World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2015, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (3): 207-211.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2015.03.008
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Harun Gunes1( ), Hayati Kandis1, Ayhan Saritas1, Suber Dikici2, Ramazan Buyukkaya3
), Hayati Kandis1, Ayhan Saritas1, Suber Dikici2, Ramazan Buyukkaya3
Received:2014-12-18
Accepted:2015-04-06
Online:2015-09-15
Published:2015-09-15
Contact:
Harun Gunes
E-mail:haroonsun@hotmail.com
Harun Gunes, Hayati Kandis, Ayhan Saritas, Suber Dikici, Ramazan Buyukkaya. The relationship between ischemic stroke and weather conditions in Duzce, Turkey[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(3): 207-211.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2015.03.008
Table 1
Demographic characteristics, hospital stay, blood pressure, complete blood count, and biochemical parameters of the patients
| Variables | Mean±standard deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| All patients | 72±10 | 38 | 94 |
| Male patients | 70±10 | 47 | 87 |
| Female patients | 74±10 | 38 | 94 |
| Hospitalization period (days ) | 10±14 | 0 | 119 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 157±32 | 90 | 290 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 88±20 | 49 | 160 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | 111±22 | 63 | 190 |
| Pulse rate (beats/minute) | 87±21 | 50 | 170 |
| White blood cell count (/μL) | 9 133±3 971 | 1 160 | 26 900 |
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 12.9±1.7 | 7.2 | 19.0 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 38±5 | 25 | 55 |
| Platelet count (/μL) | 247 559±80 288 | 92 600 | 583 000 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 148±54 | 75 | 342 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 47±25 | 19 | 172 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.08±0.78 | 0.40 | 8.29 |
| Na+ (mEq/L) | 138±4 | 124 | 166 |
| K+ (mEq/L) | 4.2±0.6 | 2.6 | 7.0 |
| Cl- (mEq/L) | 103±5 | 87 | 138 |
Table 2
The relationship between daily weather conditions and daily cases
| Time of the event | Mean±standard deviation | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 patient | 1 patient | 2 patients | 3 patients | ||
| The event day | |||||
| Mean pressure (mbar) | 997.2±5.8 | 996.5±5.0 | 995.2±4.3 | 995.3±4.8 | NS* |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 15.2±7.4 | 15.7±7.7 | 14.8±7.0 | 15.1±3.0 | NS* |
| Mean relative humidity (%) | 76.7±13.2 | 75.7±14.9 | 80.4±11.0 | 73.1±11.2 | NS* |
| Maximum wind speed (m/s) | 6.2±2.5 | 6.0±2.2 | 5.6±2.2 | 7.0±3.3 | NS* |
| One day before the event | |||||
| Mean pressure (mbar) | 996.7±5.7 | 997.5±5.3 | 996.2±4.4 | 998.9±3.9 | NS* |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 15.4±7.2 | 15.4±8.2 | 15.3±6.6 | 14.5±2.5 | NS* |
| Mean relative humidity (%) | 76.7±13.2 | 76.1±14.6 | 77.8±12.7 | 71.7±14.4 | NS* |
| Maximum wind speed (m/s) | 6.3±2.5 | 6.0±2.2 | 5.6±2.2 | 4.6±1.4 | NS* |
| Two days before the event | |||||
| Mean pressure (mbar) | 996.8±5.5 | 996.9±5.6 | 995.6±5.4 | 1 000.6±6.3 | NS* |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 15.4±7.4 | 15.4±7.6 | 15.0±7.4 | 12.9±4.4 | NS* |
| Mean relative humidity (%) | 76.5±13.5 | 76.1±13.9 | 78.1±12.3 | 75.2±16.3 | NS* |
| Maximum wind speed (m/s) | 6.3±2.4 | 6.0±2.5 | 5.6±2.2 | 5.8±1.5 | NS* |
| Three days before the event | |||||
| Mean pressure (mbar) | 996.9±5.7 | 996.7±4.9 | 995.7±5.1 | 999.0±8.7 | NS* |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 15.6±7.3 | 15.3±7.5 | 13.8±8.3 | 13.1±4.4 | NS* |
| Mean relative humidity (%) | 75.9±13.1 | 76.7±15.0 | 85.0±9.7 | 74.3±10.8 | NS* |
| Maximum wind speed (m/s) | 6.4±2.5 | 6.0±2.2 | 4.7±1.9 | 5.0±1.2 | 0.048 |
Table 3
The relationship between daily cases and change of atmospheric pressure in consecutive days
| Time points | Mean±standard deviation | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 patient | 1 patient | 2 patients | 3 patients | ||
| 0-24 hours | |||||
| Pressure change (mbar) | 6.7±5.5 | 4.9±4.8 | 4.8±4.3 | 2.8±2.9 | 0.019 |
| Temperature change (°C) | 10.0±5.7 | 10.6±5.4 | 8.9±4.4 | 14.5±6.2 | NS* |
| Relative humidity change (%) | 45.2±18.1 | 43.8±18.0 | 45.8±18.0 | 59.4±20.6 | NS* |
| 24-48 hours | |||||
| Pressure change (mbar) | 6.3±5.3 | 6.2±6.0 | 4.8±3.1 | 5.5±4.3 | NS* |
| Temperature change (°C) | 10.1±5.5 | 10.4±5.9 | 10.3±4.8 | 15.0±6.4 | NS* |
| Relative humidity change (%) | 45.4±18.3 | 44.0±17.7 | 46.5±14.2 | 49.6±25.1 | NS* |
| 48-72 hours | |||||
| Pressure change (mbar) | 6.0±5.3 | 6.7±5.4 | 5.7±4.6 | 7.3±9.0 | NS* |
| Temperature change (°C) | 10.1±5.7 | 10.3±5.4 | 11.4±4.4 | 11.7±8.8 | NS* |
| Relative humidity change (%) | 45.9±17.8 | 44.4±18.7 | 37.4±16.1 | 53.0±17.0 | NS* |
| 72-96 hours | |||||
| Pressure change (mbar) | 5.9±5.3 | 7.2±5.7 | 4.8±4.5 | 6.1±4.4 | NS* |
| Temperature change (°C) | 10.5±5.6 | 9.6±5.8 | 9.7±4.0 | 11.9±6.3 | NS* |
| Relative humidity change (%) | 45.8±18.1 | 44.1±17.5 | 42.8±17.2 | 53.4±22.9 | NS* |
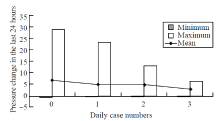
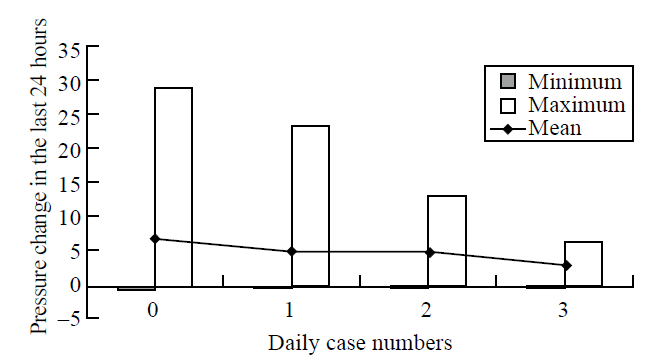
Figure 2.
Minimum, maximum and mean values of atmospheric pressure in the last 24 hours for days with no patients (0) and with 1, 2, and 3 patients. A significant difference was found between pressure change in days with no patients (0) and days with 1 patient (1) in post-hoc analysis with Sidak test (P=0.048). Actually, a more prominent difference was observed between change of atmospheric pressure in the last 24 hours in days with no patient (0) and in days with 3 patients, but this difference was not statistically significant because the number of days with 3 patients was small (only 5 days).
| 1 | Petrov D, Hidalgo A, Gandhi C, Prestigiacomo C. Decreases in temperature and relative humidity leading to an increased incidence of ischemic stroke. J NeuroIntervent Surg 2011; 3:A4. |
| 2 |
Berginer VM, Goldsmith J, Batz U, Vardi H, Shapiro Y. Clustering of strokes in association with meteorologic factors in the Negev Desert of Israel: 1981-1983. Stroke 1989; 20:65-69.
pmid: 2911837 |
| 3 | Keatinge WR, Coleshaw SRK, Cotter F, Mattock M, Murphy M, Chelliah R. Increases in platelet and red cell counts, blood viscosity, and arterial pressure during mild surface cooling: Factors in mortality from coronary and cerebral thrombosis in winter. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984; 24; 289:1405-1408. |
| 4 | Woodhouse PR, Khaw KT, Plummer M, Foley A, Meade TW. Seasonal variation of plasma fibrinogen and factor VII activity in the elderly: winter infections and death from cardiovascular disease. Lancet 1994; 343:435-439. |
| 5 | Schafer AI. The hypercoagulable states. Ann Intern Med 1985; 102:814-828. |
| 6 |
Houck PD, Lehten JE, Riggs MW, Gantt DS, Dehmer GJ. Relation of atmospheric pressure changes and the occurrences of acute myocardial infarction and stroke. Am J Cardiol 2005; 96:45-51.
pmid: 15979431 |
| 7 |
Cowperthwaite MC, Burnett MG. An analysis of admissions from 155 United States hospitals to determine the influence of weather on stroke incidence. J Clin Neurosci 2011; 18:618-623.
pmid: 21398128 |
| 8 | Chen ZY, Chang SF, Su CL. Weather and stroke in a subtropical area: Ilan, Taiwan. Stroke 1995; 26:569-572. |
| 9 | Field TS, Hill MD. Weather, Chinook, stroke occurrence. Stroke 2002; 33:1751-1757. |
| 10 |
Jimenez-Conde J, Ois A, Gomis M, Rodriguez-Campello A, Cuadrado-Godia E, Subirana I, et al. Weather as a trigger of stroke. Daily meteorological factors and incidence of stroke subtypes. Cerebrovasc Dis 2008; 26:348-354.
pmid: 18728361 |
| 11 |
Ohshige K, Hori Y, Tochikubo O, Sugiyama M. Influence of weather on emergency transport events coded as stroke: population-based study in Japan. Int J Biometeorol 2006; 50:305-311.
pmid: 16365749 |
| 12 | Feigin VL, Nikitin YP, Bots ML, Vinogradova TE, Grobbee DE. Population-based study of the associations of stroke occurrence with weather parameters in Siberia, Russia (1982-92). Eur J Neurol 2000; 7:171-178. |
| 13 |
Iwamoto T, Akazawa M, Ami M, Shimizu T, Umahara T, Takasaki M. Five elderly patients with cerebral infarction seen during a heat wave. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 1999; 36:565-571.
pmid: 10554565 |
| 14 |
Low RB, Bielory L, Qureshi AI, Dunn V, Stuhlmiller DFE, Dickey DA. The relation of stroke admissions to recent weather, airborne allergens, air pollution, seasons, upper respiratory infections, and asthma incidence, September 11, 2001, and day of the week. Stroke 2006; 37:951-957.
pmid: 16527994 |
| 15 |
Hong YC, Rha JH, Lee JT, Ha EH, Kwon HJ, Kim H. Ischemic stroke associated with decrease in temperature. Epidemiology 2003; 14:473-478.
pmid: 12843774 |
| 16 |
Shinkawa A, Ueda K, Hasuo Y, Kiyohara Y, Fujishima M. Seasonal variation in stroke incidence in Hisayama, Japan. Stroke 1990; 21:1262-1267.
pmid: 2396260 |
| 17 |
Rufca GF, Zaffani E, Zerbini R, Gaia FF, Oliveira Fde N, Tognolla WA. Influence of circadian and temperature variations on the ischemic stroke. Rev Assoc Med Bras 2009; 55:60-63.
pmid: 19360280 |
| 18 |
Gomes J, Damasceno A, Carrilho C, Lobo V, Lopes H, Madede T, et al. The effect of season and temperature variation on hospital admissions for incident stroke events in Maputo, Mozambique. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2014; 23:271-277.
pmid: 23523200 |
| 19 | Gomes J, Damasceno A, Carrilho C, Lobo V, Lopes H, Madede T, et al. Triggering of stroke by ambient temperature variation: A case-crossover study in maputo, mozambique. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2015; 129:72-77. |
| 20 |
Mostofsky E, Wilker EH, Schwartz J, Zanobetti A, Gold DR, Wellenius GA, et al. Short-Term Changes in Ambient Temperature and Risk of Ischemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra 2014; 4:9-18.
pmid: 24575110 |
| [1] | Jing-fen Jin, Zhi-ting Guo, Yu-ping Zhang, Yuan-yuan Chen. Prediction of motor recovery after ischemic stroke using diffusion tensor imaging: A meta-analysis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(2): 99-105. |
| [2] | Umut Canbek, Ahmet İmerci, Ulaş Akgün, Murat Yeşil, Ali Aydin, Yasemin Balci. Characteristics of injuries caused by paragliding accidents: A cross-sectional study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(3): 221-224. |
| [3] | Seyran Bozkurt, Engin Deniz Arslan, Ataman Köse, Cüneyt Ayrık, Arda Yılmaz, Güllü Akbaydoğan Dündar. Lingual angioedema after alteplase treatment in a patient with acute ischemic stroke [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 74-76. |
| [4] | Lin Li, Lin-hong Zhang, Wu-ping Xu, Jun-min Hu. Risk assessment of ischemic stroke associated pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(3): 209-213. |
| [5] | Gan-nan Wang, Jin-song Zhang, Wei-juan Cao, Hao Sun, Jing Zhang, Yao Wang, Hang Xiao. Association of ALOX5, LTA4H and LTC4S gene polymorphisms with ischemic stroke risk in a cohort of Chinese in east China [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(1): 32-37. |
| [6] | Yao Wang, Gan-nan Wang, Hao Sun, Chen Chen, Hang Xiao, Jin-song Zhang. Association of ALOX5AP with ischemic stroke in eastern Chinese [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(2): 108-113. |
| [7] | Misbahuddin Mohammad, Anish F. James, Raheel S. Qureshi, Sapan Saraf, Tina Ahluwalia, Joy Dev Mukherji, Tamorish Kole. Acute ischemic stroke in a child with cyanotic congenital heart disease due to non-compliance of anticoagulation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(2): 154-156. |
| [8] | Jing Zhang, Yao Wang, Gan-nan Wang, Hao Sun, Tao Sun, Jian-quan Shi, Hang Xiao, Jin-song Zhang. Clinical factors in patients with ischemic versus hemorrhagic stroke in East China [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(1): 18-23. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
