World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (3): 179-185.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.041
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jia-bao Li1,2, Miao-rong Xie2, Mei-li Duan1,2, Ya-nan Yu3, Chen-chen Hang3, Zi-ren Tang3, Chun-sheng Li1,2( )
)
Received:2022-11-16
Online:2023-03-29
Published:2023-05-01
Contact:
Chun-sheng Li
E-mail:lcscyyy@163.com
Jia-bao Li, Miao-rong Xie, Mei-li Duan, Ya-nan Yu, Chen-chen Hang, Zi-ren Tang, Chun-sheng Li. Over-expression of programmed death-ligand 1 and programmed death-1 on antigen-presenting cells as a predictor of organ dysfunction and mortality during early sepsis: a prospective cohort study[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(3): 179-185.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.041
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the participants
| Characteristics | Healthy control (n=40) | Overall sepsis (n=198) | P-value (control vs. overall) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 68 (57-74) | 71 (56-80) | 0.389 |
| Male/Female | 20/20 | 111/87 | 0.121 |
| White blood cell count, ×109 | 5.81 (4.85-6.52) | 12.83 (8.00-19.28) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil percentage, % | 56.25 (48.03-63.33) | 88.55 (81.98-92.75) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil count, ×109 | 4.70 (3.62-5.65) | 11.59 (7.08-17.69) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte percentage, % | 2.30 (1.70-2.70) | 6.10 (3.30-11.13) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte count, ×109 | 2.12 (1.74-2.36) | 0.77 (0.48-1.14) | <0.001 |
| Monocyte count, ×109 | 0.29 (0.27-0.38) | 0.56 (0.28-0.98) | <0.001 |
| Lactate, mmol/L | 1.00 (0.60-1.38) | 1.95 (1.30-3.23) | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 0 (0-1) | 7 (4-10) | <0.001 |
| APACHE Ⅱ score | 1 (0-2) | 15 (10-21) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity more than one | 0 | 140 (70.7) | <0.001 |
| Primary infection sites | |||
| Respiratory infection | 105 (53.0) | - | |
| Intra-abdominal infection | 47 (23.7) | - | |
| Cerebral infection | 19 (9.6) | - | |
| Urinary infection | 22 (11.1) | - | |
| Others | 5 (2.5) | - |
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of subgroups of sepsis patients on admission
| Characteristics | Sepsis (n=121) | Septic shock (n=77) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 72 (55-82) | 70 (56-79) | 0.412 |
| Male/Female | 71/50 | 40/37 | 0.232 |
| White blood cell count, ×109 | 13.02 (9.02-18.68) | 11.74 (7.59-23.79) | 0.640 |
| Neutrophil percentage, % | 87.90 (81.95-91.50) | 90.30 (81.55-94.05) | 0.087 |
| Neutrophil count, ×109 | 11.80 (7.87-16.93) | 11.41 (6.54-20.90) | 0.915 |
| Lymphocyte percentage, % | 6.40 (3.45-11.05) | 5.00 (3.15-12.70) | 0.384 |
| Lymphocyte count, ×109 | 0.82 (0.52-1.20) | 0.65 (0.39-1.09) | 0.236 |
| Monocyte count, ×109 | 0.67 (0.38-1.00) | 0.45 (0.19-0.74) | 0.004 |
| Lactate, mmol/L | 1.60 (1.15-2.25) | 2.90 (1.72-6.70) | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 5 (3-7) | 10 (8-12) | <0.001 |
| APACHE Ⅱ score | 13 (8-17) | 19 (14-26) | <0.001 |
| 28-day mortality | 30 (24.8) | 40 (51.9) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity more than one | 78 (64.5) | 62 (80.5) | 0.853 |
| Primary infection sites | |||
| Respiratory infection | 68 (56.2) | 37 (48.1) | 0.263 |
| Intra-abdominal infection | 27 (22.3) | 20 (26.0) | 0.555 |
| Cerebral infection | 12 (9.9) | 7 (9.1) | 0.847 |
| Urinary infection | 11 (9.1) | 11 (14.3) | 0.257 |
| Others | 3 (2.5) | 2 (2.6) | 0.959 |

Figure 1.
Surface biomarker expression on leukocyte subsets in controls (n=40) and patients with sepsis (n=121) or septic shock (n=77). PD-1 and PD-L1 expression was evaluated on B cells (A, E), monocytes (B, F), myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) (C, G), and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) (D, H). *P<0.05. ns: no significance. PD-L1: programmed death-ligand 1; PD-1: programmed death-1.
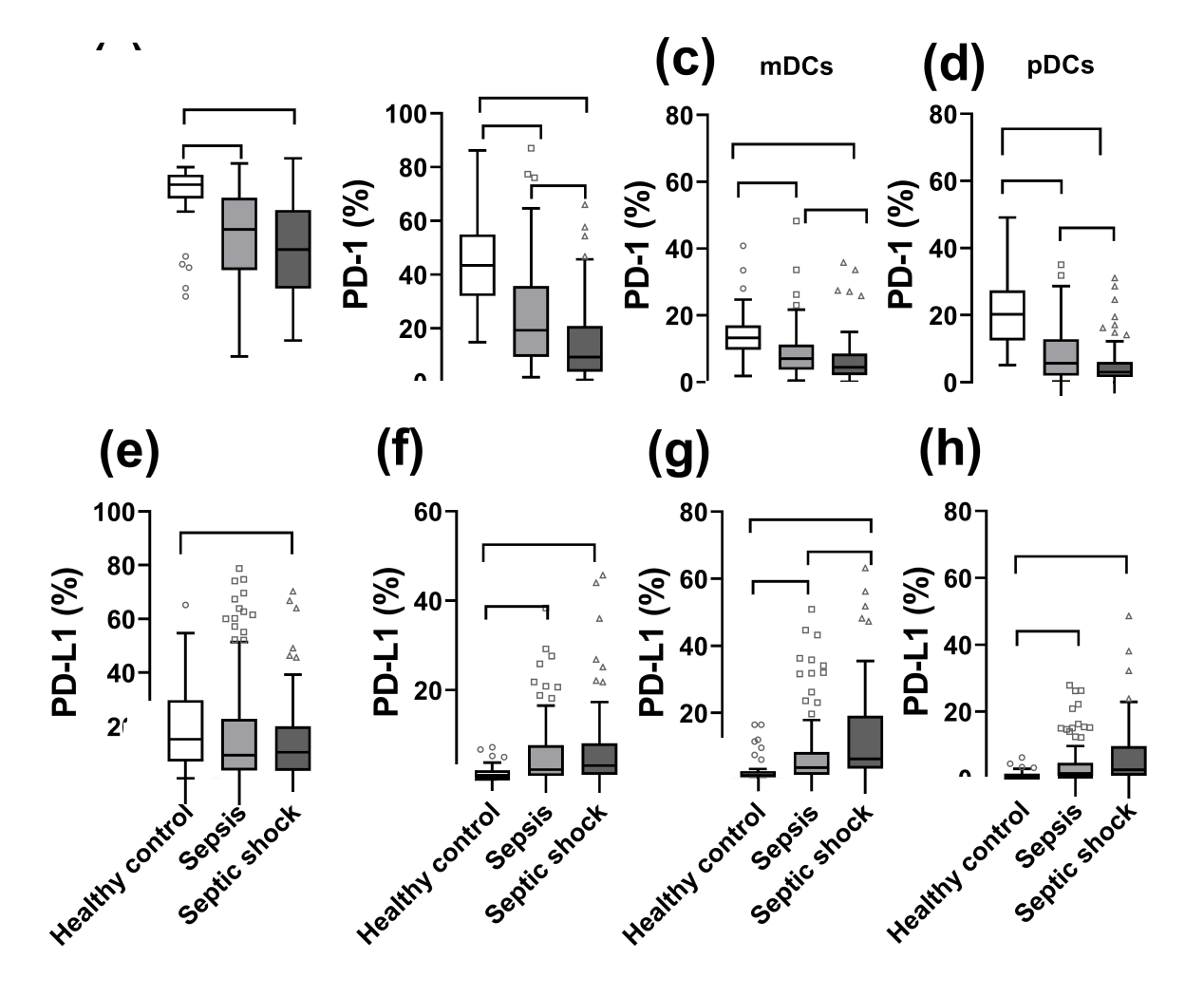

Figure 2.
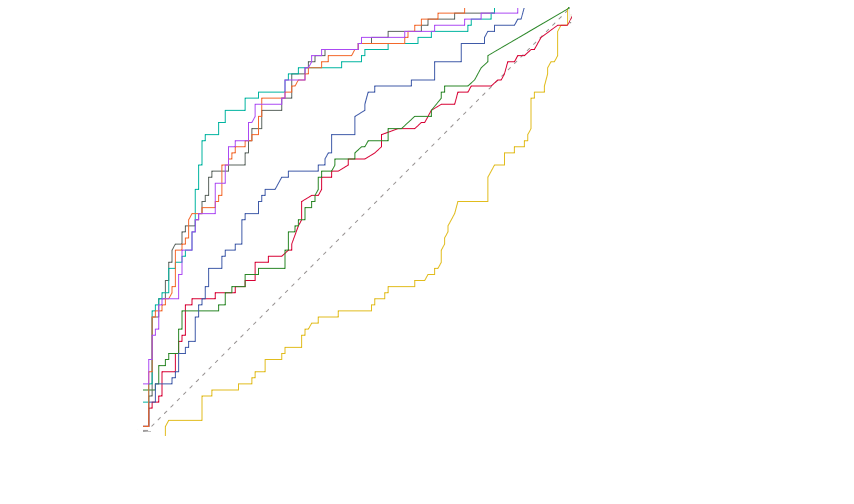
The receiver operating characteristic curve of PD-1 or PD-L1 expression of antigen-presenting cells, scores, cytokines alone or in combination in predicting 28-day outcome.PD-1: programmed death-1; PD-L1: programmed death-ligand 1; mDC: myeloid dendritic cell; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-10: interleukin-10; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; APACHE II: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II.
| [1] |
Duan LW, Qu JL, Wan J, Xu YH, Shan Y, Wu LX, et al. Effects of viral infection and microbial diversity on patients with sepsis: A retrospective study based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing. World J Emerg Med. 2021; 12(1):29-35.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.01.005 |
| [2] |
Yin J, Chen Y, Huang JL, Yan L, Kuang ZS, Xue MM, et al. Prognosis-related classification and dynamic monitoring of immune status in patients with sepsis: A prospective observational study. World J Emerg Med. 2021; 12(3):185-91.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.03.004 pmid: 34141032 |
| [3] |
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NKJ, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, et al. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated Sepsis. current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016; 193(3):259-72.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC |
| [4] |
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315(8):801-10.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 pmid: 26903338 |
| [5] |
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013; 13(12):862-74.
doi: 10.1038/nri3552 pmid: 24232462 |
| [6] |
Patera AC, Drewry AM, Chang K, Beiter ER, Osborne D, Hotchkiss RS. Frontline science: defects in immune function in patients with sepsis are associated with PD-1 or PD-L1 expression and can be restored by antibodies targeting PD-1 or PD-L1. J Leukoc Biol. 2016; 100(6):1239-54.
doi: 10.1189/jlb.4HI0616-255R |
| [7] |
Wakeley ME, Gray CC, Monaghan SF, Heffernan DS, Ayala A. Check point inhibitors and their role in immunosuppression in sepsis. Crit Care Clin. 2020; 36(1):69-88.
doi: S0749-0704(19)30069-7 pmid: 31733683 |
| [8] |
Li L, Yan J, Ma LQ, Bi W, Wu CJ. Effects of Maxingloushi decoction on immune inflammation and programmed death markers in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. World J Emerg Med. 2022; 13(1):32-7.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.023 pmid: 35003414 |
| [9] |
Boomer JS, To K, Chang KC, Takasu O, Osborne DF, Walton AH, et al. Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis and multiple organ failure. JAMA. 2011; 306(23):2594-605.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.1829 pmid: 22187279 |
| [10] |
Shankar-Hari M, Datta D, Wilson J, Assi V, Stephen J, Weir CJ, et al. Early PREdiction of sepsis using leukocyte surface biomarkers: the ExPRES-sepsis cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2018; 44(11):1836-48.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5389-0 pmid: 30291379 |
| [11] |
Shao R, Fang YY, Yu H, Zhao LX, Jiang ZF, Li CS. Monocyte programmed death ligand-1 expression after 3-4 days of sepsis is associated with risk stratification and mortality in septic patients: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2016; 20(1):124.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1301-x |
| [12] |
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017; 43(3):304-77.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6 pmid: 28101605 |
| [13] |
Knaus WA, Wagner DP, Draper EA, Zimmerman JE, Bergner M, Bastos PG, et al. The APACHE III prognostic system. Risk prediction of hospital mortality for critically ill hospitalized adults. Chest. 1991; 100(6):1619-36.
doi: 10.1378/chest.100.6.1619 pmid: 1959406 |
| [14] |
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, Bruining H, et al. The SOFA (sepsis-related organ failure assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med. 1996; 22(7):707-10.
doi: 10.1007/BF01709751 |
| [15] |
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 2000; 192(7):1027-34.
doi: 10.1084/jem.192.7.1027 pmid: 11015443 |
| [16] |
Avendaño-Ortiz J, Maroun-Eid C, Martín-Quirós A, Toledano V, Cubillos-Zapata C, Gómez-Campelo P, et al. PD-L1 overexpression during endotoxin tolerance impairs the adaptive immune response in septic patients via HIF1α. J Infect Dis. 2018; 217(3):393-404.
doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix279 pmid: 28973671 |
| [17] |
Young WA, Fallon EA, Heffernan DS, Efron PA, Cioffi WG, Ayala A. Improved survival after induction of sepsis by cecal slurry in PD-1 knockout murine neonates. Surgery. 2017; 161(5):1387-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.11.008 |
| [18] |
Huang X, Venet F, Wang YL, Lepape A, Yuan ZL, Chen YP, et al. PD-1 expression by macrophages plays a pathologic role in altering microbial clearance and the innate inflammatory response to sepsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(15):6303-8.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809422106 |
| [19] | Zasada M, Lenart M, Rutkowska-Zapała M, Stec M, Durlak W, Grudzień A, et al. Analysis of PD-1 expression in the monocyte subsets from non-septic and septic preterm neonates. PLoS One. 2017; 12(10):e0186819. |
| [20] |
Yun J, Yu GH, Hu PP, Chao Y, Li XY, Chen XB, et al. PD-1 expression is elevated in monocytes from hepatocellular carcinoma patients and contributes to CD 8 T cell suppression. Immunol Res. 2020; 68(6):436-44.
doi: 10.1007/s12026-020-09155-3 |
| [21] |
Guignant C, Lepape A, Huang X, Kherouf H, Denis L, Poitevin F, et al. Programmed death-1 levels correlate with increased mortality, nosocomial infection and immune dysfunctions in septic shock patients. Crit Care. 2011; 15(2):R99.
doi: 10.1186/cc10112 |
| [22] |
Li J, Tang Z, Xie M, Hang C, Yu Y, Li C. Association between elevation of plasma biomarkers and monocyte dysfunction and their combination in predicting sepsis: an observational single-centre cohort study. Innate Immun. 2020; 26(6):514-27.
doi: 10.1177/1753425920926602 |
| [23] |
Jiang WQ, Li XS, Wen MY, Liu XY, Wang KR, Wang QS, et al. Increased percentage of PD-L1+ natural killer cells predicts poor prognosis in sepsis patients: a prospective observational cohort study. Crit Care. 2020; 24(1):617.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03329-z |
| [24] |
Keir ME, Liang SC, Guleria I, Latchman YE, Qipo AD, Albacker LA, et al. Tissue expression of PD-L1 mediates peripheral T cell tolerance. J Exp Med. 2006; 203(4):883-95.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20051776 pmid: 16606670 |
| [25] |
Latchman YE, Liang SC, Wu Y, Chernova T, Sobel RA, Klemm M, et al. PD-L1-deficient mice show that PD-L1 on T cells, antigen-presenting cells, and host tissues negatively regulates T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101(29):10691-6.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307252101 pmid: 15249675 |
| [26] | Chen LP, Flies DB. Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013; 13(4):227-42. |
| [27] |
Xiong HZ, Mittman S, Rodriguez R, Moskalenko M, Pacheco-Sanchez P, Yang YG, et al. Anti-PD-L1 treatment results in functional remodeling of the macrophage compartment. Cancer Res. 2019; 79(7):1493-506.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3208 pmid: 30679180 |
| [28] |
Sun NY, Chen YL, Wu WY, Lin HW, Chiang YC, Chang CF, et al. Blockade of PD-L 1 enhances cancer immunotherapy by regulating dendritic cell maturation and macrophage polarization. Cancers. 2019; 11(9):1400.
doi: 10.3390/cancers11091400 |
| [29] |
Arnalich F, Garcia-Palomero E, López J, Jiménez M, Madero R, Renart J, et al. Predictive value of nuclear factor kappa B activity and plasma cytokine levels in patients with sepsis. Infect Immun. 2000; 68(4):1942-5.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.4.1942-1945.2000 pmid: 10722586 |
| [30] |
Böhrer H, Qiu F, Zimmermann T, Zhang Y, Jllmer T, Männel D, et al. Role of NFkappa B in the mortality of sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100(5):972-85.
doi: 10.1172/JCI119648 pmid: 9276714 |
| [31] | Asgarova A, Asgarov K, Godet Y, Peixoto P, Nadaradjane A, Boyer-Guittaut M, et al. PD-L1 expression is regulated by both DNA methylation and NF-κB during EMT signaling in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 2018; 7(5):e1423170. |
| [32] |
Bouillez A, Rajabi H, Jin C, Samur M, Tagde A, Alam M, et al. MUC1-C integrates PD-L 1 induction with repression of immune effectors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 2017; 36(28):4037-46.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.47 pmid: 28288138 |
| [33] |
Peng J, Hamanishi J, Matsumura N, Abiko K, Murat K, Baba T, et al. Chemotherapy induces programmed cell death-ligand 1 overexpression via the nuclear factor-κB to foster an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2015; 75(23):5034-45.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3098 pmid: 26573793 |
| [1] | Mei-jia Shen, Li-chao Sun, Xiao-yu Liu, Meng-chen Xiong, Shan Li, A-ling Tang, Guo-qiang Zhang. Trichostatin A improves the inflammatory response and liver injury in septic mice through the FoxO3a/autophagy signaling pathway [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(3): 182-188. |
| [2] | Li Li, Jun Yan, Lin-qin Ma, Wei Bi, Cai-jun Wu. Effects of Maxingloushi decoction on immune inflammation and programmed death markers in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(1): 40-45. |
| [3] | Ruo Wu, Luo-gen Peng, Hui-min Zhao. Diverse coagulopathies in a rabbit model with different abdominal injuries [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(2): 141-147. |
| [4] | Jia-jun Xu, Jian-tao Zhen, Li Tang, Qing-ming Lin. Intravenous injection of Xuebijing attenuates acute kidney injury in rats with paraquat intoxication [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(1): 61-64. |
| [5] | Wei-ping Sun, Guang-xiong Yuan, Yan-juan Hu, Li-zhen Liao, Lin Fu. Effect of low-dose glucocorticoid on corticosteroid insufficient patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 34-39. |
| [6] | Peng Sun, Qian Li, Qing Zhang, Li Xu, Ji-yuan Han. Upregulated expression of S100A8 in mice brain after focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(3): 210-214. |
| [7] | Zhi-hong Liu, Xin-ri Zhang, Xiao-yun Hu, Meng-yu Cheng, Jian-ying Xu, Yong-cheng Du. Effect of glucocorticoid on MIP-1α and NF-кb expressing in the lung of rats undergoing mechanical ventilation with a high tidal volume [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(1): 66-69. |
| [8] | Man Huang, Xiao-Qiao Dong, Yue-Yu Hu, Wen-Hua Yu, Zu-Yong Zhang. High S100B levels in cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood of patients with acute basal ganglial hemorrhage are associated with poor outcome [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2010, 1(1): 22-31. |
| [9] | Yu-cai Zhang, Wen-qiong Zuo, Qun-fang Rong, Guo-liang Teng, Yu-ming Zhang. Glucocorticoid receptor expression on acute lung injury induced by endotoxin in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2010, 1(1): 65-69. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
