World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (6): 448-454.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.073
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Marechika Tsubouchi1( ), Ryohei Matsui1, Mami Tsubota1, Yota Yamagishi1, Yuka Miyazaki1, Hideki Murakami2, Tomonori Hattori1, Hiroshi Sasano1
), Ryohei Matsui1, Mami Tsubota1, Yota Yamagishi1, Yuka Miyazaki1, Hideki Murakami2, Tomonori Hattori1, Hiroshi Sasano1
Received:2023-12-05
Accepted:2024-02-23
Online:2024-11-21
Published:2024-11-01
Contact:
Marechika Tsubouchi, Email: Marechika Tsubouchi, Ryohei Matsui, Mami Tsubota, Yota Yamagishi, Yuka Miyazaki, Hideki Murakami, Tomonori Hattori, Hiroshi Sasano. Effect of sphygmomanometer cuff pressure on the differentiation of veins from arteries on ultrasound imaging: an observational cross-sectional study[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(6): 448-454.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.073
Figure 2.
The magnitude of arterial pulsation (MAP) at six tourniquet pressure levels (0 mmHg, DBP/2, DBP, [DBP+SBP]/2, SBP, and SBP+20 mmHg) under four levels of ultrasound probe compression (inner diameter 100%, 75%, 50%, and 25%). At tourniquet pressures between 0 mmHg and (DBP+SBP)/2, the magnitude of the pulsation increased by 75% and 50%, respectively, compared to that at 100%. There is minimal pulsation at an inner diameter of 100%. DBP: diastolic blood pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure. *P<0.05.
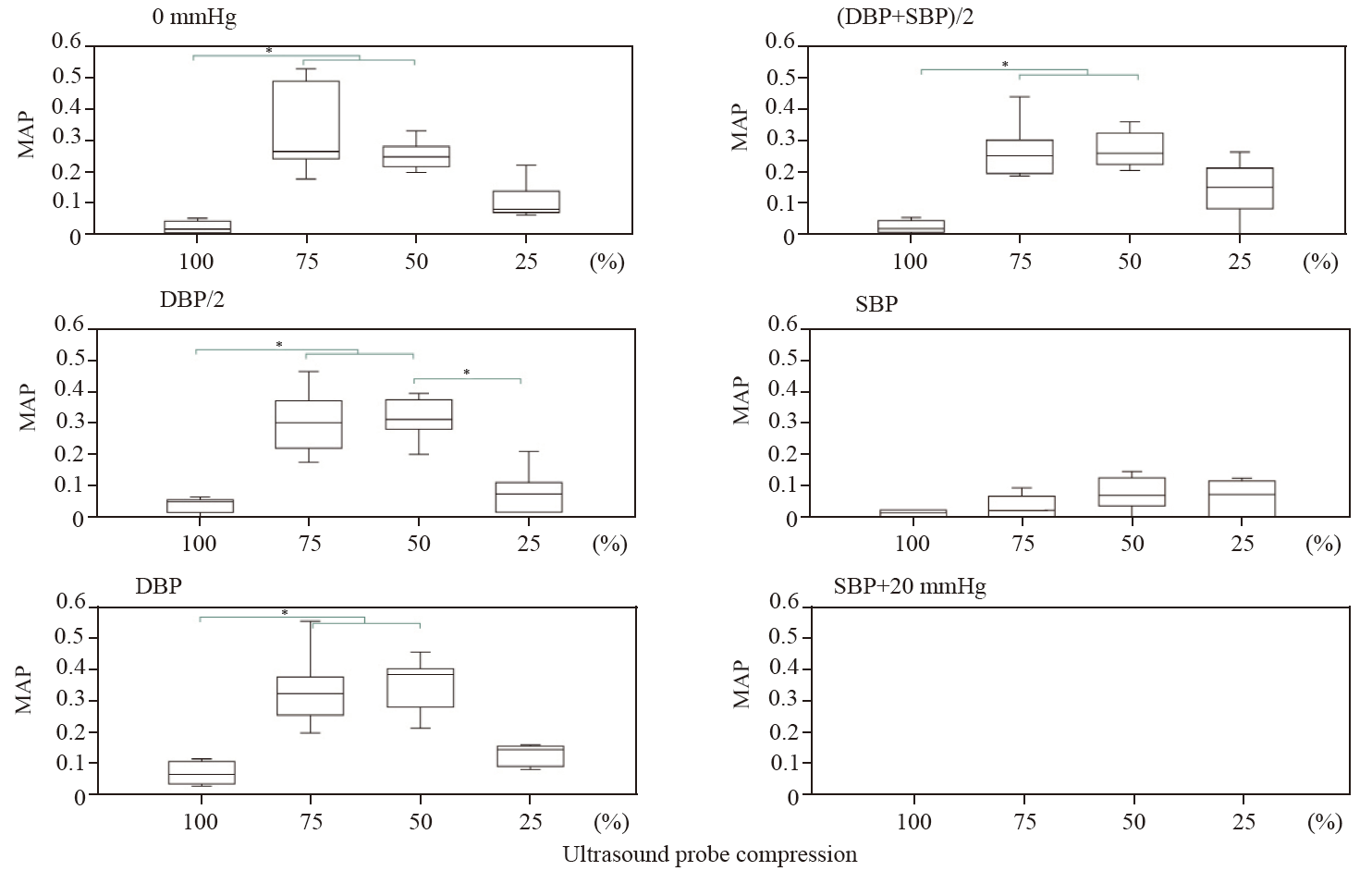
Figure 3.
Representative arterial pulsations obtained at six tourniquet pressure levels (0 mmHg, DBP/2, DBP, [DBP+SBP]/2, SBP, and SBP+20 mmHg) under four levels of ultrasound probe compression (inner diameter 100%, 75%, 50%, and 25% during systole) in a 27-year-old man. Each panel shows collated M-mode ultrasound images of an artery in the cubital fossa obtained from selected vertical lines corresponding to 3-s periods in Supplementary Video 1. The dotted line in the left part of each panel shows the inside of the artery. DBP: diastolic blood pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure.
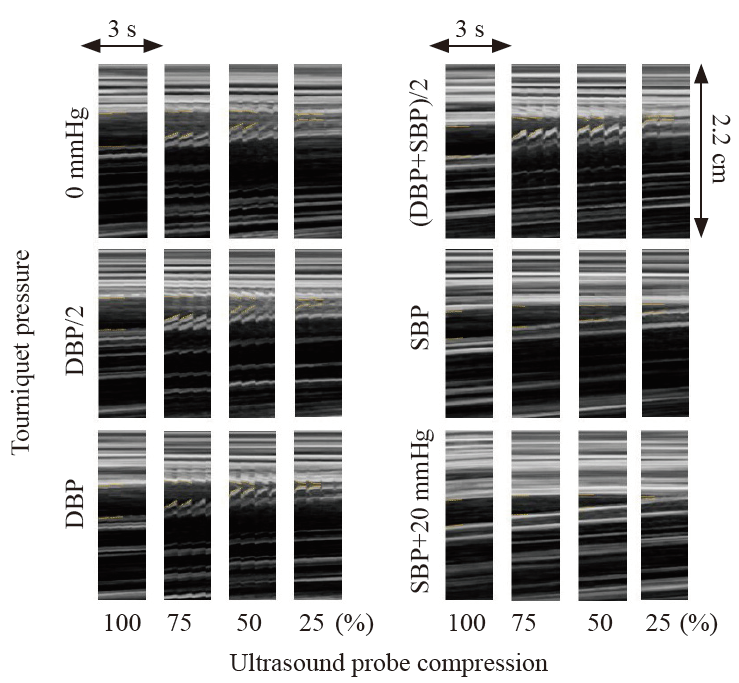
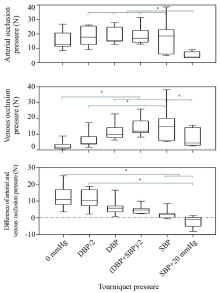
Figure 4.
Arterial (A) and venous (V) occlusion pressures and the difference in pressure (A-V) at six tourniquet pressure levels (0 mmHg, DBP/2, DBP, [DBP+SBP]/2, SBP, and SBP+20 mmHg). The arterial occlusion pressure at a tourniquet pressure of SBP+20 mmHg was lower than that at tourniquet pressures between DBP/2 and SBP (P<0.05). The venous occlusion pressure at tourniquet pressures between DBP and SBP was greater than that at 0 mmHg, but it was not greater at SBP+20 mmHg than at 0 mmHg. The difference in occlusion pressure between the artery and vein (A-V) at SBP and SBP+20 mmHg was smaller than that at 0 mmHg (P<0.05). The corresponding median value at an SBP+20 mmHg was less than 0. N: Newton; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure. *P<0.05.
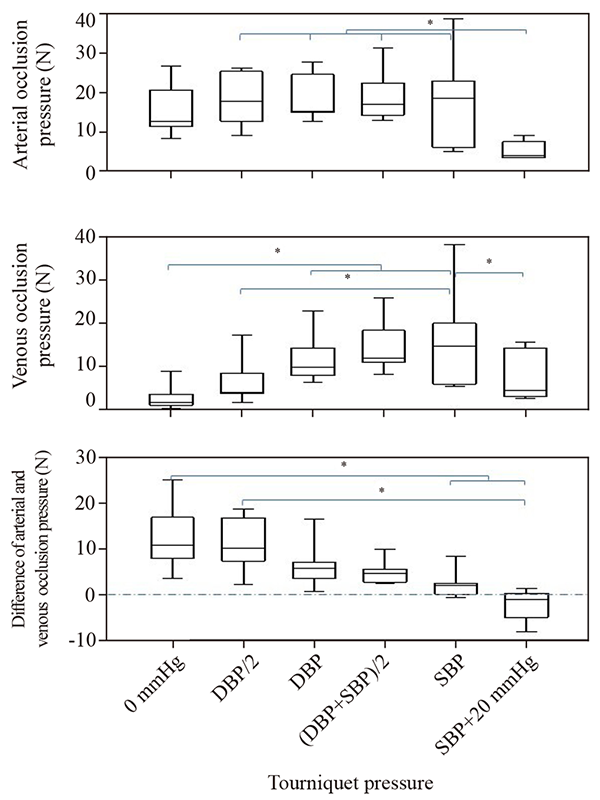

Figure 5.
The venous vertical diameter and wrist pulse pressure at six tourniquet pressure levels (0 mmHg, DBP/2, DBP, [DBP+SBP]/2, SBP, and SBP+20 mmHg). The venous vertical diameter at tourniquet pressures between the DBP and SBP was greater than that at 0 mmHg. The wrist pulse pressure is maintained at tourniquet pressures between 0 mmHg and (DBP+SBP)/2. Wrist pulse pressure measurement is not feasible at tourniquet pressures between SBP and SBP+20 mmHg; therefore, there are no wrist pulse pressure data at these pressures. *P<0.05.
| [1] |
Tran QK, Fairchild M, Yardi I, Mirda D, Markin K, Pourmand A. Efficacy of ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous cannulation versus standard of care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021; 47(11): 3068-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2021.07.002 pmid: 34353670 |
| [2] |
Tran T, Lund SB, Nichols MD, Kummer T. Effect of two tourniquet techniques on peripheral intravenous cannulation success: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2019; 37(12): 2209-14.
doi: S0735-6757(19)30183-4 pmid: 30948254 |
| [3] | Panebianco NL, Fredette JM, Szyld D, Sagalyn EB, Pines JM, Dean AJ. What you see (sonographically) is what you get: vein and patient characteristics associated with successful ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous placement in patients with difficult access. Acad Emerg Med. 2009; 16(12): 1298-303. |
| [4] |
Witting MD, Schenkel SM, Lawner BJ, Euerle BD. Effects of vein width and depth on ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous success rates. J Emerg Med. 2010; 39(1): 70-5.
doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2009.01.003 pmid: 19272730 |
| [5] |
Nelson D, Jeanmonod R, Jeanmonod D. Randomized trial of tourniquet vs blood pressure cuff for target vein dilation in ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous access. Am J Emerg Med. 2014; 32(7): 761-4.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.04.020 pmid: 24856748 |
| [6] |
Kule A, Hang B, Bahl A. Preventing the collapse of a peripheral vein during cannulation: an evaluation of various tourniquet techniques on vein compressibility. J Emerg Med. 2014; 46(5): 659-66.
doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.08.088 pmid: 24485698 |
| [7] | Xiong J, Wang HJ, Zhan PF, Ding YM, Bao Y, Ji CL, et al. Which, tourniquet or inflation of blood pressure cuff, can dilate peripheral vein adequately for intravenous access? Biomed J Sci Tech Res. 2019; 20(1): BJSTR. MS.ID.003398. |
| [8] |
Sasaki S, Murakami N, Matsumura Y, Ichimura M, Mori M. Relationship between tourniquet pressure and a cross-section area of superficial vein of forearm. Acta Med Okayama. 2012; 66(1): 67-71.
pmid: 22358141 |
| [9] |
Ng M, Mark LKF, Fatimah L. Management of difficult intravenous access: a qualitative review. World J Emerg Med. 2022; 13(6): 467-78.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.104 pmid: 36636560 |
| [10] | Angles E, Robin F, Moal B, Roy M, Sesay M, Ouattara A, et al. Pre-operative peripheral intravenous cannula insertion failure at the first attempt in adults: development of the VENSCORE predictive scale and identification of risk factors. J Clin Anesth. 2021;75: 110435. |
| [11] |
Sasano H, Morita M, Azami T, Ito S, Sasano N, Kato R, et al. Skin-traction method prevents the collapse of the internal jugular vein caused by an ultrasound probe in real-time ultrasound-assisted guidance. J Anesth. 2009; 23(1): 41-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00540-008-0703-6 pmid: 19234821 |
| [12] |
Morita M, Sasano H, Azami T, Sasano N, Fujita Y, Ito S, et al. A novel skin-traction method is effective for real-time ultrasound-guided internal jugular vein catheterization in infants and neonates weighing less than 5 kilograms. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109(3): 754-9.
doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e3181b01ae3 pmid: 19690242 |
| [13] | Morita M, Sasano H, Azami T, Sasano N, Katsuya H. The skintraction method increases the cross-sectional area of the internal jugular vein by increasing its anteroposterior diameter. J Anesth. 2007;21(4): 467-71. |
| [1] | David Ahmad Haidar, David Mintz, Brandon M Wubben, Omar Rizvi, Srikar Adhikari. Evaluation of hand infections in the emergency department using point-of-care ultrasound [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(4): 283-288. |
| [2] | Mark Slader, Hayley Young, Margot Barker, Kylie Prentice, Katherine Bogaard, Charlene Yuan, Soheil Saadat, Shadi Lahham. A comparison of handheld and standard ultrasound in Swiss medical students [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(2): 85-90. |
| [3] | Shan-xiang Xu, Chun-shuang Wu, Shao-yun Liu, Xiao Lu. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy and noninvasive ventilation for preventing extubation failure during weaning from mechanical ventilation assessed by lung ultrasound score: A single-center randomized study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(4): 274-280. |
| [4] | Lori Stolz, Elaine Situ-LaCasse, Josie Acuña, Matthew Thompson, Nicolaus Hawbaker, Josephine Valenzuela, Uwe Stolz, Srikar Adhikari. What is the ideal approach for emergent pericardiocentesis using point-of-care ultrasound guidance? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(3): 169-173. |
| [5] | Kun Cui, You-quan Shi, Yuan-zheng Zhang, Zheng-gong Li, Chang-ling Li. Optimized strategy of rotational atherectomy of underexpanded coronary stents in patients with acute coronary syndrome [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(3): 198-201. |
| [6] | Muhammad Akhter Hamid, Ruqiya Afroz, Uqba Nawaz Ahmed, Aneela Bawani, Dilnasheen Khan, Rabia Shahab, Asim Salim. The importance of visualization of appendix on abdominal ultrasound for the diagnosis of appendicitis in children: A quality assessment review [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(3): 140-144. |
| [7] | Samantha Shwe, Lauren Witchey, Shadi Lahham, Ethan Kunstadt, Inna Shniter, John C. Fox. Retrospective analysis of eFAST ultrasounds performed on trauma activations at an academic level-1 trauma center [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(1): 12-17. |
| [8] | Elaine Situ-LaCasse, Helpees Guirguis, Lucas Friedman, Asad E. Patanwala, Seth E. Cohen, Srikar Adhikari. Can emergency physicians perform extended compression ultrasound for the diagnosis of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(4): 205-209. |
| [9] | Ali Pourmand, Matthew Pyle, David Yamane, Kazi Sumon, Sarah E. Frasure. The utility of point-of-care ultrasound in the assessment of volume status in acute and critically ill patients [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(4): 232-238. |
| [10] | Sagar Shah, Steven Tohmasi, Emily Frisch, Amanda Anderson, Roy Almog, Shadi Lahham, Roland Bingisser, John C. Fox. A comparison of simulation versus didactics for teaching ultrasound to Swiss medical students [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(3): 169-176. |
| [11] | Alexander S. Kwon, Shadi Lahham, John C. Fox. Can an 8th grade student learn point of care ultrasound? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(2): 109-113. |
| [12] | Genevieve Mazza, Carina Mireles Romo, Marlene Torres, Ali Duffens, Annasha Vyas, Katherine Moran, Joshua Livingston, Savannah Gonzales, Shadi Lahham, Inna Shniter, Maxwell Thompson, John Christian Fox. Assessment of clinical dehydration using point of care ultrasound for pediatric patients in rural Panama [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(1): 46-50. |
| [13] | Amar Pujari, Deepa R Swamy, Rashmi Singh, Ritika Mukhija, Rohan Chawla, Pradeep Sharma. Ultrasonographic assessment of paediatric ocular emergencies: A tertiary eye hospital based observation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(4): 272-275. |
| [14] | Elaine Situ-LaCasse, Ryan W. Grieger, Stephen Crabbe, Anna L. Waterbrook, Lucas Friedman, Srikar Adhikari. Utility of point-of-care musculoskeletal ultrasound in the evaluation of emergency department musculoskeletal pathology [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(4): 262-266. |
| [15] | Sarah E. Frasure, Amy F. Hildreth, Raghu Seethala, Heidi H. Kimberly. Accuracy of abdominal ultrasound for the diagnosis of small bowel obstruction in the emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(4): 267-271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
