World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (6): 441-447.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.095
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hao Wu1,2, Yu Zhou1, Baogen Xu3, Wen Liu1, Jinquan Li1, Chuhan Zhou1, Hao Sun4,5( ), Yu Zheng6(
), Yu Zheng6( )
)
Received:2024-01-29
Accepted:2024-06-20
Online:2024-11-21
Published:2024-11-01
Contact:
Hao Sun, Email: Hao Wu, Yu Zhou, Baogen Xu, Wen Liu, Jinquan Li, Chuhan Zhou, Hao Sun, Yu Zheng. Assessment of rehabilitation treatment for patients with acute poisoning-induced toxic encephalopathy[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(6): 441-447.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.095
Table 1.
Comparison of characteristics between patients with different severity of toxic encephalopathy
| Characteristics | Total (n=464) | Mild (n=104) | Moderate (n=108) | Severe (n=252) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year, mean±SD | 47.0±23.0 | 40.7±23.3 | 46.9±25.0 | 49.2±21.8 | 0.30 |
| Male, n (%) | 252 (54.3) | 56 (53.9) | 60 (55.6) | 136 (54.0) | 0.73 |
| Toxic species, n (%) | <0.01 | ||||
| Pharmaceutical/biological products | 234 (50.43) | 59 (56.7) | 47 (43.5) | 128 (50.8) | |
| Quetiapine | 68 | 25 | 13 | 30 | |
| Estazolam | 59 | 12 | 35 | 14 | |
| Zopiclone | 55 | 4 | 6 | 45 | |
| Sertraline | 55 | 53 | 1 | 1 | |
| Alprazolam | 32 | 4 | 3 | 25 | |
| Oxazepam | 29 | 19 | 3 | 7 | |
| Diazepam | 24 | 16 | 1 | 7 | |
| Citalopram | 13 | 3 | 1 | 9 | |
| Midazolam | 10 | 1 | 2 | 7 | |
| Pesticide type toxins, n (%) | 208 (44.83) | 36 (34.6) | 53 (49.0) | 119 (47.2) | |
| Diquat | 151 | 21 | 34 | 96 | |
| Paraquat | 21 | 3 | 5 | 13 | |
| Emamectin benzoate | 17 | 5 | 6 | 6 | |
| Acetamiprid | 6 | 2 | 0 | 4 | |
| Monosultap | 5 | 2 | 3 | 0 | |
| Buprofezin | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 | |
| Bromadiolone | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| Industrial chemical substances, n (%) | 22 (4.74) | 9 (8.7) | 8 (7.4) | 5 (2.0) | |
| Ethanol | 12 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Ethylene glycol | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | |
| Eethyl hippuric acid | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| Parachloroaniline | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dimethylbenzyl ammonium bromide | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Heptane | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Time from toxics exposure to detection, h, mean±SD | 16.2±32.9 | 24.6±41.9 | 12.6±16.1 | 14.4±34.2 | 0.35 |
| Clinical symptoms, n (%) | <0.01 | ||||
| Dizziness/headache/limb numbness and fatigue | 142 (30.60) | 102 (98.1) | 40 (37.0) | 0 (0) | |
| Convulsions/irritability/delirium | 85 (18.32) | 2 (1.9) | 68 (63.0) | 15 (6.0) | |
| Coma | 237 (51.08) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 237 (94.1) | |
| ICU hospitalization rate, n (%) | 163 (35.13) | 35 (33.7) | 12 (11.1) | 116 (46.0) | <0.01 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 108 (23.28) | 5 (4.8) | 19 (17.6) | 84 (33.3) | 0.02 |
Table 2.
Comparison of baseline data between the groups of with and without rehabilitation intervention in patients with TE (n=464)
| Variables | Patients with rehabilitation (n=184) | Patients without rehabilitation (n=280) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year, mean±SD | 46.9±23.0 | 47.1±23.1 | 0.95 |
| Male, n (%) | 88 (47.8) | 164 (58.6) | 0.26 |
| Toxic species, n (%) | 0.10 | ||
| Pharmaceutical/biological products | 95 (51.6) | 139 (49.6) | |
| Pesticide type toxins | 85 (46.2) | 123 (43.9) | |
| Industrial chemical substances | 4 (2.2) | 18 (6.4) | |
| Time from toxics exposure to detection, h, mean±SD | 12.7±15.6 | 18.3±40.2 | 0.37 |
| Severity, n (%) | 0.80 | ||
| Mild TE | 44 (23.9) | 60 (21.4) | |
| Moderate TE | 41 (22.3) | 67 (23.9) | |
| Severe TE | 99 (53.8) | 153 (54.6) | |
| ICU hospitalization, n (%) | 40 (21.7) | 124 (44.3) | 0.01 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 38 (20.7) | 70 (25.0) | 0.54 |
Figure 2.
Comparison of survival curves among different subgroups. A: survival analysis of the severe patients with/without rehabilitation intervention; B: survival analysis of the pesticide-induced toxic encephalopathy patients with and without rehabilitation intervention; C: survival analysis of the pharmaceutical/biological products-induced toxic encephalopathy patients with and without rehabilitation intervention. TE: toxic encephalopathy; HR: hazard ratio.
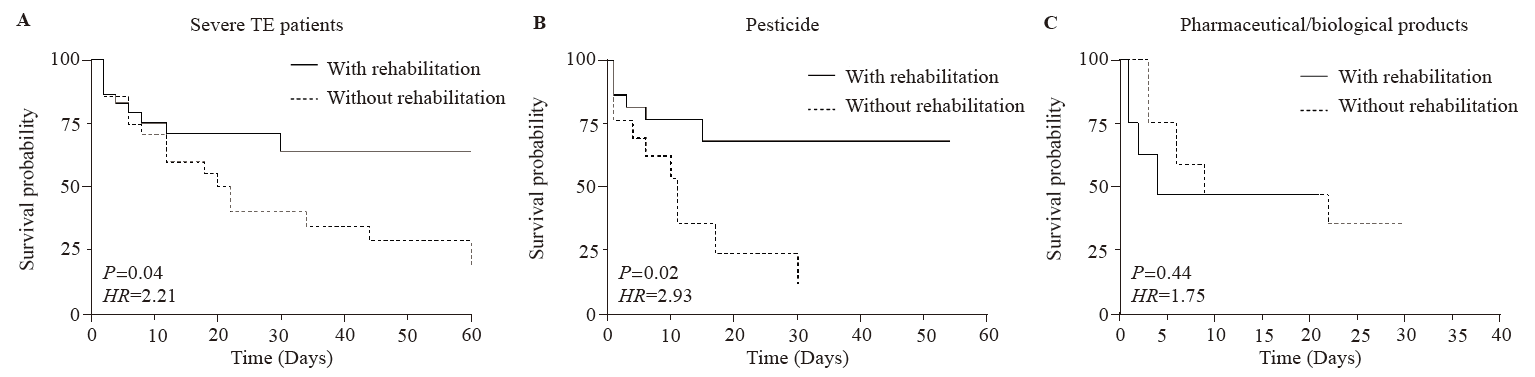
Table 3.
The levels of various indicators before and after rehabilitation intervention for severe TE patients (n=99)
| Variables | Before rehabilitation (day 3) | After rehabilitation (day 14) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Awareness | |||
| GCS score | 3 (3, 4) | 8 (7, 11) | < 0.01 |
| Muscle strength and motor function | |||
| FMA | 25 (4, 30) | 66 (57, 81) | < 0.01 |
| Swallowing function | |||
| WST | / | 4 (2, 4) | / |
| SSA | / | 29 (25, 33) | / |
| [1] |
de Oliveira AM, Paulino MV, Vieira APF, McKinney AM, da Rocha AJ, dos Santos GT, et al. Imaging patterns of toxic and metabolic brain disorders. Radiographics. 2019; 39(6): 1672-95.
doi: 10.1148/rg.2019190016 pmid: 31589567 |
| [2] | Dsouza D, Baddala R, Sharath Kumar GG, Nadig R. MRI brain features in nitrobenzene toxic encephalopathy. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2022; 25(2): 267-8. |
| [3] |
Lerner DP, Tadevosyan A, Burns JD. Toxin-induced subacute encephalopathy. Neurol Clin. 2020; 38(4): 799-824.
doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2020.07.006 pmid: 33040862 |
| [4] | Li Q, Yu W, Qu Y, Wang JQ, Mao N, Kang H. Acute toxic encephalopathy following bromadiolone intoxication: a case report. BMC Neurol. 2021; 21(1): 8. |
| [5] | Lott C, Truhlář A, Alfonzo A, Barelli A, González-Salvado V, Hinkelbein J, et al. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: cardiac arrest in special circumstances. Resuscitation. 2021;161: 152-219. |
| [6] |
Magalhães N, Carvalho F, Dinis-Oliveira RJ. Human and experimental toxicology of diquat poisoning: Toxicokinetics, mechanisms of toxicity, clinical features, and treatment. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2018; 37(11): 1131-60.
doi: 10.1177/0960327118765330 pmid: 29569487 |
| [7] | Yu GC, Cui SQ, Jian TZ, Kan BT, Jian XD. Diquat poisoning in a pregnant woman resulting in a miscarriage and maternal death. Clin Toxicol. 2021; 59(12): 1275-7. |
| [8] | Yu GC, Jian TZ, Cui SQ, Shi LK, Kan BT, Jian XD. Acute diquat poisoning resulting in toxic encephalopathy: a report of three cases. Clin Toxicol. 2022; 60(5): 647-50. |
| [9] |
Carvalho AF, Heilig M, Perez A, Probst C, Rehm J. Alcohol use disorders. Lancet. 2019; 394(10200): 781-92.
doi: S0140-6736(19)31775-1 pmid: 31478502 |
| [10] |
Santos Andrade C, Tavares Lucato L, da Graça Morais Martin M, Joaquina Marques-Dias M, Antonio Pezzi Portela L, Scarabôtolo Gattás G, et al. Non-alcoholic Wernicke’s encephalopathy: broadening the clinicoradiological spectrum. Br J Radiol. 2010; 83(989): 437-46.
doi: 10.1259/bjr/27226205 pmid: 20223908 |
| [11] | Lo CP, Chen SY, Lee KW, Chen WL, Chen CY, Hsueh CJ, et al. Brain injury after acute carbon monoxide poisoning: early and late complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189(4): W205-W211. |
| [12] | Kim DM, Lee IH, Park JY, Hwang SB, Yoo DS, Song CJ. Acute carbon monoxide poisoning: MR imaging findings with clinical correlation. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2017; 98(4): 299-306. |
| [13] |
Raub JA, Benignus VA. Carbon monoxide and the nervous system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2002; 26(8): 925-40.
pmid: 12667497 |
| [14] | Dobbs MR. Toxic encephalopathy. Semin Neurol. 2011; 31(2): 184-93. |
| [15] |
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Aschner M. Manganese toxicity in the central nervous system: the glutamine/glutamate-γ-aminobutyric acid cycle. J Intern Med. 2013; 273(5): 466-77.
doi: 10.1111/joim.12040 pmid: 23360507 |
| [16] | Zhou JN, Lu YQ. Lethal diquat poisoning manifests as acute central nervous system injury and circulatory failure: a retrospective cohort study of 50 cases. EClinicalMedicine. 2022;52: 101609. |
| [17] |
Wu BL, Song B, Tian SZ, Huo SH, Cui CX, Guo YS, et al. Central nervous system damage due to acute paraquat poisoning: a neuroimaging study with 3.0 T MRI. Neurotoxicology. 2012; 33(5): 1330-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.08.007 pmid: 22947519 |
| [18] |
Richardson JR, Fitsanakis V, Westerink RHS, Kanthasamy AG. Neurotoxicity of pesticides. Acta Neuropathol. 2019; 138(3): 343-62.
doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-02033-9 pmid: 31197504 |
| [19] | Kreitzer N, Rath K, Kurowski BG, Bakas T, Hart K, Lindsell CJ, et al. Rehabilitation practices in patients with moderate and severe traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2019; 34(5): E66-E72. |
| [20] | Yu GC, Wang JR, Jian TZ, Shi LK, Zhao LW, Li YQ, et al. Case series: Diquat poisoning with acute kidney failure, myocardial damage, and rhabdomyolysis. Front Public Health. 2022;10: 991587. |
| [21] | Xing JH, Chu Z, Han DF, Jiang XM, Zang XX, Liu YJ, et al.Lethal diquat poisoning manifesting as central pontine myelinolysis and acute kidney injury: a case report and literature review. J Int Med Res. 2020; 48(7): 300060520943824. |
| [22] | Le Danseur M. Stroke rehabilitation. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2020; 32(1): 97-108. |
| [23] | Singletary EM, Zideman DA, Bendall JC, Berry DC, Borra V, Carlson JN, et al. 2020 international consensus on first aid science with treatment recommendations. Circulation. 2020; 142(16_suppl_1): S284-S334. |
| [24] | Kim Y, Kim JW. Toxic encephalopathy. Saf Health Work. 2012; 3(4): 243-56. |
| [25] | Anand KV, Shahid PT, Shameel KK. Assessment of GCS and FOUR score as prognostic indicators for hospital stay and morbidity in traumatic brain injury patients: an observational study. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024; 16(Suppl 1): S601-S604. |
| [26] | Ambesi V, Miller C, Fitzgerald MC, Mitra B. The GCS-Pupils (GCS-P) score to assess outcomes after traumatic brain injury: a retrospective study. Br J Neurosurg. 2024: 1-4. |
| [27] | Wang YM, Zhu N, Zhou YM, Su R, Li HL, Zhou JX. The combination of arterial lactate level with GCS-pupils score to evaluate short term prognosis in traumatic brain injury: a retrospective study. BMC Neurol. 2022; 22(1): 430. |
| [28] | Cheng A, Nadkarni VM, Mancini MB, Hunt EA, Sinz EH, Merchant RM, et al. Resuscitation education science: educational strategies to improve outcomes from cardiac arrest: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018; 138(6): e82-e122. |
| [29] |
Waldauf P, Jiroutková K, Krajčová A, Puthucheary Z, Duška F. Effects of rehabilitation interventions on clinical outcomes in critically ill patients: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care Med. 2020; 48(7): 1055-65.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004382 pmid: 32345834 |
| [30] |
van Hout MS, Wekking EM, Berg IJ, Deelman BG. Psychosocial and cognitive rehabilitation of patients with solvent-induced chronic toxic encephalopathy: a randomised controlled study. Psychother Psychosom. 2008; 77(5): 289-97.
doi: 10.1159/000140088 pmid: 18560254 |
| [31] | Esmaeilian S, Teimouri A, Hooshmandi S, Nikoo MH, Heydari ST, Mohajeri E, et al. Methanol poisoning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran: a retrospective cross-sectional study of clinical, laboratory, and brain imaging characteristics and outcomes. Health Sci Rep. 2023; 6(12): e1752. |
| [32] | Hu JJ, Yu EY, Liao ZL. Changes in cognitive function and related brain regions in chronic benzene poisoning: a case report. Ann Transl Med. 2021; 9(1): 81. |
| [33] |
Varona A, Echevarria E, Irazusta J, Serrano R, Gil J, Casis L. Effects of acute benzene exposure on brain enkephalin immunostaining and degradation. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1998; 20(6): 611-6.
pmid: 9831122 |
| [34] | Feulefack J, Khan A, Forastiere F, Sergi CM. Parental pesticide exposure and childhood brain cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis confirming the IARC/WHO monographs on some organophosphate insecticides and herbicides. Children. 2021; 8(12): 1096. |
| [35] | Anand KV, Shahid PT, Shameel KK. Assessment of GCS and FOUR score as prognostic indicators for hospital stay and morbidity in traumatic brain injury patients: an observational study. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024; 16(Suppl 1): S601-S604. |
| [36] |
Park S, Choi J, Kim Y, You JSH. Clinical machine learning predicting best stroke rehabilitation responders to exoskeletal robotic gait rehabilitation. NeuroRehabilitation. 2024; 54(4): 619-28.
doi: 10.3233/NRE-240070 pmid: 38943406 |
| [37] | Kusumi H, Kimura Y, Otobe Y, Suzuki M, Tanaka S, Yamamoto S, et al. Effect of early rehabilitation services after discharge on social activity among chronic stroke survivors: a multicenter prospective study. World Neurosurg. 2024;188: e591-e596. |
| [38] | Golding-Day M, Young J, Charlton P, Houston B, Thomas S, Walker M. Orthotist involvement in early gait rehabilitation after stroke: a cross-sectional survey of orthotists in the United Kingdom. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2024; 10.1097/PXR.0000000000000365. |
| [39] | Geng HX, Li M, Tang J, Lv Q, Li RL, Wang L. Early rehabilitation exercise after stroke improves neurological recovery through enhancing angiogenesis in patients and cerebral ischemia rat model. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(18): 10508. |
| [40] | Zhang JH, Fei CQ, Qi SL, Fu JQ, Zhou S, Wang Z, et al. The toxicity response of the electrochemical signal of the cell to the drug metabolized by the S9 system. Analyst. 2024; 149(6): 1921-8. |
| [41] | Jiang P, Chen T, Chu LF, Xu RP, Gao JT, Wang L, et al. Enhancing drug-drug interaction prediction by integrating physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model with fraction metabolized by CYP3A4. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2023; 19(10): 721-31. |
| [42] |
De Sousa Mendes M, Lui G, Zheng Y, Pressiat C, Hirt D, Valade E, et al. A physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model to predict human fetal exposure for a drug metabolized by several CYP450 pathways. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017; 56(5): 537-50.
doi: 10.1007/s40262-016-0457-5 pmid: 27766562 |
| [43] | Fan CY, Zhang CG, Zhang PS, Chen Y, He JQ, Yin H, et al. Acute diquat poisoning case with multiorgan failure and a literature review: a case report. World J Clin Cases. 2023; 11(27): 6565-72. |
| [44] | Dai XH, Liu MZ, Xu SY, Zhao H, Li XZ, Bai YJ, et al. Metabolomics profile of plasma in acute diquat-poisoned patients using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023;176: 113765 |
| [1] | Ji Cheng, Yulu Chen, Weidong Wang, Xueqi Zhu, Zhenluo Jiang, Peng Liu, Liwen Du. Chlorfenapyr poisoning: mechanisms, clinical presentations, and treatment strategies [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(3): 214-219. |
| [2] | Qifang Shi, Gen Ba, Zhenyu Xia, Zhengsheng Mao, Hao Sun, Jinsong Zhang. The value of toxicological analysis in acute poisoning patients with uncertain exposure histories: a retrospective and descriptive study from an institute of poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(2): 98-104. |
| [3] | Fei Zeng, Lingyun Cai, Luyao Guo, Meijuan Lan, Jiangshuyuan Liang, Peipei Gu. Pulmonary rehabilitation protocols in urgent lung transplantation patients [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(1): 47-51. |
| [4] | Ning Dong, Zhe-xi Lu, Xing-liang Li, Wei Li, Li Pang, Ji-hong Xing. Clinical correlates of hypotension in patients with acute organophosphorus poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(1): 24-28. |
| [5] | Yun-fei Jiang, Jian Kang, Pei-pei Huang, Jia-xi Yao, Zhong-he Wang, Lei Jiang, Jun Wang, Li Qiao, Bao-li Zhu, Hao Sun, Jin-song Zhang. Evaluation of gastric lavage efficiency and utility using a rapid quantitative method in a swine paraquat poisoning model [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(3): 174-181. |
| [6] | Shi-yuan Yu, Yan-xia Gao, Joseph Walline, Xin Lu, Li-na Zhao, Yuan-xu Huang, Jiang Tao, An-yong Yu, Na Ta, Ren-ju Xiao, Yi Li. Role of penehyclidine in acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(1): 37-47. |
| [7] | Shahin Shadnia, Nasim Zaman, Hossein Hassanian-Moghaddam, Hamed Shafaroodi, Mina Padandar, Mohammad Hasan Rezaeizadeh. Prognostic value of cortisol and thyroid function tests in poisoned patients admitted to toxicology ICU [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(1): 51-55. |
| [8] | Hojjat Sheikhbardsiri, Mohammad H. Yarmohammadian, Fatemeh Rezaei, Mohammad Reza Maracy. Rehabilitation of vulnerable groups in emergencies and disasters: A systematic review [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(4): 253-263. |
| [9] | Peyman Erfantalab, Kambiz Soltaninejad, Shahin Shadnia, Nasim Zamani, Hossein Hassanian-Moghaddam, Arezou Mahdavinejad, Behrooz Hashemi Damaneh. Trend of blood lactate level in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(2): 116-120. |
| [10] | Eyosias Teklemariam, Shibiru Tesema, Awol Jemal. Pattern of acute poisoning in Jimma University Specialized Hospital, South West Ethiopia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2016, 7(4): 290-293. |
| [11] | Tigist Bacha, Birkneh Tilahun. A cross-sectional study of children with acute poisoning: A three-year retrospective analysis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(4): 265-269. |
| [12] | Ertugrul Kaya, Aylin Yilmaz, Ayhan Saritas, Serdar Colakoglu, Davut Baltaci, Hayati Kandis, Ismail Hamdi Kara. Acute intoxication cases admitted to the emergency department of a university hospital [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 54-59. |
| [13] | Suat Zengin, Behcet A, Sahin Karta, Basri Can, Mustafa Orkmez, Abdullah Taskın, Ugur Lok, Bediha Gulen, Cuma Yildirim, Seyithan Taysi. An assessment of antioxidant status in patients with carbon monoxide poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 91-95. |
| [14] | Ze-hua Dong, Bang-xu Yu, Yun-bo Sun, Wei Fang, Lei Li. Effects of early rehabilitation therapy on patients with mechanical ventilation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(1): 48-52. |
| [15] | Zhi-qiang Cheng, Ji-yuan Han, Peng Sun, Yu-ying Weng, Jiao Chen, Guo-yan Wu, Hong-xia Ma. Edaravone attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress in human type II alveolar epithelial cells [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(1): 55-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
