBS, SOFA, MEDS, qSOFA, and PBS scores in the validation group. EBS: Emergency Community-Acquired Bloodstream Infection; MEDS: Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis; PBS: Pitt Bacteremia Score; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; qSOFA: quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
| 1 | Gupta RG, Hartigan SM, Kashiouris MG, Sessler CN, Bearman GM. Early goal-directed resuscitation of patients with septic shock: current evidence and future directions. Crit Care. 2015; 19(1): 286. |
| 2 |
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345(19): 1368-77.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa010307 |
| 3 |
Goto M, Al-Hasan MN. Overall burden of bloodstream infection and nosocomial bloodstream infection in North America and Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013; 19(6): 501-9.
doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12195 |
| 4 | Liu Y, Cui BC, Pi CM, Yu XH, Liu ZW, Li X, et al. Analysis of prognostic risk factors of bloodstream infections in Beijing communities: a retrospective study from 2015 to 2019. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2021; 13(1): e2021060. |
| 5 |
Mehl A, Åsvold BO, Lydersen S, Paulsen J, Solligård E, Damås JK, et al. Burden of bloodstream infection in an area of Mid-Norway 2002-2013: a prospective population-based observational study. BMC Infect Dis. 2017; 17(1): 205.
doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2291-2 pmid: 28284196 |
| 6 |
Laupland KB, Pasquill K, Parfitt EC, Naidu P, Steele L. Burden of community-onset bloodstream infections, western interior, British Columbia, Canada. Epidemiol Infect. 2016; 144(11): 2440-6.
doi: 10.1017/S0950268816000613 pmid: 26996433 |
| 7 |
Deen J, von Seidlein L, Andersen F, Elle N, White NJ, Lubell Y. Community-acquired bacterial bloodstream infections in developing countries in south and southeast Asia: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012; 12(6):480-7.
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70028-2 pmid: 22632186 |
| 8 |
Kanoksil M, Jatapai A, Peacock SJ, Limmathurotsakul D. Epidemiology, microbiology and mortality associated with community-acquired bacteremia in northeast Thailand: a multicenter surveillance study. PLoS One. 2013; 8(1): e54714.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054714 |
| 9 | Berman P, Hogan DB, Fox RA. The atypical presentation of infection in old age. Age Ageing. 1987; 16(4): 201-7. |
| 10 |
Dat VQ, Long NT, Hieu VN, Phuc NDH, Kinh NV, Trung NV, et al. Clinical characteristics, organ failure, inflammatory markers and prediction of mortality in patients with community acquired bloodstream infection. BMC Infect Dis. 2018; 18(1): 535.
doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3448-3 pmid: 30367601 |
| 11 |
Lee CC, Lee CH, Hong MY, Tang HJ, Ko WC. Timing of appropriate empirical antimicrobial administration and outcome of adults with community-onset bacteremia. Crit Care. 2017; 21(1): 119.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1696-z |
| 12 |
Lee CC, Lee CH, Chuang MC, Hong MY, Hsu HC, Ko WC. Impact of inappropriate empirical antibiotic therapy on outcome of bacteremic adults visiting the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30(8):1447-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2011.11.010 |
| 13 |
Shapiro NI, Wolfe RE, Moore RB, Smith E, Burdick E, Bates DW. Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis (MEDS) score: a prospectively derived and validated clinical prediction rule. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31(3): 670-5.
doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000054867.01688.D1 pmid: 12626967 |
| 14 |
Hsieh CC, Yang CY, Lee CH, Chi CH, Lee CC. Validation of MEDS score in predicting short-term mortality of adults with community-onset bacteremia. Am J Emerg Med. 2020; 38(2):282-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.05.002 |
| 15 |
Lesens O, Methlin C, Hansmann Y, Remy V, Martinot M, Bergin C, et al. Role of comorbidity in mortality related to Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a prospective study using the Charlson weighted index of comorbidity. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2003; 24(12): 890-6.
doi: 10.1086/502156 |
| 16 |
Søgaard M, Schønheyder HC, Riis A, Sørensen HT, Nørgaard M. Short-term mortality in relation to age and comorbidity in older adults with community-acquired bacteremia: a population-based cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008; 56(9): 1593-600.
doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.01855.x pmid: 18691276 |
| 17 |
Friedman ND, Kaye KS, Stout JE, McGarry SA, Trivette SL, Briggs JP, et al. Health care-associated bloodstream infections in adults: a reason to change the accepted definition of community-acquired infections. Ann Intern Med. 2002; 137(10): 791-7.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-137-10-200211190-00007 pmid: 12435215 |
| 18 |
Osaki S, Kikuchi K, Moritoki Y, Motegi C, Ohyatsu S, Nariyama T, et al. Distinguishing coagulase-negative Staphylococcus bacteremia from contamination using blood-culture positive bottle detection pattern and time to positivity. J Infect Chemother. 2020; 26(7):672-5.
doi: S1341-321X(20)30045-3 pmid: 32131983 |
| 19 |
Mauri T, Spinelli E, Pavlovsky B, Grieco DL, Ottaviani I, Basile MC, et al. Respiratory drive in patients with sepsis and septic shock: modulation by high-flow nasal cannula. Anesthesiology. 2021; 135(6): 1066-75.
doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004010 pmid: 34644374 |
| 20 |
Seni J, Mwakyoma AA, Mashuda F, Marando R, Ahmed M, DeVinney R, et al. Deciphering risk factors for blood stream infections, bacteria species and antimicrobial resistance profiles among children under five years of age in North-Western Tanzania: a multicentre study in a cascade of referral health care system. BMC Pediatr. 2019; 19(1): 32.
doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1411-0 pmid: 30684964 |
| 21 |
Adam N, Kandelman S, Mantz J, Chrétien F, Sharshar T. Sepsis-induced brain dysfunction. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013; 11(2): 211-21.
doi: 10.1586/eri.12.159 pmid: 23409826 |
| 22 |
Angioni D, Hites M, Jacobs F, De Breucker S. Predictive factors of in-hospital mortality in older adults with community-acquired bloodstream infection. J Frailty Aging. 2020; 9(4): 232-7.
doi: 10.14283/jfa.2019.45 pmid: 32996560 |
| 23 |
Holmbom M, Andersson M, Berg S, Eklund D, Sobczynski P, Wilhelms D, et al. Prehospital delay is an important risk factor for mortality in community-acquired bloodstream infection (CA-BSI): a matched case-control study. BMJ Open. 2021; 11(11): e052582.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052582 |
| 24 |
Hernández C, Fehér C, Soriano A, Marco F, Almela M, Cobos-Trigueros N, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of elderly patients with community-onset bacteremia. J Infect. 2015; 70(2): 135-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.09.002 pmid: 25224642 |
| 25 |
Blot S, Cankurtaran M, Petrovic M, Vandijck D, Lizy C, Decruyenaere J, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of nosocomial bloodstream infection in elderly critically ill patients: a comparison between middle-aged, old, and very old patients. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37(5): 1634-41.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819da98e pmid: 19325489 |
| 26 |
Waterer GW, Wunderink RG. The influence of the severity of community-acquired pneumonia on the usefulness of blood cultures. Respir Med. 2001; 95(1): 78-82.
doi: 10.1053/rmed.2000.0977 |
| [1] | Fady Y. Hijji, Andrew D. Schneider, Matthew D. Thomas, Joseph G. Lyons, Daniel D. Bohl, Jennifer L. Jerele, Michael J. Prayson. Knowledge of radiation exposure associated with common trauma imaging modalities among orthopaedic surgeons, emergency medicine physicians, and general surgeons in the United States [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(4): 294-301. |
| [2] | Ahmed Faidh Ramzee, Ayman El-Menyar, Mohammad Asim, Ahad Kanbar, Khalid Ahmed, Bahaa Daoud, Saji Mathradikkal, Ahmad Kloub, Hassan Al-Thani, Sandro Rizoli. The impact of emergency department length of stay on the outcomes of trauma patients requiring hospitalization: a retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(2): 96-105. |
| [3] | Jee Yen Kuck, Abdul Muhaimin Noor Azhar, Neena Wee, Rishya Manikam. Diagnostic accuracy of the tongue blade test combined with clinical signs to detect maxillary and mandibular fractures in the emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(2): 122-127. |
| [4] | Ralph Bou Chebl, Nadim Kattouf, Mohamad Assaf, Saadeddine Haidar, Gilbert Abou Dagher, Sarah Abdul Nabi, Rana Bachir, Mazen El Sayed. Comparing the demographic data and outcomes of septic shock patients presenting to teaching or non-teaching metropolitan hospitals in the United States [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(6): 433-440. |
| [5] | Guang-mei Wang, Yong Li, Shuo Wu, Wen Zheng, Jing-jing Ma, Feng Xu, Jia-qi Zheng, He Zhang, Jia-li Wang, Yu-guo Chen. The combination of creatine kinase-myocardial band isoenzyme and point-of-care cardiac troponin/ contemporary cardiac troponin for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(3): 163-168. |
| [6] | Hai Hu, Jing-yuan Jiang, Ni Yao. Comparison of different versions of the quick sequential organ failure assessment for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients: A retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(2): 114-119. |
| [7] | Ittai Shichman, Or Shaked, Shai Factor, Ahuva Weiss-Meilik, Amal Khoury. Emergency department electric scooter injuries after the introduction of shared e-scooter services: A retrospective review of 3,331 cases [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(1): 5-10. |
| [8] | Ralphe Bou Chebl, Nader El Souki, Mirabelle Geha, Imad Majzoub, Rima Kaddoura, Hady Zgheib. Two-point compression ultrasonography: Enough to rule out lower extremity deep venous thrombosis? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(4): 268-273. |
| [9] | Hong-yan Wei, Wen-jie Liang, Bin Li, Ling-yu Wei, An-qi Jiang, Wei-dong Chen, Peng-hao Guo, Jia Xu. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of Talaromyces marneffei infection in human immunodeficiency virus-negative patients: A retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(4): 281-286. |
| [10] | Lori Stolz, Elaine Situ-LaCasse, Josie Acuña, Matthew Thompson, Nicolaus Hawbaker, Josephine Valenzuela, Uwe Stolz, Srikar Adhikari. What is the ideal approach for emergent pericardiocentesis using point-of-care ultrasound guidance? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(3): 169-173. |
| [11] | Kasım Turgut, Erdal Yavuz, Mine Kayacı Yıldız, Mehmet Kaan Poyraz. Violence toward emergency physicians: A prospective-descriptive study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(2): 111-116. |
| [12] | Marin Pavlov, Lucija Klobučar, Iva Klobučar, Kristina Žgela, Vesna Degoricija. Does shifting to professional emergency department staffing affect the decision for chest radiography? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(2): 87-92. |
| [13] | Hady Zgheib, Aline El Zakhem, Cynthia Wakil, Mohamad Ali Cheaito, Rola Cheaito, Antoine Finianos, Ralphe Bou Chebl, Rima Kaddoura, Nader Al Souky, Imad El Majzoub. Role of urine studies in asymptomatic febrile neutropenic patients presenting to the emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(2): 99-104. |
| [14] | William Gilliam, Jackson F. Barr, Brandon Bruns, Brandon Cave, Jordan Mitchell, Tina Nguyen, Jamie Palmer, Mark Rose, Safura Tanveer, Chris Yum, Quincy K. Tran. Factors associated with refractory pain in emergency patients admitted to emergency general surgery [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(1): 12-17. |
| [15] | Rebekah Shaw, Erica Popovsky, Alyssa Abo, Marni Jacobs, Nicole Herrera, James Chamberlain, Andrea Hahn. Improving antibiotic prescribing in the emergency department for uncomplicated community-acquired pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 199-205. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
