World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2021, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (1): 29-35.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.01.005
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Li-wei Duan1, Jin-long Qu1, Jian Wan2, Yong-hua Xu1, Yi Shan1, Li-xue Wu1, Jin-hao Zheng1, Wei-wei Jiang1, Qi-tong Chen1, Yan Zhu1, Jian Zhou1, Wen-bo Yu1, Lei Pei1, Xi Song2, Wen-fang Li1( ), Zhao-fen Lin1(
), Zhao-fen Lin1( )
)
Received:2020-01-15
Accepted:2020-07-20
Online:2021-01-01
Published:2021-01-01
Contact:
Wen-fang Li,Zhao-fen Lin
E-mail:chzhedlwf@163.com;linzhaofen@smmu.edu.cn
Li-wei Duan, Jin-long Qu, Jian Wan, Yong-hua Xu, Yi Shan, Li-xue Wu, Jin-hao Zheng, Wei-wei Jiang, Qi-tong Chen, Yan Zhu, Jian Zhou, Wen-bo Yu, Lei Pei, Xi Song, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Effects of viral infection and microbial diversity on patients with sepsis: A retrospective study based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(1): 29-35.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.01.005
Table 1
Demographic data and clinical characteristics of patients in this study
| Parameters | Virus-negative group (n=37) | Virus-positive group (n=37) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data | |||
| Gender (male/female) | 27/10 | 23/14 | 0.456 |
| Age (years) | 53.86±17.03 | 62.35±14.43 | 0.024 |
| Duration of ICU (days) | 24.62±28.05 | 39.11±28.18 | 0.030 |
| ICU scores at admission | |||
| APACHE II score | 16.51±6.93 | 22.22±5.75 | <0.001 |
| SOFA | 6.35±3.23 | 8.24±2.22 | 0.004 |
| Laboratory infection parameters | |||
| WBC (×109/L) | 14.69±6.85 | 12.54±7.18 | 0.191 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 85.97±6.82 | 82.75±17.67 | 0.304 |
| Leukomonocyte (%) | 8.14±4.20 | 7.93±5.57 | 0.857 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 174.08±83.50 | 199.46±153.52 | 0.380 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | 5.12±9.31 | 4.85±13.67 | 0.924 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 118.85±159.95 | 128.10±114.75 | 0.776 |
| Lactic acid (g/L) | 1.03±1.45 | 1.10±2.39 | 0.889 |
Table 2
Univariate Cox proportional hazards analysis for the 90-day mortality
| Parameters | β HR | 95% CI for HR | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.023 | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | 0.077 |
| Sex | -0.831 | 0.44 (0.21-0.89) | 0.023 |
| WBC | 0.054 | 1.10 (1.00-1.10) | 0.028 |
| Neutrophil | -0.002 | 1.00 (0.97-1.00) | 0.910 |
| Leukomonocyte | -0.052 | 0.95 (0.87-1.00) | 0.230 |
| Platelet | -0.001 | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | 0.380 |
| Procalcitonin | -0.001 | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | 0.220 |
| C-reactive protein | 0.033 | 1.00 (1.00-1.10) | 0.033 |
| Lactic acid | 0.211 | 1.20 (1.00-1.50) | 0.023 |
| APACHE II score | 0.162 | 1.20 (1.10-1.20) | <0.001 |
| SOFA | 0.203 | 1.20 (1.10-1.40) | <0.001 |
| Concomitant viral infection | 0.981 | 2.70 (1.20-5.80) | 0.014 |
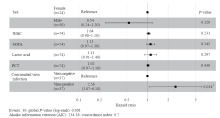
Figure 1.
Forest plots of multivariable Cox model adjusted hazard ratios with 95% confidence interval for the 90-day mortality. The multivariable Cox model was adjusted for sex, WBC count, SOFA, lactic acid, PCT, and concomitant virus infection at admission. WBC: white blood cell; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; PCT: procalcitonin.
| 1 |
Yin WP, Li JB, Zheng XF, An L, Shao H, Li CS. Effect of neutrophil CD64 for diagnosing sepsis in emergency department. World J Emerg Med. 2020; 11(2):79-86.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2020.02.003 pmid: 32076472 |
| 2 |
Ferrer R, Martin-Loeches I, Phillips G, Osborn TM, Townsend S, Dellinger RP, et al. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42(8):1749-55.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000330 pmid: 24717459 |
| 3 |
Bloos F, Ruddel H, Thomas-Ruddel D, Schwarzkopf D, Pausch C, Harbarth S, et al. Effect of a multifaceted educational intervention for anti-infectious measures on sepsis mortality: a cluster randomized trial. Intensive Care Med. 2017; 43(11):1602-12.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4782-4 pmid: 28466151 |
| 4 |
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017; 43(3):304-77.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6 pmid: 28101605 |
| 5 |
Mancini N, Carletti S, Ghidoli N, Cichero P, Burioni R, Clementi M. The era of molecular and other non-culture-based methods in diagnosis of sepsis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010; 23(1):235-51.
doi: 10.1128/CMR.00043-09 pmid: 20065332 |
| 6 |
Paul M, Shani V, Muchtar E, Kariv G, Robenshtok E, Leibovici L. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of appropriate empiric antibiotic therapy for sepsis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54(11):4851-63.
pmid: 20733044 |
| 7 |
Kumar A. An alternate pathophysiologic paradigm of sepsis and septic shock: implications for optimizing antimicrobial therapy. Virulence. 2014; 5(1):80-97.
doi: 10.4161/viru.26913 pmid: 24184742 |
| 8 |
Kaleta EJ, Clark AE, Johnson DR, Gamage DC, Wysocki VH, Cherkaoui A, et al. Use of PCR coupled with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for rapid identification of bacterial and yeast bloodstream pathogens from blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49(1):345-53.
pmid: 21048006 |
| 9 |
Wilson MR, Naccache SN, Samayoa E, Biagtan M, Bashir H, Yu G, et al. Actionable diagnosis of neuroleptospirosis by next-generation sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370(25):2408-17.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1401268 pmid: 24896819 |
| 10 |
Traen S, Bochanen N, Ieven M, Schepens T, Bruynseels P, Verbrugghe W, et al. Is acyclovir effective among critically ill patients with herpes simplex in the respiratory tract? J Clin Virol. 2014; 60(3):215-21.
pmid: 24800905 |
| 11 |
Schuierer L, Gebhard M, Ruf HG, Jaschinski U, Berghaus TM, Wittmann M, et al. Impact of acyclovir use on survival of patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia and high load herpes simplex virus replication. Crit Care. 2020; 24(1):12.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2701-5 pmid: 31924246 |
| 12 | Brenner T, Decker SO, Grumaz S, Stevens P, Bruckner T, Schmoch T, et al. Next-generation sequencing diagnostics of bacteremia in sepsis (Next GeneSiS-Trial): study protocol of a prospective, observational, noninterventional, multicenter, clinical trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(6):e9868. |
| 13 |
Grumaz S, Grumaz C, Vainshtein Y, Stevens P, Glanz K, Decker SO, et al. Enhanced performance of next-generation sequencing diagnostics compared with standard of care microbiological diagnostics in patients suffering from septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2019; 47(5):e394-402.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003658 pmid: 30720537 |
| 14 |
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009; 25(14):1754-60.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 pmid: 19451168 |
| 15 |
Langelier C, Zinter MS, Kalantar K, Yanik GA, Christenson S, O’Donovan B, et al. Metagenomic sequencing detects respiratory pathogens in hematopoietic cellular transplant patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197(4):524-8.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201706-1097LE pmid: 28686513 |
| 16 |
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990; 215(3):403-10.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 pmid: 2231712 |
| 17 |
Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Suzuki S, Pilcher D, Bellomo R. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000-2012. JAMA. 2014; 311(13):1308-16.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.2637 pmid: 24638143 |
| 18 |
Whitley RJ, Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus infections. Lancet. 2001; 357(9267):1513-8.
pmid: 11377626 |
| 19 |
Luyt CE, Combes A, Deback C, Aubriot-Lorton MH, Nieszkowska A, Trouillet JL, et al. Herpes simplex virus lung infection in patients undergoing prolonged mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175(9):935-42.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.200609-1322OC pmid: 17234903 |
| 20 |
Engelmann I, Gottlieb J, Meier A, Sohr D, Ruhparwar A, Henke-Gendo C, et al. Clinical relevance of and risk factors for HSV-related tracheobronchitis or pneumonia: results of an outbreak investigation. Crit Care. 2007; 11(6):R119.
doi: 10.1186/cc6175 pmid: 17996032 |
| 21 |
de Vos N, van Hoovels L, Vankeerberghen A, van Vaerenbergh K, Boel A, Demeyer I, et al. Monitoring of herpes simplex virus in the lower respiratory tract of critically ill patients using real-time PCR: a prospective study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009; 15(4):358-63.
pmid: 19260875 |
| 22 |
Ong DSY, Bonten MJM, Spitoni C, Verduyn Lunel FM, Frencken JF, Horn J, et al. Epidemiology of multiple herpes viremia in previously immunocompetent patients with septic shock. Clin Infect Dis. 2017; 64(9):1204-10.
doi: 10.1093/cid/cix120 pmid: 28158551 |
| 23 |
Grumaz S, Stevens P, Grumaz C, Decker SO, Weigand MA, Hofer S, et al. Next-generation sequencing diagnostics of bacteremia in septic patients. Genome Med. 2016; 8(1):73.
pmid: 27368373 |
| 24 |
Long Y, Zhang Y, Gong Y, Sun R, Su L, Lin X, et al. Diagnosis of sepsis with cell-free DNA by next-generation sequencing technology in ICU patients. Arch Med Res. 2016; 47(5):365-71.
pmid: 27751370 |
| 25 |
Carpenter ML, Tan SK, Watson T, Bacher R, Nagesh V, Watts A, et al. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for identification and quantitation of transplant-related DNA viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2019; 57(12):e01113-19.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.01113-19 pmid: 31554674 |
| 26 |
Blauwkamp TA, Thair S, Rosen MJ, Blair L, Lindner MS, Vilfan ID, et al. Analytical and clinical validation of a microbial cell-free DNA sequencing test for infectious disease. Nat Microbiol. 2019; 4(4):663-74.
doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0349-6 pmid: 30742071 |
| [1] | Hai-jiang Zhou, Tian-fei Lan, Shu-bin Guo. Outcome prediction value of National Early Warning Score in septic patients with community-acquired pneumonia in emergency department: A single-center retrospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 206-215. |
| [2] | Yu-ming Wang, Yan-jun Zheng, Ying Chen, Yun-chuan Huang, Wei-wei Chen, Ran Ji, Li-li Xu, Zhi-tao Yang, Hui-qiu Sheng, Hong-ping Qu, En-qiang Mao, Er-zhen Chen. Effects of fluid balance on prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients secondary to sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 216-222. |
| [3] | Miao Yuan, Ding-yi Yan, Fang-shi Xu, Yi-di Zhao, Yang Zhou, Long-fei Pan. Effects of sepsis on hippocampal volume and memory function [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 223-230. |
| [4] | Wen-peng Yin, Jia-bao Li, Xiao-fang Zheng, Le An, Huan Shao, Chun-sheng Li. Effect of neutrophil CD64 for diagnosing sepsis in emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 79-86. |
| [5] | Shao-hua Liu, Huo-yan Liang, Hong-yi Li, Xian-fei Ding, Tong-wen Sun, Jing Wang. Effect of low high-density lipoprotein levels on mortality of septic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 109-116. |
| [6] | Yi-wen Fan, Shao-wei Jiang, Jia-meng Chen, Hui-qi Wang, Dan Liu, Shu-ming Pan, Cheng-jin Gao. A pulmonary source of infection in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury leads to a worse outcome and poor recovery of kidney function [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(1): 18-26. |
| [7] | Kimberly A. Chambers, Adam Y. Park, Rosa C. Banuelos, Bryan F. Darger, Bindu H. Akkanti, Annamaria Macaluso, Manoj Thangam, Pratik B. Doshi. Outcomes of severe sepsis and septic shock patients after stratification by initial lactate value [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(2): 113-117. |
| [8] | Muhammad Akbar Baig, Hira Shahzad, Erfan Hussain, Asad Mian. Validating a point of care lactate meter in adult patients with sepsis presenting to the emergency department of a tertiary care hospital of a low- to middle-income country [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(3): 184-189. |
| [9] | Chao Cao, Tao Ma, Yan-fen Chai, Song-tao Shou. The role of regulatory T cells in immune dysfunction during sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 5-9. |
| [10] | Kun Chen, Qiu-xiang Zhou, Hong-wei Shan, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Prognostic value of CD4+CD25+ Tregs as a valuable biomarker for patients with sepsis in ICU [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 40-43. |
| [11] | Hui Fu, Qiao-sheng Wang, Qiong Luo, Si Tan, Hua Su, Shi-lin Tang, Zheng-liang Zhao, Li-ping Huang. Simvastatin inhibits apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by sepsis through upregulating the expression of Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(4): 291-297. |
| [12] | Qi Zou, Wei Wen, Xin-chao Zhang. Presepsin as a novel sepsis biomarker [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(1): 16-19. |
| [13] | Nishant Raj Pandey, Yu-yao Bian, Song-tao Shou. Significance of blood pressure variability in patients with sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(1): 42-47. |
| [14] | Huan Ding, Xiang-yuan Cao, Xi-gang Ma, Wen-jie Zhou. Endothelial cell injury with inflammatory cytokine and coagulation in patients with sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(4): 285-289. |
| [15] | Yan-jun Qin, Xin-liang Zhang, Yue-qing Yu, Xiao-hua Bian, Shi-min Dong. Cardioprotective effect of erythropoietin on sepsis-induced myocardial injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(3): 215-223. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
