World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2014, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (2): 128-134.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.02.009
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Guo-ming Zhang1,2, Yu Wang2( ), Tian-de Li3, Xiao-yan Li1, Shao-ping Su4, Yuan-yuan Sun5, Xiu-hua Liu6
), Tian-de Li3, Xiao-yan Li1, Shao-ping Su4, Yuan-yuan Sun5, Xiu-hua Liu6
Received:2013-09-20
Accepted:2014-03-16
Online:2014-06-15
Published:2014-06-15
Contact:
Yu Wang
E-mail:guomingpaper@126.com
Guo-ming Zhang, Yu Wang, Tian-de Li, Xiao-yan Li, Shao-ping Su, Yuan-yuan Sun, Xiu-hua Liu. Post-conditioning with gradually increased reperfusion provides better cardioprotection in rats[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 128-134.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.02.009
Table 1
Hemodynamic data obtained 24 hours after reperfusion (mean±SD, n=12).
| Groups | HR (beats/min) | MAP (mmHg) | RPP (1000*mmHg*beats/min) | +dp/dt (mmHg/sec) | -dp/dt (mmHg/sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | 418.00±65.93 | 119.33±11.21 | 49.35±0.74*Δ | 1019.09±318.65*Δ | 752.31±231.05*Δ |
| I/R | 396.17±62.21 | 105.95±31.68 | 41.97±1.98#Δ | 526.37±123.99#Δ | 445.44±79.58#Δ |
| GDR | 423.21±50.00 | 108.00±14.32 | 45.70±0.72* | 721.45±89.97* | 546.23±100.12* |
| ER | 427.21±36.03 | 109.57±10.36 | 46.81±0.37* | 855.42±150.54* | 645.90±132.24* |
| GIR | 396.57±61.23 | 123.00±15.42 | 48.78±0.94*#Δ | 913.24±63.25*Δ | 721.45±110.23*Δ |
Figure 2.
Detection of apoptotic cells using TUNEL staining (A), with TUNEL-positive cells dyed green. Apoptotic indexes (B) were lower in the GIR group than those in the R/I, GDR and ER groups. Compared with the R/I group, *P<0.05; compared with the ER group, #P<0.05; compared with the GDR group, ΔP<0.05.
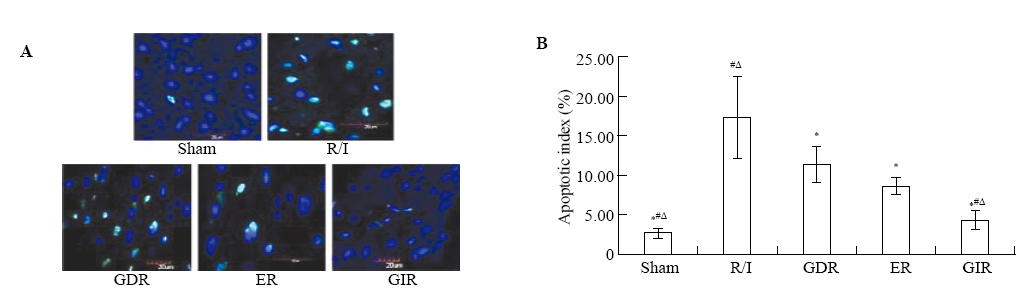

Figure 3.
Expression of phosphorylated ERK, p38 and JNK MAPK in all groups. The GIR group had a higher expression of P-ERK and a lower level of P-p38/JNK compared with the R/I, GDR and ER groups. Compared with the R/I group, *P<0.05; compared with the ER group, #P<0.05; compared with the GDR group, ΔP<0.05.

| 1 |
Braunwald E, Kloner RA. Myocardial reperfusion: a double-edged sword? J Clin Invest 1985; 76:1713-1719.
doi: 10.1172/JCI112160 pmid: 4056048 |
| 2 | Zhao ZQ1, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, Kerendi F, Wang NP, Guyton RA, et al. Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2003; 285:H579-588. |
| 3 |
Sanada S, Komuro I, Kitakaze M. Pathophysiology of myocardial reperfusion injury: preconditioning, post-conditioning, and translational aspects of protective measures. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2011; 301:H1723-1741.
doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00553.2011 pmid: 21856909 |
| 4 |
Liu X, Chen H, Zhan B, Xing B, Zhou J, Zhu H, et al. Attenuation of reperfusion injury by renal ischemic post-conditioning: the role of NO. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 359:628-634.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.129 pmid: 17548062 |
| 5 | Zhang WH, Lu FH, Zhao YJ, Wang LN, Tian Y, Pan ZW, et al. Postconditioning protects rat cardiomyocytes via PKCepsilon-mediated calcium-sensing receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 361:659-664. |
| 6 |
Thuny F, Lairez O, Roubille F, Mewton N, Rioufol G, Sportouch C, et al. Postconditioning reduces infarct size and edema in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 59:2175-2181.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.03.026 pmid: 22676937 |
| 7 |
Penna C, Mancardi D, Raimondo S, Geuna S, Pagliaro P. The paradigm of postconditioning to protect the heart. J Cell Mol Med 2008; 12:435-458.
doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00210.x pmid: 18182064 |
| 8 |
Skyschally A, van Caster P, Iliodromitis EK, Schulz R, Kremastinos DT, Heusch G. Ischemic postconditioning: experimental models and protocol algorithms. Basic Res Cardiol 2009; 104:469-483.
doi: 10.1007/s00395-009-0040-4 |
| 9 |
Iliodromitis EK, Downey JM, Heusch G, Kremastinos DT. What is the optimal postconditioning algorithm? J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 2009; 14:269-273.
doi: 10.1177/1074248409344328 pmid: 19741111 |
| 10 |
Cai M, Li Y, Xu Y, Swartz HM, Chen CL, Chen YR, et al. Endothelial NOS activity and myocardial oxygen metabolism define the salvageable ischemic time window for ischemic postconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2011; 300:H1069-1077.
pmid: 21217066 |
| 11 |
Kin H, Zhao ZQ, Sun HY, Wang NP, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, et al. Postconditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting events in the early minutes of reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res 2004; 62:74-85.
doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.01.006 pmid: 15023554 |
| 12 | Yang XM, Proctor JB, Cui L, Krieg T, Downey JM, Cohen MV. Multiple, brief coronary occlusions during early reperfusion protect rabbit hearts by targeting cell signaling pathways. Cardiovasc Res 2004; 44:1103-1110. |
| 13 |
Vinten-Johansen J, Zhao ZQ, Zatta AJ, Kin H, Halkos ME, Kerendi F. Postconditioning--A new link in nature's armor against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 2005; 100:295-310.
doi: 10.1007/s00395-005-0523-x |
| 14 |
Argaud L, Gateau-Roesch O, Raisky O, Loufouat J, Robert D, Ovize M. Postconditioning inhibits mitochondrial permeability transition. Circulation 2005; 111:194-197.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000151290.04952.3B pmid: 15642769 |
| 15 |
Kin H, Zatta AJ, Lofye MT, Amerson BS, Halkos ME, Kerendi F, et al. Postconditioning reduces infarct size via adenosine receptor activation by endogenous adenosine. Cardiovasc Res 2005; 67:124-133.
pmid: 15949476 |
| 16 |
Penna C, Cappello S, Mancardi D, Raimondo S, Rastaldo R, Gattullo D, et al. Post-conditioning reduces infarct size in the isolated rat heart: role of coronary flow and pressure and the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway. Basic Res Cardiol 2006; 101:168-179.
doi: 10.1007/s00395-005-0543-6 pmid: 16132172 |
| 17 |
Wang JY, Shen J, Gao Q, Ye ZG, Yang SY, Liang HW, et al. Ischemic postconditioning protects against global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Stroke 2008; 39:983-990.
pmid: 18239163 |
| 18 |
Li Y, Ge X, Liu X. The cardioprotective effect of post-conditioning is mediated by ARC through inhibiting mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Apoptosis 2009; 14:164-172.
doi: 10.1007/s10495-008-0296-4 pmid: 19130235 |
| 19 |
Sumi S, Kobayashi H, Yasuda S, Iwasa M, Yamaki T, Yamada Y, et al. Postconditioning effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is mediated through activation of risk pathway and opening of the mitochondrial KATP channels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2010; 299:H1174-1182.
doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00116.2010 pmid: 20693399 |
| 20 |
Sun HY, Wang NP, Halkos M, Kerendi F, Kin H, Guyton RA, et al. Postconditioning attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis via inhibition of JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Apoptosis 2006; 11:1583-1593.
pmid: 16820962 |
| 21 |
Hausenloy DJ, Ong SB, Yellon DM. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore as a target for preconditioning and postconditioning. Basic Res Cardiol 2009; 104:189-202.
doi: 10.1007/s00395-009-0010-x pmid: 19242644 |
| 22 |
Paillard M, Gomez L, Augeul L, Loufouat J, Lesnefsky EJ, Ovize M. Postconditioning inhibits mPTP opening independent of oxidative phosphorylation and membrane potential. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2009; 46:902-909.
doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.02.017 pmid: 19254723 |
| 23 |
Weiss JN, Korge P, Honda HM, Ping P. Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in myocardial disease. Circ Res 2003; 93:292-301.
pmid: 12933700 |
| 24 |
Park SS, Zhao H, Mueller RA, Xu Z. Bradykinin prevents reperfusion injury by targeting mitochondrial permeability transition pore through glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2006; 40:708-716.
doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.01.024 pmid: 16516918 |
| 25 |
Sato H, Jordan JE, Zhao ZQ, Sarvotham SS, Vinten-Johansen J. Gradual reperfusion reduces infarct size and endothelial injury but augments neutrophil accumulation. Ann Thorac Surg 1997; 64:1099-1107.
pmid: 9354535 |
| 26 |
Zhou SH, Sun YF, Wang G. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on intestinal mucosa apoptosis caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. World J Emerg Med 2012; 3:135-140.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2012.02.010 pmid: 25215052 |
| 27 |
Shi E, Jiang X, Kazui T, Washiyama N, Yamashita K, Terada H, et al. Controlled low-pressure perfusion at the beginning of reperfusion attenuates neurologic injury after spinal cord ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007; 133:942-948.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.12.017 pmid: 17382631 |
| [1] | Hui Fu, Qiao-sheng Wang, Qiong Luo, Si Tan, Hua Su, Shi-lin Tang, Zheng-liang Zhao, Li-ping Huang. Simvastatin inhibits apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by sepsis through upregulating the expression of Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(4): 291-297. |
| [2] | Pei-ren Shan, Wei-wei Xu, Zhou-qing Huang, Jun Pu, Wei-jian Huang. Protective role of retinoid X receptor in H9c2 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 122-127. |
| [3] | Yan-jun Qin, Xin-liang Zhang, Yue-qing Yu, Xiao-hua Bian, Shi-min Dong. Cardioprotective effect of erythropoietin on sepsis-induced myocardial injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(3): 215-223. |
| [4] | Qiang Su, Lang Li, Yang-chun Liu, You Zhou, Wei-ming Wen. Effect of metoprolol on myocardial apoptosis after coronary microembolization in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(2): 138-143. |
| [5] | Zhi-jian Zhang, Li-bo Peng, Ya-juan Luo, Cong-yang Zhou. Prospective experimental studies on the renal protective effect of ulinastatin after paraquat poisoning [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(4): 299-304. |
| [6] | Ying-zhen Wang, Shi-wen Wang, You-cheng Zhang, Zhi-jiang Sun. Protective effect of exogenous IGF-I on the intestinal mucosal barrier in rats with severe acute pancreatitis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(3): 213-220. |
| [7] | Shi-hui Zhou, Yan-fei Sun, Gang Wang. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on intestinal mucosa apoptosis caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(2): 135-140. |
| [8] | Ping Yan, Shou-quan Chen, Zhang-ping Li, Jie Zhang, Ji-ke Xue, Wan-tie Wang, Wei-jia Huang, Jun-yan Cheng, Hui-ping Li. Effect of exogenous phosphocreatine on cardiomycytic apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(4): 291-295. |
| [9] | Ying Wang, Zhi-yang Sun, Kui-ming Zhang, Guo-qiang Xu, Guang Li. Bcl-2 in suppressing neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(1): 38-44. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
