World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (3): 248-255.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.063
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhongshu Kuang1, Runrong Li2, Su Lu1, Yusong Wang2, Yue Luo1, Yongqi Shen1, Li Yuan1, Yilin Yang1, Zhenju Song1,3,4( ), Ning Jiang2(
), Ning Jiang2( ), Chaoyang Tong1(
), Chaoyang Tong1( )
)
Received:2024-10-16
Accepted:2025-04-10
Online:2025-05-19
Published:2025-05-01
Contact:
Chaoyang Tong, Email: Zhongshu Kuang, Runrong Li, Su Lu, Yusong Wang, Yue Luo, Yongqi Shen, Li Yuan, Yilin Yang, Zhenju Song, Ning Jiang, Chaoyang Tong. Uncovering host response in adults with severe community-acquired pneumonia: a proteomics and metabolomics perspective study[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(3): 248-255.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.063
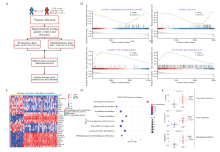
Figure 1.
Study design and omic differences analysis between healthy control and CAP groups. A: overview of the plasma proteomic and metabolomic workflow, including samples collection (healthy control/HC: n=19, non-severe CAP/NS-CAP: n=19, severe CAP/S-CAP: n=27); B: GSEA analysis showed up- and down-regulated pathways in CAP group compared with healthy control group. C: a heatmap listed proteins linked to the pathways shown in B; D: metabolomic pathway enrichment results. E: representative metabolite levels of enriched pathways in D. CAP: community-acquired pneumonia; GSEA: gene set enrichment analysis.
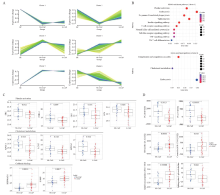
Figure 2.
Proteomic and metabolomic differences between non-severe and severe CAP. A: clustering illustrating six protein variation patterns across three groups. The purple line is the center line of the trend for each cluster. B: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis result of cluster 3 and cluster 6 in A. C: the relative abundance of proteins in platelet activation, cholesterol metabolism and cadherin binding pathway between NS-CAP and S-CAP groups. D: lipid-related metabolite levels between NS-CAP and S-CAP groups. PC: phosphatidylcholine; SM: sphingomyelin.
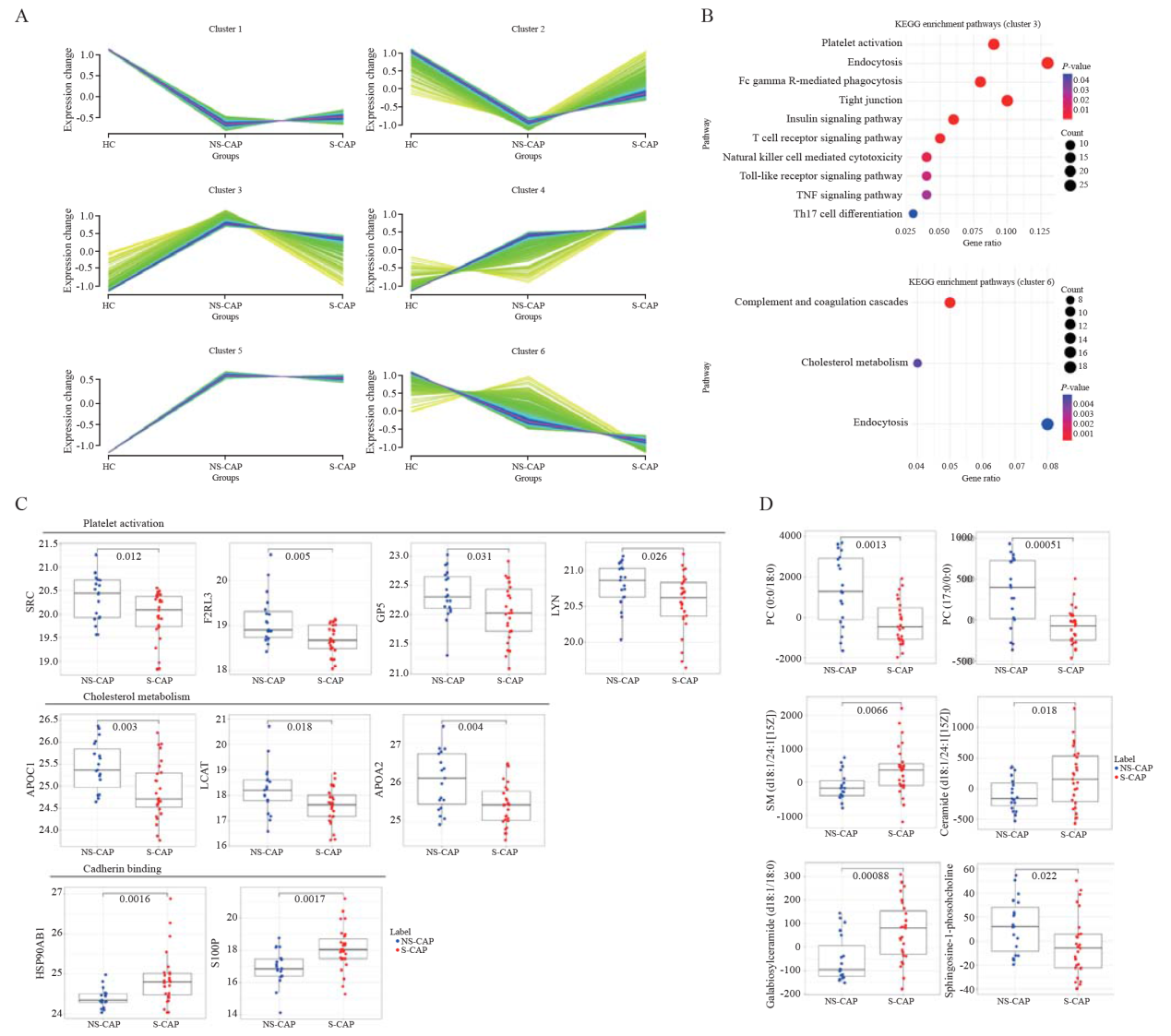

Figure 3.
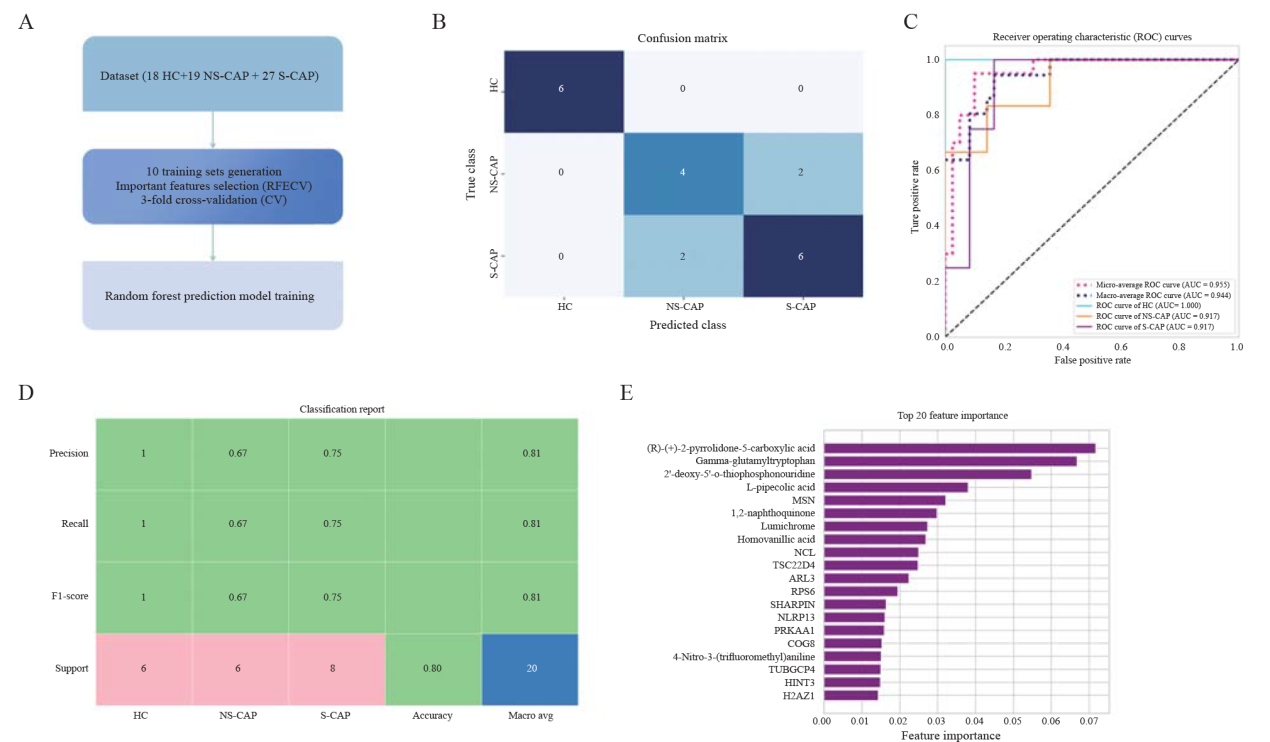
Identification of potential biomarkers and prediction model training for CAP classification. A: overview of the feature selection and model training workflow; B: confusion matrix of the random forest prediction model in the test set; C: receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the prediction model; AUC: area under the curve; D: classification report of the prediction model; E: top 20 proteins and metabolites with the highest feature importance obtained by the prediction model.
| 1 |
Aliberti S, Dela Cruz CS, Amati F, Sotgiu G, Restrepo MI. Community-acquired pneumonia. Lancet. 2021; 398(10303): 906-19.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00630-9 pmid: 34481570 |
| 2 | Jain S, Self WH, Wunderink RG, Fakhran S, Balk R, Bramley AM, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373(5): 415-27. |
| 3 |
Ramirez JA, Wiemken TL, Peyrani P, Arnold FW, Kelley R, Mattingly WA, et al. Adults hospitalized with pneumonia in the United States: incidence, epidemiology, and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2017; 65(11): 1806-12.
doi: 10.1093/cid/cix647 pmid: 29020164 |
| 4 |
Sun Y, Sun B, Ren Z, Xue M, Zhu C, Liu Q. Heparin-binding protein as a predictor of mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus and community-acquired pneumonia in intensive care unit : a propensity score matched study. World J Emerg Med. 2024; 15(4):263-72.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.033 pmid: 39050224 |
| 5 |
Laguna-Goya R, Utrero-Rico A, Talayero P, Lasa-Lazaro M, Ramirez-Fernandez A, Naranjo L, et al. IL-6-based mortality risk model for hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020; 146(4): 799-807.e9.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.009 pmid: 32710975 |
| 6 | Costanzo M, Caterino M, Fedele R, Cevenini A, Pontillo M, Barra L, et al. COVIDomics: the proteomic and metabolomic signatures of COVID-19. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(5): 2414. |
| 7 |
Cao B, Huang Y, She DY, Cheng QJ, Fan H, Tian XL, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in adults: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Chinese Thoracic Society, Chinese Medical Association. Clin Respir J. 2018; 12(4): 1320-60.
doi: 10.1111/crj.12674 pmid: 28756639 |
| 8 |
Yan C, Xue GH, Zhao HQ, Feng YL, Cui JH, Yuan J. Current status of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in China. World J Pediatr. 2024; 20(1):1-4.
doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00783-x pmid: 38185707 |
| 9 | Pang ZQ, Lu Y, Zhou GY, Hui F, Xu L, Viau C, et al. MetaboAnalyst 6.0: towards a unified platform for metabolomics data processing, analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024; 52(W1): W398-W406. |
| 10 |
Lopez-Ibañez J, Pazos F, Chagoyen M. MBROLE3: improved functional enrichment of chemical compounds for metabolomics data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023; 51(W1): W305-W309.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad405 pmid: 37178003 |
| 11 |
Kumar L, Futschik ME. Mfuzz: a software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation. 2007; 2(1): 5-7.
doi: 10.6026/97320630002005 pmid: 18084642 |
| 12 |
Fung HB, Monteagudo-Chu MO. Community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2010; 8(1): 47-62.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2010.01.003 pmid: 20226392 |
| 13 | Wang Y, Huang XL, Li F, Jia XB, Jia N, Fu J, et al. Serum-integrated omics reveal the host response landscape for severe pediatric community-acquired pneumonia. Crit Care. 2023; 27(1): 79. |
| 14 |
Lekkou A, Mouzaki A, Siagris D, Ravani I, Gogos CA. Serum lipid profile, cytokine production, and clinical outcome in patients with severe sepsis. J Crit Care. 2014; 29(5): 723-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.04.018 pmid: 24891152 |
| 15 | Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018; 19(3): 175-91. |
| 16 | Piotti A, Novelli D, Meessen JMTA, Ferlicca D, Coppolecchia S, Marino A, et al. Endothelial damage in septic shock patients as evidenced by circulating syndecan-1, sphingosine-1-phosphate and soluble VE-cadherin: a substudy of ALBIOS. Crit Care. 2021; 25(1): 113. |
| 17 | Lin MN, Xu FX, Sun J, Song JF, Shen Y, Lu S, et al. Integrative multiomics analysis unravels the host response landscape and reveals a serum protein panel for early prognosis prediction for ARDS. Crit Care. 2024; 28(1): 213. |
| 18 | Wang KM, Khoramjoo M, Srinivasan K, Gordon PMK, Mandal R, Jackson D, et al. Sequential multi-omics analysis identifies clinical phenotypes and predictive biomarkers for long COVID. Cell Rep Med. 2023; 4(11): 101254. |
| 19 |
Neugebauer S, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Pelekanou A, Marioli A, Baziaka F, Tsangaris I, et al. Metabolite profiles in sepsis: developing prognostic tools based on the type of infection. Crit Care Med. 2016; 44(9): 1649-62.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001740 pmid: 27097292 |
| 20 |
Arshad H, Alfonso JCL, Franke R, Michaelis K, Araujo L, Habib A, et al. Decreased plasma phospholipid concentrations and increased acid sphingomyelinase activity are accurate biomarkers for community-acquired pneumonia. J Transl Med. 2019; 17(1): 365.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2112-z pmid: 31711507 |
| 21 |
Prica F, Radon T, Cheng YZ, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T. The life and works of S100P - from conception to cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2016; 6(2): 562-76.
pmid: 27186425 |
| 22 |
Lu JY, Li Q, Wu ZM, Zhong ZM, Ji P, Li HY, et al. Two gene set variation indexes as potential diagnostic tool for sepsis. Am J Transl Res. 2020; 12(6): 2749-59.
pmid: 32655806 |
| 23 | Zhao YJ, Yuan JL, Xiao D, Zhang LW, Li C, Hu JF, et al. HSP90AB 1 is a host factor that promotes porcine deltacoronavirus replication. J Biol Chem. 2024; 300(1): 105536. |
| 24 | Zhang SJ, Huang WZ, Ren LL, Ju XH, Gong ML, Rao J, et al. Comparison of viral RNA-host protein interactomes across pathogenic RNA viruses informs rapid antiviral drug discovery for SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2022; 32(1): 9-23. |
| 25 | Song DL, Zhao YJ, Sun Y, Liang YX, Chen R, Wen YP, et al. HSP90AB 1 is a host factor required for transmissible gastroenteritis virus infection. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(21): 15971. |
| 26 |
Lagresle-Peyrou C, Luce S, Ouchani F, Soheili TS, Sadek H, Chouteau M, et al. X-linked primary immunodeficiency associated with hemizygous mutations in the moesin (MSN) gene. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 138(6): 1681-9.e8.
doi: S0091-6749(16)30423-7 pmid: 27405666 |
| 27 | Gerlach B, Cordier SM, Schmukle AC, Emmerich CH, Rieser E, Haas TL, et al. Linear ubiquitination prevents inflammation and regulates immune signalling. Nature. 2011; 471: 591-6. |
| 28 | Amin J, Boche D, Rakic S. What do we know about the inflammasome in humans? Brain Pathol. 2017; 27(2): 192-204. |
| 29 |
Armitage EG, Godzien J, Alonso-Herranz V, López-Gonzálvez Á, Barbas C. Missing value imputation strategies for metabolomics data. Electrophoresis. 2015; 36(24): 3050-60.
doi: 10.1002/elps.201500352 pmid: 26376450 |
| [1] | Weiming Wu, Min Li, Huilin Jiang, Min Sun, Yongcheng Zhu, Gongxu Zhu, Yanling Li, Yunmei Li, Junrong Mo, Xiaohui Chen, Haifeng Mao. Development of an emergency department length-of-stay prediction model based on machine learning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(3): 220-224. |
| [2] | Qingyuan Liu, Yixin Zhang, Jian Sun, Kaipeng Wang, Yueguo Wang, Yulan Wang, Cailing Ren, Yan Wang, Jiashan Zhu, Shusheng Zhou, Mengping Zhang, Yinglei Lai, Kui Jin. Early identification of high-risk patients admitted to emergency departments using vital signs and machine learning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2025, 16(2): 113-120. |
| [3] | Jingyuan Xie, Jiandong Gao, Mutian Yang, Ting Zhang, Yecheng Liu, Yutong Chen, Zetong Liu, Qimin Mei, Zhimao Li, Huadong Zhu, Ji Wu. Prediction of sepsis within 24 hours at the triage stage in emergency departments using machine learning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(5): 379-385. |
| [4] | Yuhan Sun, Baoqing Sun, Zhigang Ren, Mingshan Xue, Changju Zhu, Qi Liu. Heparin-binding protein as a predictor of mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus and community-acquired pneumonia in intensive care unit : a propensity score matched study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(4): 263-272. |
| [5] | Rebekah Shaw, Erica Popovsky, Alyssa Abo, Marni Jacobs, Nicole Herrera, James Chamberlain, Andrea Hahn. Improving antibiotic prescribing in the emergency department for uncomplicated community-acquired pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 199-205. |
| [6] | Hai-jiang Zhou, Tian-fei Lan, Shu-bin Guo. Outcome prediction value of National Early Warning Score in septic patients with community-acquired pneumonia in emergency department: A single-center retrospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 206-215. |
| [7] | Zhong-shu Kuang, Yi-lin Yang, Wei Wei, Jian-li Wang, Xiang-yu Long, Ke-yong Li, Chao-yang Tong, Zhan Sun, Zhen-ju Song. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of community-acquired pneumonia in autoimmune disease-induced immunocompromised host: A retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(3): 145-151. |
| [8] | Li-ping Chen, Jun-hui Chen, Ying Chen, Chao Wu, Xiao-hong Yang. Efficacy and safety of glucocorticoids in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(3): 172-178. |
| [9] | Jing Li, Huan Ye, Li Zhao. B-type natriuretic peptide in predicting the severity of community-acquired pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(2): 131-136. |
| [10] | Samuel George Campbell, R. Andrew McIvor, Vincent Joanis, David Graydon Urquhart. Can we predict which patients with community-acquired pneumonia are likely to have positive blood cultures? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(4): 272-278. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
