World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2018, Vol. 9 ›› Issue (1): 56-63.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2018.01.009
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yan Ma( ), Xiang-you Yu, Yi Wang
), Xiang-you Yu, Yi Wang
Received:2017-02-20
Accepted:2017-08-16
Online:2018-03-15
Published:2018-03-15
Contact:
Yan Ma
E-mail:82902823@qq.com
Yan Ma, Xiang-you Yu, Yi Wang. Dose-related effects of dexmedetomidine on immunomodulation and mortality to septic shock in rats[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(1): 56-63.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2018.01.009
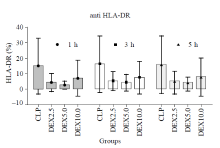
Figure 1.
HLA-DR during the experimental period. Note that a significant difference was observed between four groups (Pgroup=0.0202). HLA-DR values (given as means±SD) were measured at 1 hour (1 h), 3 hours (3 h) and 5 hours (5 h) of normal saline or dexmedetomidine infusion. CLP: cecal ligation and puncture, normal saline treated (n=12); DEX2.5: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 2.5 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX5.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 5.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX10.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 10.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12).
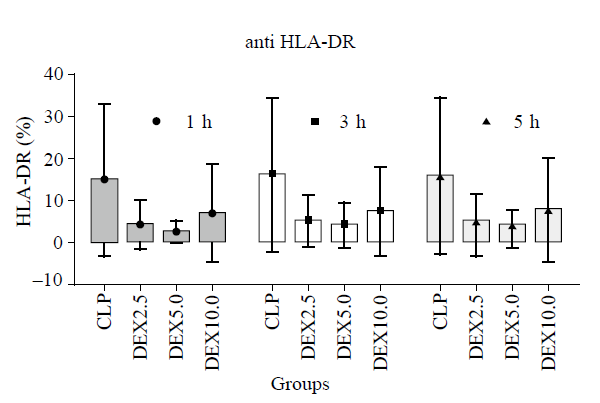
Figure 2.
Levels of interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and plasma tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) at diffrents time points (1 h, 3 h and 5 h) after normal saline or dexmedetomidine infusion (means±SD). CLP: cecal ligation and puncture, normal saline treated (n=12); DEX2.5: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 2.5 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX5.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 5.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX10.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 10.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12). #P<0.05 as compared with CLP groups at 3 h.
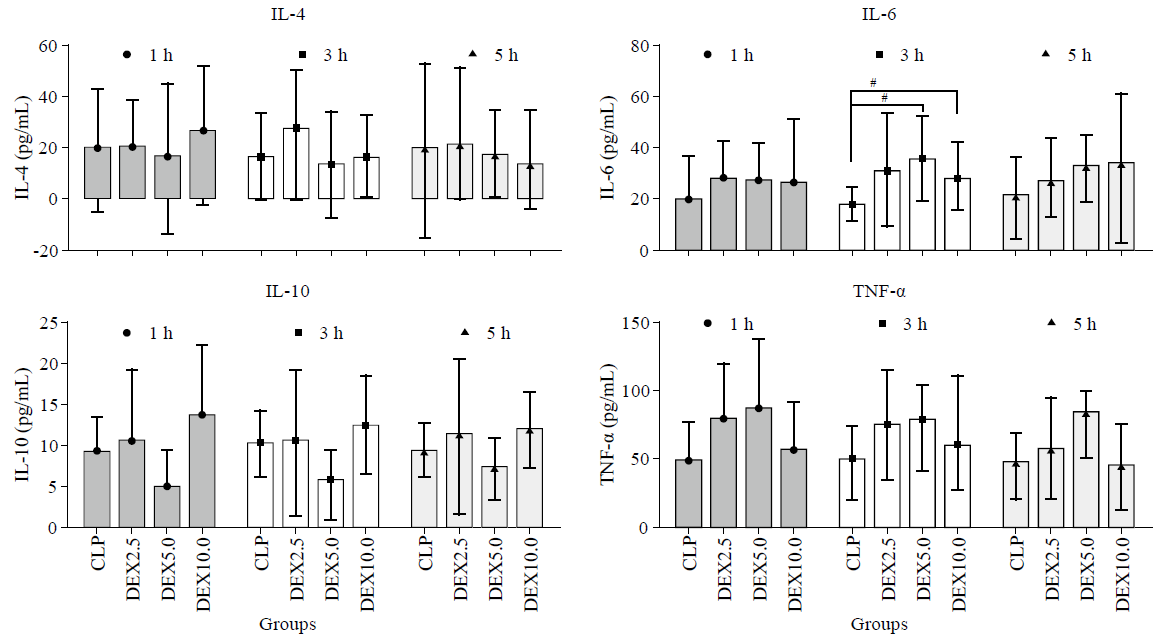
Figure 3.
Heart rate (HR) and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) evolution during the experimental period. Values (given as means±SD) were measured at 1 hour (1 h), 3 hours (3 h) and 5 hours (5 h) of normal saline or dexmedetomidine infusion. CLP: cecal ligation and puncture, normal saline treated (n=12); DEX2.5: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 2.5 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX5.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 5.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX10.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 10.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12). △P<0.001 as compared with 3h, *P<0.001 as compared with CLP groups in 5 h, #P<0.01 as compared in 1 h.
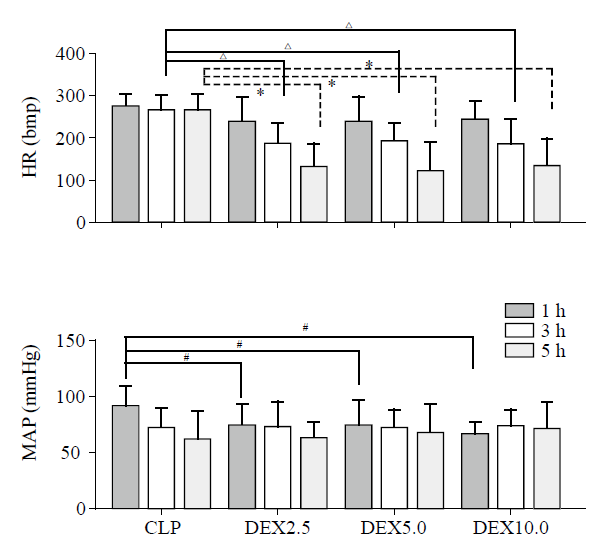
Figure 4.
Arterial blood gases and lactate analysis during the experimental period. Values (given as means±SD) were measured at 3 hours (3 h) and 5 hours (5 h) of normal saline or dexmedetomidine infusion. CLP: cecal ligation and puncture, normal saline treated (n=12); DEX2.5: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 2.5 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX5.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 5.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX10.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 10.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12). *P<0.001 as compared with CLP groups, △P<0.0001 as compared with CLP groups.
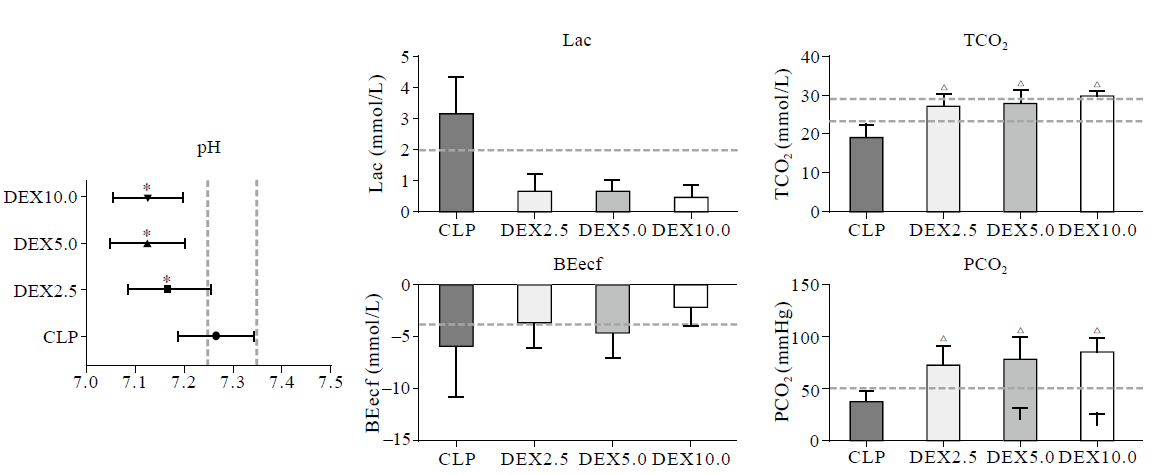
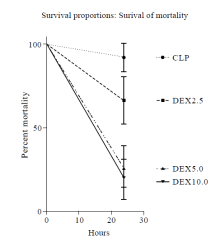
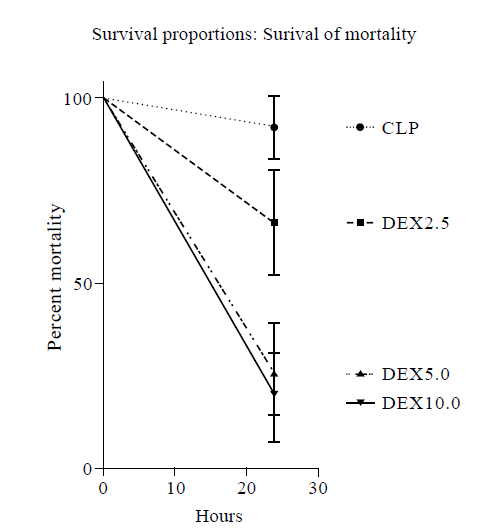
Figure 5.
Survival curve for CLP, DEX2.5, DEX5.0, DEX10.0 groups at 24 hours. CLP: cecal ligation and puncture, normal saline treated (n=12); DEX2.5: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 2.5 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX5.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 5.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12); DEX10.0: cecal ligation and puncture, dexmedetomidine treated, 10.0 mg·kg-1·h-1 infusion (n=12).
| 1 | Ma Y, Yu XY. Dose-related effects of dexmedetomidine on immunomodulation and mortality to septic shock in rats. Chin J Emerg Med. 2016;25(9):1149-50. |
| 2 | Ma Y, Yu XY. Wang Y. Dose-related effects of dexmedetomidine on hemodynamics and mortality in sepsis shock: experiment with rats. Chin J Emerg Resusc Disaster Med. 2017;12(9):838-41. |
| 3 |
Kawasaki T, Kawasaki C, Ueki M, Hamada K, Habe K, Sata T. Dexmedetomidine suppresses proinflammatory mediator production in human whole blood in vitro. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;74(5):1370-5.
doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31828db978 pmid: 23609293 |
| 4 |
Taniguchi T, Kurita A, Kobayashi K, Yamamoto K, Inaba H. Dose- and time-related effects of dexmedetomidine on mortality and inflammatory responses to endotoxin-induced shock in rats. J Anesth. 2008;22(3):221-8.
doi: 10.1007/s00540-008-0611-9 |
| 5 |
Memiş D, Hekimoğlu S, Vatan I, Yandim T, Yüksel M, Süt N. Effects of midazolam and dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and gastric intramucosal pH to sepsis, in critically ill patients. Br J Anaesth. 2007;98(4):550-2.
doi: 10.1093/bja/aem017 pmid: 17363413 |
| 6 |
Taniguchi T, Kidani Y, Kanakura H, Takemoto Y, Yamamoto K. Effects of dexmedetomidine on mortality rate and inflammatory responses to endotoxin-induced shock in rats. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(6):1322-6.
doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000128579.84228.2a pmid: 15187514 |
| 7 |
Ge Y, Huang M, Ma YF. The effects of microRNA-34a regulating Notch-1/NF-κB signaling pathway on lipopolysaccharide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells. World J Emerg Med. 2017;8(4):292-6.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2017.04.008 pmid: 29123608 |
| 8 |
Qiao H, Sanders RD, Ma D, Wu X, Maze M. Sedation improves early outcome in severely septic Sprague Dawley rats. Crit Care. 2009;13(4):R136.
doi: 10.1186/cc8012 pmid: 19691839 |
| 9 |
Hofer S, Steppan J, Wagner T, Funke B, Lichtenstern C, Martin E, et al. Central sympatholytics prolong survival in experimental sepsis. Crit Care. 2009;13(1):R11.
doi: 10.1186/cc7709 pmid: 19196475 |
| 10 |
Pandharipande PP, Sanders RD, Girard TD, McGrane S, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on outcome in patients with sepsis: An a priori-designed analysis of the MENDS randomized controlled trial. Crit Care. 2010;14(2):R38.
doi: 10.1186/cc8916 pmid: 20233428 |
| 11 |
Venn M, Newman J, Grounds M. A phase II study to evaluate the efficacy of dexmedetomidine for sedation in the medical intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29(2):201-7. Epub 2002 Nov 22.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06308-8 pmid: 33161451 |
| 12 |
Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: A randomized trial. JAMA. 2009;301(5):489-99.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.56 pmid: 19188334 |
| 13 |
Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M, Girard TD, Miller RR, et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: The MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;298(22):2644-53.
doi: 10.1001/jama.298.22.2644 pmid: 18073360 |
| 14 |
Tan JA, Ho KM. Use of dexmedetomidine as a sedative and analgesic agent in critically ill adult patients: A meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2010 ;36(6):926-39.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1877-6 pmid: 20376429 |
| 15 |
Marik PE, Baram M. Noninvasive hemodynamic monitoring in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Clin. 2007;23(3):383-400.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2007.05.002 |
| 16 |
Miranda ML, Balarini MM, Bouskela E. Dexmedetomidine attenuates the microcirculatory derangements evoked by experimental sepsis. Anesthesiology. 2015;122(3):619-30.
doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000491 pmid: 25313879 |
| [1] | Xin Lu, Wei Han, Yan-xia Gao, Shi-gong Guo, Shi-yuan Yu, Xue-zhong Yu, Hua-dong Zhu, Yi Li. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids in immunocompetent patients with septic shock [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(2): 124-130. |
| [2] | Liang-shan Peng, Juan Li, Gao-sheng Zhou, Lie-hua Deng, Hua-guo Yao. Relationships between genetic polymorphisms of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 and septic shock in a Chinese Han population [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(2): 123-130. |
| [3] | Yuan-hua Lu, Ling Liu, Xiao-hua Qiu, Qin Yu, Yi Yang, Hai-bo Qiu. Effect of early goal directed therapy on tissue perfusion in patients with septic shock [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(2): 117-122. |
| [4] | Xue-zhong Xing, Yong Gao, Hai-jun Wang, Quan-hui Yang, Chu-lin Huang, Shi-ning Qu, Hao Zhang, Hao Wang, Qing-ling Xiao, Ke-lin Sun. Risk factors and prognosis of critically ill cancer patients with postoperative acute respiratory insufficiency [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(1): 43-47. |
| [5] | Hong-sheng Ren, Shi-xue Gao, Chun-ting Wang, Yu-feng Chu, Jin-jiao Jiang, Ji-cheng Zhang, Mei Meng, Guo-qian Qi, Min Ding. Effects of high-volume hemofiltration on alveolar-arterial oxygen exchange in patients with refractory septic shock [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(2): 127-131. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
