World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (2): 113-120.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.031
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qingyuan Liu1, Yixin Zhang2, Jian Sun3, Kaipeng Wang4, Yueguo Wang3, Yulan Wang3, Cailing Ren3, Yan Wang3, Jiashan Zhu3, Shusheng Zhou3, Mengping Zhang2( ), Yinglei Lai2(
), Yinglei Lai2( ), Kui Jin3(
), Kui Jin3( )
)
Received:2024-04-29
Accepted:2024-09-20
Online:2025-03-19
Published:2025-03-01
Contact:
Mengping Zhang, Email: Qingyuan Liu, Yixin Zhang, Jian Sun, Kaipeng Wang, Yueguo Wang, Yulan Wang, Cailing Ren, Yan Wang, Jiashan Zhu, Shusheng Zhou, Mengping Zhang, Yinglei Lai, Kui Jin. Early identification of high-risk patients admitted to emergency departments using vital signs and machine learning[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 113-120.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.031
Table 1.
Comparison of baseline characteristics of emergency department patients with low risk and high risk
| Variables | Patients with low risk (n=31,723) | Patients with high risk (n=7,074) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 64.0 (51.0, 74.0) | 66.0 (53.0, 77.0) | <0.01 |
| Gender, n (%) | <0.01 | ||
| Male | 19,561 (61.7) | 4,646 (65.7) | |
| Female | 12,162 (38.3) | 2,428 (34.3) | |
| State of consciousness, n (%) | <0.01 | ||
| I (Alert) | 24,127 (76.1) | 4,394 (62.1) | |
| II (Obtunded) | 3,926 (12.3) | 612 (8.7) | |
| III (Coma) | 3,670 (11.6) | 2,068 (29.2) | |
| BT, ℃, median (IQR) | 36.5 (36.3, 36.6) | 36.5 (36.3, 36.7) | <0.01 |
| HR, beats per minute, median (IQR) | 82.0 (72.0, 97.0) | 90.0 (75.0, 110.0) | <0.01 |
| RR, breath per minute, median (IQR) | 20.0 (20.0, 20.0) | 20.0 (20.0, 22.0) | <0.01 |
| SBP, mmHg, median (IQR) | 137.0 (119.0, 158.0) | 126.0 (105.0, 147.0) | <0.01 |
| DBP, mmHg, median (IQR) | 81.0 (70.0, 94.0) | 75.0 (62.0, 89.0) | <0.01 |
| SpO2, %, median (IQR) | 97.0 (95.0, 98.0) | 96.0 (88.0, 98.0) | <0.01 |
Figure 2.
Receiver operating characteristic curve analyses of classifications of ED patients with high risk (A), area under the precision-recall curve (B), and calibration curve (C). LR: logistic regression; DT: decision tree; GNB: Gaussian Na?ve Bayes; KNN: k-nearest neighbor; MLP: multilayer perceptron; NEWS: National Early Warning Score.
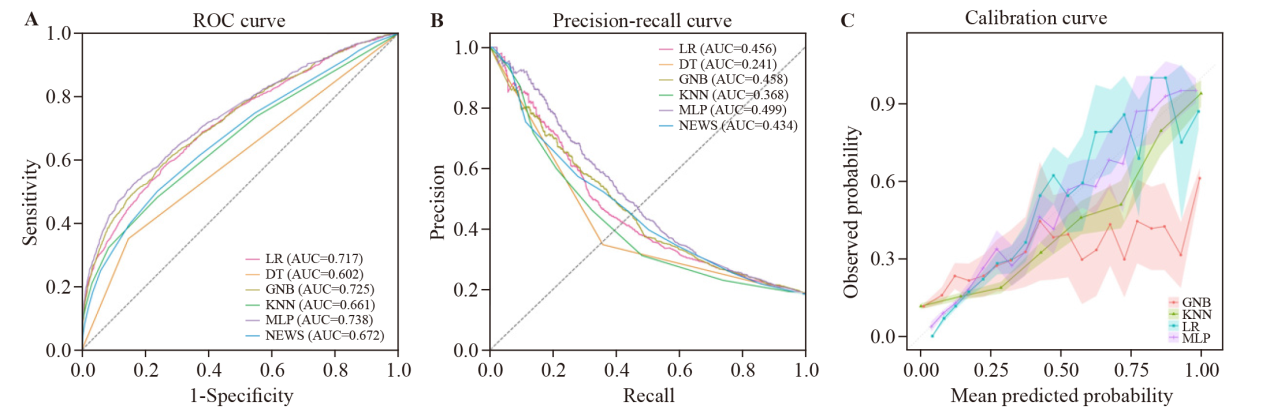
Table 2.
Comparison of performance of all the classification methods
| Methods | Accuracy | Specificity | Sensitivity | F1-score | Cut-off value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | 0.726 | 0.734 | 0.586 | 0.422 | 0.183 |
| DT | 0.753 | 0.850 | 0.358 | 0.352 | 1 |
| GNB | 0.691 | 0.742 | 0.594 | 0.432 | 0.025 |
| KNN | 0.716 | 0.762 | 0.482 | 0.378 | 0.286 |
| MLP | 0.779 | 0.844 | 0.517 | 0.467 | 0.175 |
| Scenario I (with at least 80% sensitivity) | |||||
| LR | 0.510 | 0.442 | 0.801 | 0.373 | 0.130 |
| DT | 0.182 | 0 | 1 | 0.308 | 0 |
| GNB | 0.521 | 0.461 | 0.800 | 0.378 | 0.006 |
| KNN | 0.182 | 0 | 1 | 0.308 | 0 |
| MLP | 0.528 | 0.460 | 0.800 | 0.382 | 0.134 |
| Scenario II (with at least 80% specificity) | |||||
| LR | 0.750 | 0.800 | 0.516 | 0.425 | 0.204 |
| DT | 0.760 | 0.842 | 0.372 | 0.352 | 1 |
| GNB | 0.790 | 0.810 | 0.511 | 0.446 | 0.175 |
| KNN | 0.808 | 0.919 | 0.305 | 0.380 | 0.429 |
| MLP | 0.785 | 0.835 | 0.532 | 0.462 | 0.183 |
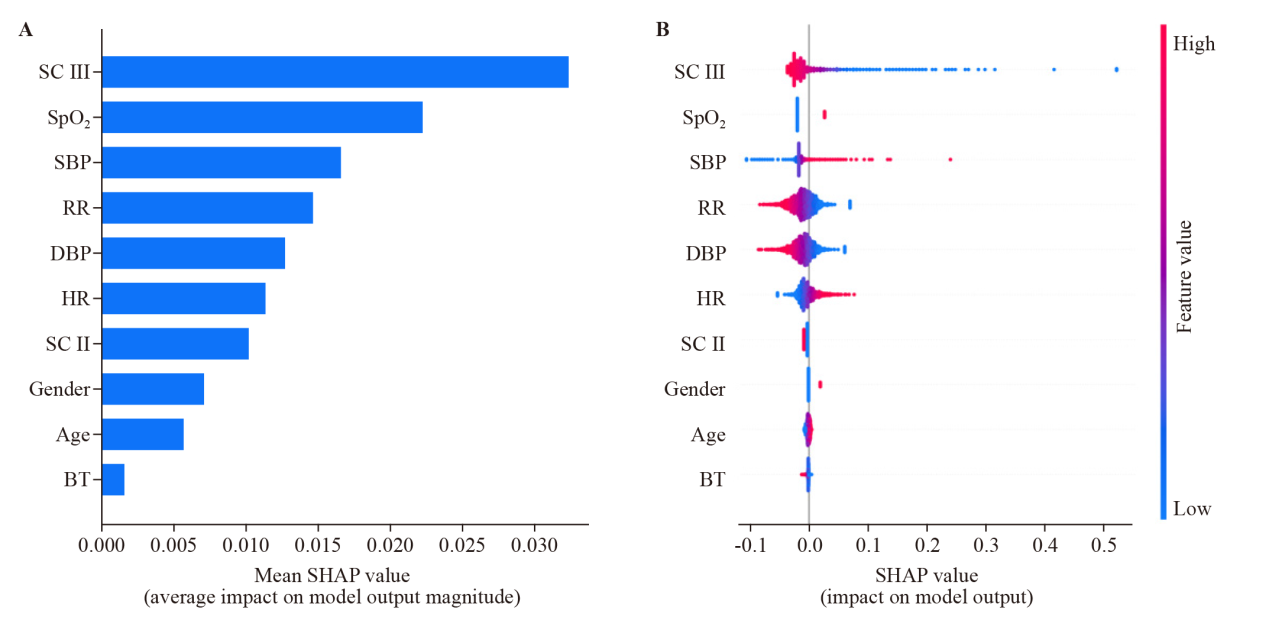
Figure 3.
Visualization of feature importance in multilayer perceptron (MLP) model based on SHAP value. A: the mean SHAP value of each predictor in MLP model; B: the dotted SHAP values from randomly selected 500 individuals; red points indicated higher predictor values and blue points indicated lower values. SC: state of consciousness (SC II, obtunded; SCIII coma); SpO2: peripheral capillary oxygen saturation; SBP: systolic blood pressure; RR: respiratory rate; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; HR: heart rate; BT: body temperature; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations.
| 1 | Raita Y, Goto T, Faridi MK, Brown DFM, Camargo CA Jr, Hasegawa K. Emergency department triage prediction of clinical outcomes using machine learning models. Crit Care. 2019; 23(1): 64. |
| 2 | Jin K, Zhang H, Seery S, Fu YY, Yu SS, Zhang LL, et al. Comparing public and private emergency departments in China: early evidence from a national healthcare quality survey. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2020; 35(2): 581-91. |
| 3 |
Sun BC, Hsia RY, Weiss RE, Zingmond D, Liang LJ, Han W, et al. Effect of emergency department crowding on outcomes of admitted patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2013; 61(6): 605-11.e6.
doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2012.10.026 pmid: 23218508 |
| 4 |
Higginson I. Emergency department crowding. Emerg Med J. 2012; 29(6): 437-43.
doi: 10.1136/emermed-2011-200532 pmid: 22223713 |
| 5 |
Jin B, Zhao YF, Hao SY, Shin AY, Wang Y, Zhu CQ, et al. Prospective stratification of patients at risk for emergency department revisit: resource utilization and population management strategy implications. BMC Emerg Med. 2016; 16: 10.
doi: 10.1186/s12873-016-0074-5 pmid: 26842066 |
| 6 | Bates DW, Saria S, Ohno-Machado L, Shah A, Escobar G. Big data in health care: using analytics to identify and manage high-risk and high-cost patients. Health Aff. 2014; 33(7): 1123-31. |
| 7 | Bologheanu R, Kapral L, Laxar D, Maleczek M, Dibiasi C, Zeiner S, et al. Development of a reinforcement learning algorithm to optimize corticosteroid therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis. J Clin Med. 2023; 12(4): 1513. |
| 8 |
de Paiva BBM, Pereira PD, Gomes VMR, Souza-Silva MVR, Martins KPMP, et al. Potential and limitations of machine meta-learning (ensemble) methods for predicting COVID-19 mortality in a large inhospital Brazilian dataset. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1): 3463.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28579-z pmid: 36859446 |
| 9 |
Mistry B, Stewart De Ramirez S, Kelen G, Schmitz PSK, Balhara KS, Levin S, et al. Accuracy and reliability of emergency department triage using the emergency severity index: an international multicenter assessment. Ann Emerg Med. 2018; 71(5): 581-7.e3.
doi: S0196-0644(17)31745-6 pmid: 29174836 |
| 10 |
Dugas AF, Kirsch TD, Toerper M, Korley F, Yenokyan G, France D, et al. An electronic emergency triage system to improve patient distribution by critical outcomes. J Emerg Med. 2016; 50(6): 910-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2016.02.026 pmid: 27133736 |
| 11 |
Torabi M, Moeinaddini S, Mirafzal A, Rastegari A, Sadeghkhani N. Shock index, modified shock index, and age shock index for prediction of mortality in Emergency Severity Index level 3. Am J Emerg Med. 2016; 34(11): 2079-83.
doi: S0735-6757(16)30411-9 pmid: 27461887 |
| 12 |
Lam RPK, Dai Z, Lau EHY, Ip CYT, Chan HC, Zhao L, et al. Comparing 11 early warning scores and three shock indices in early sepsis prediction in the emergency department. World J Emerg Med. 2024; 15(4): 273-82.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.052 pmid: 39050223 |
| 13 | Kuhn M, Johnson K. Applied predictive modeling. Available at: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-1-4614-6849-3. |
| 14 | Levin S, Toerper M, Hamrock E, Hinson JS, Barnes S, Gardner H, et al. Machine-learning-based electronic triage more accurately differentiates patients with respect to clinical outcomes compared with the emergency severity index. Ann Emerg Med. 2018; 71(5):565-74.e2. |
| 15 |
Rajkomar A, Oren E, Chen K, Dai AM, Hajaj N, Hardt M, et al. Scalable and accurate deep learning with electronic health records. NPJ Digit Med. 2018; 1: 18.
doi: 10.1038/s41746-018-0029-1 pmid: 31304302 |
| 16 | Li WH, Dong B, Wang HS, Yuan JJ, Qian H, Zheng LL, et al. Artificial intelligence promotes shared decision-making through recommending tests to febrile pediatric outpatients. World J Emerg Med. 2023; 14(2): 106-11. |
| 17 |
Walston JM, Cabrera D, Bellew SD, Olive MN, Lohse CM, Bellolio MF. Vital signs predict rapid-response team activation within twelve hours of emergency department admission. West J Emerg Med. 2016; 17(3): 324-30.
doi: 10.5811/westjem.2016.2.28501 pmid: 27330665 |
| 18 | Freedman MS, Forno E. Initial emergency department vital signs may predict PICU admission in pediatric patients presenting with asthma exacerbation. J Asthma. 2023; 60(5): 960-8. |
| 19 |
Henning DJ, Oedorf K, Day DE, Redfield CS, Huguenel CJ, Roberts JC, et al. Derivation and validation of predictive factors for clinical deterioration after admission in emergency department patients presenting with abnormal vital signs without shock. West J Emerg Med. 2015; 16(7): 1059-66.
doi: 10.5811/westjem.2015.9.27348 pmid: 26759655 |
| 20 | Quinten VM, van Meurs M, Olgers TJ, Vonk JM, Ligtenberg JJM, Ter Maaten JC. Repeated vital sign measurements in the emergency department predict patient deterioration within 72 hours: a prospective observational study. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018; 26(1): 57. |
| 21 | Jin K, Wang KP, Liu QY, Wang YG, Wang YL, Huan CJ, et al. The influence of calling emergency medical services (EMS) on severity of disease among patients admitted to emergency room: A propensity-matched study. Chin J Emerg Med. 2021; 30(12):9. |
| 22 |
Sun J, Liu Q, Seery S, Sun L, Yuan Y, Wang W, et al. The impact of hyperkalemia on ICU admission and mortality: a retrospective study of Chinese emergency department data. BMC Emerg Med 2024, 24(1):95.
doi: 10.1186/s12873-024-01011-z pmid: 38824546 |
| 23 | Prendin F, Pavan J, Cappon G, Del Favero S, Sparacino G, Facchinetti A. The importance of interpreting machine learning models for blood glucose prediction in diabetes: an analysis using SHAP. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):16865. |
| 24 | Yang MC, Liu CY, Wang XY, Li YW, Gao HX, Liu X, et al. An explainable artificial intelligence predictor for early detection of sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2020; 48(11): e1091-e1096. |
| 25 |
Lauritsen SM, Kristensen M, Olsen MV, Larsen MS, Lauritsen KM, Jørgensen MJ, et al. Explainable artificial intelligence model to predict acute critical illness from electronic health records. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1): 3852.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17431-x pmid: 32737308 |
| 26 |
Hinson JS, Martinez DA, Schmitz PSK, Toerper M, Radu D, Scheulen J, et al. Accuracy of emergency department triage using the Emergency Severity Index and independent predictors of under-triage and over-triage in Brazil: a retrospective cohort analysis. Int J Emerg Med. 2018; 11(1): 3.
doi: 10.1186/s12245-017-0161-8 pmid: 29335793 |
| 27 | Vijayarangam S, Vasundhara S, Beherac NR, Das S, Chandre S, Rajagopal R. Machine learning with Monarch butterfly optimization for prediction of emergency patient admission status. In: 2023 Fifth International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT). 2023:1-5. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10179819 |
| 28 | Lee JT, Hsieh CC, Lin CH, Lin YJ, Kao CY. Prediction of hospitalization using artificial intelligence for urgent patients in the emergency department. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:19472. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-98961-2#citeas |
| 29 |
Choi A, Choi SY, Chung K, Chung HS, Song T, Choi B, et al. Development of a machine learning-based clinical decision support system to predict clinical deterioration in patients visiting the emergency department. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1): 8561.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35617-3 pmid: 37237057 |
| 30 |
Gabayan GZ, Gould MK, Weiss RE, Derose SF, Chiu VY, Sarkisian CA. Emergency department vital signs and outcomes after discharge. Acad Emerg Med. 2017; 24(7): 846-54.
doi: 10.1111/acem.13194 pmid: 28375565 |
| 31 |
Candel BG, Duijzer R, Gaakeer MI, Ter Avest E, Sir Ö, Lameijer H, et al. The association between vital signs and clinical outcomes in emergency department patients of different age categories. Emerg Med J. 2022; 39(12): 903-11.
doi: 10.1136/emermed-2020-210628 pmid: 35017189 |
| 32 | Weiss GM. Foundations of imbalanced learning. He HB, Ma YQ, eds. In: Imbalanced learning. Foundations, algorithms, and application. New Jersey: Wiley, 2013. |
| 33 | Nachimuthu SK, Haug PJ. Early detection of sepsis in the emergency department using Dynamic Bayesian Networks. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2012; 2012:653-62. |
| 34 | Horng S, Sontag DA, Halpern Y, Jernite Y, Shapiro NI, Nathanson LA. Creating an automated trigger for sepsis clinical decision support at emergency department triage using machine learning. PLoS One. 2017; 12(4):e0174708. |
| 35 |
Calvert JS, Price DA, Chettipally UK, Barton CW, Feldman MD, Hoffman JL, et al. A computational approach to early sepsis detection. Comput Biol Med. 2016; 74:69-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.05.003 pmid: 27208704 |
| [1] | Ping Cui, Tingting Wen, Bingduo Wang, Shuijing Wu, Shiyu Chen, Xiangming Fang, TILP consortium. Tracheal intubation in the lateral position in emergency medicine: a narrative review and clinical protocol [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 103-112. |
| [2] | Jingyuan Xie, Jiandong Gao, Mutian Yang, Ting Zhang, Yecheng Liu, Yutong Chen, Zetong Liu, Qimin Mei, Zhimao Li, Huadong Zhu, Ji Wu. Prediction of sepsis within 24 hours at the triage stage in emergency departments using machine learning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(5): 379-385. |
| [3] | Mümin Murat Yazici, Özcan Yavaşi̇. Effect of a cervical collar on optic nerve sheath diameter in trauma patients [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(2): 126-130. |
| [4] | Catherine V. Levitt, Quincy K. Tran, Hashem Hraky, Maryann Mazer-Amirshahi, Ali Pourmand. Emergency department approach to monkeypox [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2023, 14(5): 341-348. |
| [5] | Xin Lu, Shi Feng, Shi-gong Guo, Mu-bing Qin, Xiang-ning Liu, Shi-yuan Yu, Li-na Zhao, Zeng-zheng Ge, Jing-jing Chai, Sheng-yong Xu, Di Shi, Ji-hai Liu, Hua-dong Zhu, Yi Li. Development of an intensive simulating training program in emergency medicine for medical students in China [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2022, 13(1): 23-26. |
| [6] | Janett Kreutziger, Philip Puchner, Stefan Schmid, Wolfgang Mayer, Harald Prossliner, Wolfgang Lederer. Accuracy of training blood volume quantification using a visual estimation tool [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(3): 174-178. |
| [7] | Samantha Shwe, Lauren Witchey, Shadi Lahham, Ethan Kunstadt, Inna Shniter, John C. Fox. Retrospective analysis of eFAST ultrasounds performed on trauma activations at an academic level-1 trauma center [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(1): 12-17. |
| [8] | Elaine Situ-LaCasse, Helpees Guirguis, Lucas Friedman, Asad E. Patanwala, Seth E. Cohen, Srikar Adhikari. Can emergency physicians perform extended compression ultrasound for the diagnosis of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(4): 205-209. |
| [9] | Ahmad Pouyamehr, Amir Mirhaghi, Mohammad Davood Sharifi, Ali Eshraghi. Comparison between Emergency Severity Index and Heart Failure Triage Scale in heart failure patients: A randomized clinical trial [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(4): 215-221. |
| [10] | Robert D. Willmore, Damjan Veljanoski, Feray Ozdes, Bethan Stephens, James Mooney, Seamus G. Crumley, Arpan Doshi, Philippa Davies, Shreya Badhrinarayanan, Emily Day, Kristian Tattam, April Wilson, Nathan Crang, Lorna Green, Craig A. Mounsey, Howell Fu, Joseph Williams, Michelle S. D'souza, Dhanya Sebastian, Liam A. Mcgiveron, Matthew G. Percy, James Cohen, Imogen J. John, Alice Lethbridge, Imogen Watkins, Omar Amin, Mubasher A. Qamar, John Gerrard Hanrahan, Emily Cramond-Wong. Do medical students studying in the United Kingdom have an adequate factual knowledge of basic life support? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(2): 75-80. |
| [11] | Amairah Fahad Aloushan, Faisal Abdullah Almoaiqel, Raid Naysh Alghamdi, Fatmah Ismail Alnahari, Abdulaziz Fahad Aldosari, Nazish Masud, Nawfal Abdullah Aljerian. Assessment of knowledge, attitude and practice regarding oxygen therapy at emergency departments in Riyadh in 2017: A cross-sectional study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(2): 88-93. |
| [12] | Rakesh Gupta, Isaac Siemens, Sam Campbell. The use of outcome feedback by emergency medicine physicians: Results of a physician survey [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(1): 14-18. |
| [13] | Shervin Farahmand, Masoume Vafaeian, Elnaz Vahidi, Atefeh Abdollahi, Shahram Bagheri-Hariri, Ahmad Reza Dehpour. Comparison of exogenous melatonin versus placebo on sleep efficiency in emergency medicine residents working night shifts: A randomized trial [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(4): 282-287. |
| [14] | Kimberly A. Chambers, Adam Y. Park, Rosa C. Banuelos, Bryan F. Darger, Bindu H. Akkanti, Annamaria Macaluso, Manoj Thangam, Pratik B. Doshi. Outcomes of severe sepsis and septic shock patients after stratification by initial lactate value [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(2): 113-117. |
| [15] | Elnaz Vahidi, Rezvan Hemati, Mehdi Momeni, Amirhossein Jahanshir, Morteza Saeedi. Comparison of sedative effectiveness of thiopental versus midazolam in reduction of shoulder dislocation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(2): 125-129. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
