World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2014, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 182-186.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.03.004
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Li-ming Li1, Wen-bo Cai1, Qin Ye1, Jian-min Liu1, Xin Li2, Xiao-xing Liao2( )
)
Received:2014-03-03
Accepted:2014-06-19
Online:2014-09-15
Published:2014-09-15
Contact:
Xiao-xing Liao
E-mail:liaowens@163.com
Li-ming Li, Wen-bo Cai, Qin Ye, Jian-min Liu, Xin Li, Xiao-xing Liao. Comparison of plasma microRNA-1 and cardiac troponin T in early diagnosis of patients with acute myocardial infarction[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(3): 182-186.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.03.004
Table 1
Clinical characteristics of the study population
| Variables | Control (n=28) | AMI (n=56) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60.50±9.10 | 63.95±11.34 | 0.166 |
| Male/Female (n/n) | 20/8 | 44/12 | 0.468 |
| Currently smoking (n, %) | 12 (42.86) | 27 (48.21) | 0.643 |
| Diabetes mellitus (n, %) | 3 (10.71) | 10 (17.86) | 0.594 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 13 (46.43) | 33 (58.93) | 0.278 |
| Hyperlipidemia (n, %) | 12 (42.86) | 30 (53.57) | 0.355 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 124.54±10.08 | 130.57±15.34 | 0.063 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 79.25±7.02 | 81.52±9.42 | 0.264 |
| Cardiac troponin T (ng/mL) | 0.03±0.02 | 1.35±1.10 | <0.01 |
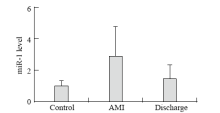
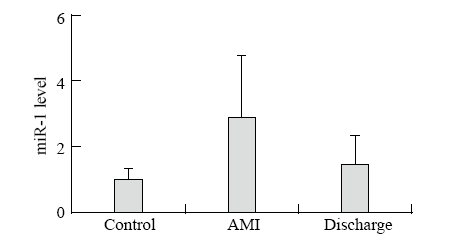
Figure 2.
Alteration of plasma miR-1 levels in the AMI patients. MiR-1 was markedly increased in plasma samples gathered within 12 hours after the onset of AMI (day 1). At hospital discharge (day 14), miR-1 had returned to baseline levels similar to those in the controls (n=28 controls, n=56 AMI patients at day 1, n=12 AMI patients at day 14). The values represent the fold changes of miR-1 in the AMI patients relative to the controls. The results are presented as the means ± standard deviation. *P<0.01 vs. the controls.
| 1 |
White HD, Chew DP. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 2008; 372:570-584.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61237-4 pmid: 18707987 |
| 2 |
Jaffe AS, Ravkilde J, Roberts R, Naslund U, Apple FS, Galvani M, et al. It's time for a change to a troponin standard. Circulation 2000; 102:1216-1220.
doi: 10.1161/01.cir.102.11.1216 pmid: 10982533 |
| 3 |
Collinson PO, Hadcocks L, Foo Y, Rosalki SB, Stubbs PJ, Morgan SH, et al. Cardiac troponins in patients with renal dysfunction. Ann Clin Biochem 1998; 35:380-386.
pmid: 9635103 |
| 4 |
Khan NA, Hemmelgarn BR, Tonelli M, Thompson CR, Levin A. Prognostic value of troponin T and I among asymptomatic patients with end-stage renal disease: a meta-analysis. Circulation 2005; 112:3088-3096.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.560128 pmid: 16286604 |
| 5 |
Pheasant M, Mattick JS. Raising the estimate of functional human sequences. Genome Res 2007; 17:1245-1253.
doi: 10.1101/gr.6406307 pmid: 17690206 |
| 6 |
Soifer HS, Rossi JJ, Saetrom P. MicroRNAs in disease and potential therapeutic applications. Mol Ther 2007; 15:2070-2079.
pmid: 17878899 |
| 7 |
van Rooij E, Liu N, Olson EN. MicroRNAs flex their muscles. Trends Genet 2008; 24:159-166.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.01.007 pmid: 18325627 |
| 8 |
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol 2002; 12:735-739.
doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00809-6 pmid: 12007417 |
| 9 |
Kloosterman WP, Plasterk RH. The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev Cell 2006; 11:441-450.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.09.009 pmid: 17011485 |
| 10 |
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008; 105:10513-10518.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804549105 pmid: 18663219 |
| 11 |
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10:1470-1476.
doi: 10.1038/ncb1800 pmid: 19011622 |
| 12 |
Zhou H, He XY, Zhuang SW, Wang J, Lai Y, Qi WG, et al. Clinical and procedural predictors of no-reflow in patients with acute myocardial infarction after primary percutaneous coronary intervention. World J Emerg Med 2014; 5:96-102.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.02.003 pmid: 25215156 |
| 13 |
Ai J, Zhang R, Li Y, Pu J, Lu Y, Jiao J, et al. Circulating microRNA-1 as a potential novel biomarker for acute myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 391:73-77.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.11.005 pmid: 19896465 |
| 14 |
Bostjancic E, Zidar N, Stajer D, Glavac D. MicroRNAs miR-1, miR-133a, miR-133b and miR-208 are dysregulated in human myocardial infarction. Cardiology 2010; 115:163-169.
doi: 10.1159/000268088 pmid: 20029200 |
| 15 |
Ji X, Takahashi R, Hiura Y, Hirokawa G, Fukushima Y, Iwai N. Plasma miR-208 as a biomarker of myocardial injury. Clin Chem 2009; 55:1944-1949.
doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.125310 pmid: 19696117 |
| 16 |
Liu M, Wang HR, Liu JF, Li HJ, Chen SX, Shen S, et al. Therapeutic effect of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on acute cerebral infarction at different times. World J Emerg Med 2013; 4:205-209.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2013.03.009 pmid: 25215120 |
| 17 |
Tijsen AJ, Creemers EE, Moerland PD, de Windt LJ, van der Wal AC, Kok WE, et al. MiR423-5p as a circulating biomarker for heart failure. Circ Res 2010; 106:1035-1039.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.218297 pmid: 20185794 |
| 18 |
Corsten MF, Dennert R, Jochems S, Kuznetsova T, Devaux Y, Hofstra L, et al. Circulating MicroRNA-208b and MicroRNA-499 reflect myocardial damage in cardiovascular disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2010; 3:499-506.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.957415 pmid: 20921333 |
| 19 |
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, Joint ESCAAHAWHFTF-ftRoMI. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 2007; 28:2525-2538.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm355 pmid: 17951287 |
| 20 |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001; 25:402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| 21 |
Myocardial infarction redefined—a consensus document of The Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 2000; 21:1502-1513.
doi: 10.1053/euhj.2000.2305 pmid: 10973764 |
| 22 |
Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, Bassand JP. Myocardial infarction redefined—a consensus document of The Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000; 36:959-969.
doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00804-4 pmid: 10987628 |
| [1] | Yi Han, Su-cheng Mu, Jian-li Wang, Wei Wei, Ming Zhu, Shi-lin Du, Min Min, Yun-jie Xu, Zhen-ju Song, Chao-yang Tong. MicroRNA-145 plays a role in mitochondrial dysfunction in alveolar epithelial cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(1): 54-60. |
| [2] | Wen-peng Yin, Jia-bao Li, Xiao-fang Zheng, Le An, Huan Shao, Chun-sheng Li. Effect of neutrophil CD64 for diagnosing sepsis in emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 79-86. |
| [3] | Wan-qin Xie, Lin Zhou, Yong Chen, Bin Ni. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of congenital heart defects [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2016, 7(2): 85-89. |
| [4] | Jing Li, Huan Ye, Li Zhao. B-type natriuretic peptide in predicting the severity of community-acquired pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(2): 131-136. |
| [5] | Kun Chen, Qiu-xiang Zhou, Hong-wei Shan, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Prognostic value of CD4+CD25+ Tregs as a valuable biomarker for patients with sepsis in ICU [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 40-43. |
| [6] | Hua Zhou, Xiao-yan He, Shao-wei Zhuang, Juan Wang, Yan Lai, Wei-gang Qi, Yi-an Yao, Xue-bo Liu. Clinical and procedural predictors of no-reflow in patients with acute myocardial infarction after primary percutaneous coronary intervention [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 96-102. |
| [7] | Li-li Ji, Xiao-feng Long, Hui Tian, Yu-fei Liu. Effect of transplantation of bone marrow stem cells on myocardial infarction size in a rabbit model [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(4): 304-310. |
| [8] | Yan Chen, Wei Yang, Gan-nan Wang, Jun Li, Xiao-rong Li, Jian Zhang, Wei Yuan, Dao-wu Wang, Jin-song Zhang, Ke-jiang Cao. Circulating microRNAs, novel biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction: a systemic review [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(4): 257-260. |
| [9] | Xiao-dong Liu, Chun-lei Sun, Su-ping Mu, Xiao-mei Qiu, Hai-ying Yu. Acute myocardial infarction in a child with myocardial bridge [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(1): 70-72. |
| [10] | Yu Chen, Zhi-jian Chen, Yu-hua Liao, Zhe Cao, Jia-ding Xia, Hua Yang, Yi-mei Du. Effect of tumor necrosis factor-α on ventricular arrhythmias in rats with acute myocardial infarction in vivo [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2010, 1(1): 53-58. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
