World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2012, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (1): 49-54.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2012.01.009
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yi Lu1, Chun-sheng Li2( ), Shuo Wang2
), Shuo Wang2
Received:2011-07-23
Accepted:2012-01-11
Online:2012-03-15
Published:2012-03-15
Contact:
Chun-sheng Li
E-mail:lcscyyy@sohu.com
Yi Lu, Chun-sheng Li, Shuo Wang. Effect of hypertransfusion on the gastrointestinal tract after cardiac arrest in a porcine model[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2012, 3(1): 49-54.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2012.01.009
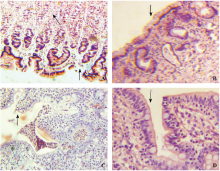
Figure 3.
The pathological changes of gastrointestinal tissue structures observed by a light microscope in the control and hypothermia groups. A: Gastric mucosa (×100) showing defect of mucosal epithelial cells (black arrow), the arrangement of cells in lamina propria layer loose and disordered, representing ischemic changes (white arrow head) in the control group; B: Gastric mucosa (×100) showing mucosal epithelium complete (black arrow head) in the hypertransfusion group; C: Intestinal mucosa (×100) showing the structure of intestinal villi basically complete, but the arrangement of cells irregular (black arrow) and a plenty of inflammatory cells in the mucosal layer (white arrow) in the control group; D: Intestinal mucosa (×400) showing the structure of intestinal villi complete and the arrangement of cells regular and dense (black arrow) in the hypertransfusion group.
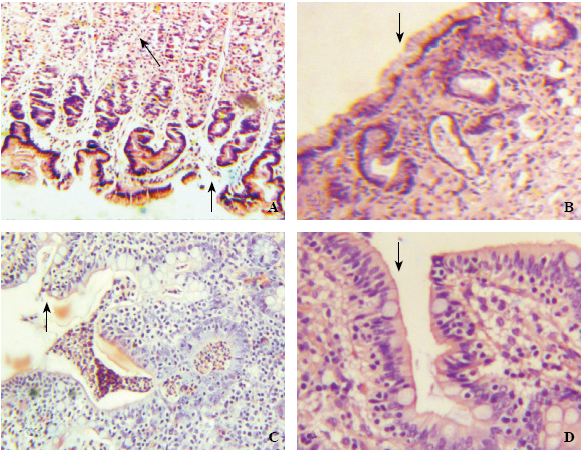

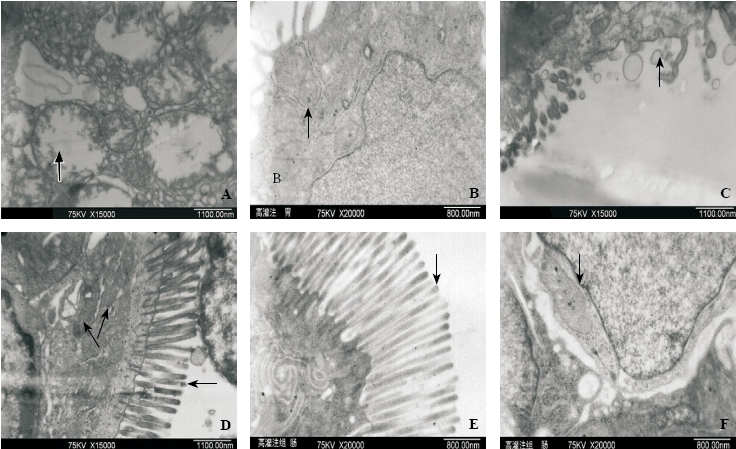
Figure 4.
The pathological ultra-structural changes of gastric tissues observed with an electron microscope in the control and hypothermia groups. A: Gastric mitochondria were highly swollen; vacuole-like changes with ridges fragmental could be observed (black arrow) in the control group; B: The structure of gastric mitochondria was complete with their ridges relatively clear (black arrow) in the hypertransfusion group; C: Defect of part of intestinal microvilli (black arrow) in the control group; D: In the control group, the arrangement of intestinal microvilli loose (black arrow) and the structure of intestinal mitochondria not distinct with their ridges hazy (black arrow); E: The arrangement of intestinal microvilli dense and regular (black arrow) in the hypertransfusion group; F: The intestinal mitochondria with their ridges manifesting basically clear (black arrow) in the hypertransfusion group.
| 1 |
Nadkarni VM, Larkin GL, Peberdy MA, Carey SM, Kaye W, Mancini ME. et al. First documented rhythm and clinical outcome from in-hospital cardiac arrest among children and adults. JAMA 2006; 295:50-57.
doi: 10.1001/jama.295.1.50 pmid: 16391216 |
| 2 |
Swank GM, Deitch EA. Role of the gut in multiple organ failure: bacterial translocation and permeability changes. World J Surg 1996; 20:411-417.
doi: 10.1007/s002689900065 pmid: 8662128 |
| 3 |
Korth U, Krieter H, Denz C, Janke C, Ellinger K, Bertsch T. et al. Intestinal ischemia during cardiac arrest and resuscitation: comparative analysis of extracellular metabolites by microdialysis. Resuscitation 2003; 58:209-217.
doi: 10.1016/s0300-9572(03)00119-9 pmid: 12909384 |
| 4 |
Guyot LL, Diaz FG, O'Regan MH, Song D, Phillis JW. Topical glucose and accumulation of excitotoxic and other amino acids in ischemic cerebral cortex. Horm Metab Res 2000; 32:6-9.
doi: 10.1055/s-2007-978577 pmid: 10727006 |
| 5 |
Sappey-Marinier D, Chileuitt L, Weiner MW, Faden AI, Weinstein PR. Hypoglycemia prevents increase in lactic acidosis during reperfusion after temporary cerebral ischemia in rats. NMR Biomed 1995; 8:171-178.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940080406 pmid: 8771092 |
| 6 |
Stadlbauer KH, Rheinberger K, Wenzel V, Raedler C, Krismer AC, Strohmenger HU. et al. The effects of nifedipine on ventricular fibrillation mean frequency in a porcine model of prolonged cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Anesth Analg 2003; 97:226-230.
doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000068801.28430.ed pmid: 12818971 |
| 7 | Meybohm P, Cavus E, Dörges V, Steinfath M, Sibbert L, Wenzel V. et al. Revised resuscitation guidelines: adrenaline versus adrenaline/vasopressin in a pig model of cardiopulmonary resuscitation--a randomised, controlled trial. Resuscitation 2007; 75:380-388. Epub 2007 Jun 20. |
| 8 |
Guérin JP, Levraut J, Samat-Long C, Leverve X, Grimaud D, Ichai C. Effects of dopamine and norepinephrine on systemic and hepatosplanchnic hemodynamics, oxygen exchange, and energy balance in vasoplegic septic patients. Shock 2005; 23:18-24.
doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000150549.45338.6c pmid: 15614126 |
| 9 |
Schaer GL, Fink MP, Parrillo JE. Norepinephrine alone versus norepinephrine plus lowdose dopamine : enhance renal blood flow with combination pressortherapy. Crit Care Med 2005; 13:492-499.
doi: 10.1097/00003246-198506000-00011 pmid: 3996002 |
| 10 |
Nordmark J, Rubertsson S. Induction of mild hypothermia with infusion of cold (4 degrees C) fluid during ongoing experimental CPR. Resuscitation 2005; 66:357-365.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2005.04.002 pmid: 16081199 |
| 11 |
Voelckel WG, Lindner KH, Wenzel V, Bonatti JO, Krismer AC, Miller EA. et al. Effect of small-dose dopamine on mesenteric blood flow and renal function in a pig model of cardiopulmonary resuscitation with vasopressin. Anesth Analg 1999; 89:1430-1436.
doi: 10.1097/00000539-199912000-00020 pmid: 10589622 |
| [1] | Xue-jie Dong, Lin Zhang, Yue-lin Yu, Shu-xiao Shi, Xiao-chen Yang, Xiao-qian Zhang, Shuang Tian, Helge Myklebust, Guo-hong Li, Zhi-jie Zheng. The general public’s ability to operate automated external defibrillator: A controlled simulation study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 238-245. |
| [2] | Alexei Birkun, Fatima Trunkwala, Adhish Gautam, Miriam Okoroanyanwu, Adesokan Oyewumi. Availability of basic life support courses for the general populations in India, Nigeria and the United Kingdom: An internet-based analysis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(3): 133-139. |
| [3] | Jung Wan Kim, Jin Woong Lee, Seung Ryu, Jung Soo Park, InSool Yoo, Yong Chul Cho, Hong Joon Ahn. Changes in peak inspiratory flow rate and peak airway pressure with endotracheal tube size during chest compression [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 97-101. |
| [4] | Ye-cheng Liu, Yan-meng Qi, Hui Zhang, Joseph Walline, Hua-dong Zhu. A survey of ventilation strategies during cardiopulmonary resuscitation [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(4): 222-227. |
| [5] | Israel Olatunji Gabriel, Joel O. Aluko. Theoretical knowledge and psychomotor skill acquisition of basic life support training programme among secondary school students [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(2): 81-87. |
| [6] | Alexei Birkun, Yekaterina Kosova. Social attitude and willingness to attend cardiopulmonary resuscitation training and perform resuscitation in the Crimea [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(4): 237-248. |
| [7] | Alexei Birkun, Maksim Glotov, Herman Franklin Ndjamen, Esther Alaiye, Temidara Adeleke, Sergey Samarin. Pre-recorded instructional audio vs. dispatchers’ conversational assistance in telephone cardiopulmonary resuscitation: A randomized controlled simulation study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(3): 165-171. |
| [8] | Alexei Birkun, Maksim Glotov. Education in cardiopulmonary resuscitation in Russia: A systematic review of the available evidence [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(4): 245-252. |
| [9] | Ling Zhou, Hui Li, Hong-yan Wei, Chun-lin Hu, Xiao-li Jing, Hong Zhan, Xiao-xing Liao, Xin Li. Study on the development and usage of a cardiopulmonary resuscitation time point recorder [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(3): 195-199. |
| [10] | Chennappa Kalvatala Krishna, Hakim Irfan Showkat, Meenakshi Taktani, Vikram Khatri. Out of hospital cardiac arrest resuscitation outcome in North India — CARO study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(3): 200-205. |
| [11] | Vinej Somaraj, Rekha P Shenoy, Ganesh Shenoy Panchmal, Praveen S Jodalli, Laxminarayan Sonde, Ravichandra Karkal. Knowledge, attitude and anxiety pertaining to basic life support and medical emergencies among dental interns in Mangalore City, India [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(2): 131-135. |
| [12] | Ji Ung Na, Sang Kuk Han, Pil Cho Choi, Dong Hyuk Shin. Effect of metronome rates on the quality of bag-mask ventilation during metronome-guided 30:2 cardiopulmonary resuscitation: A randomized simulation study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(2): 136-140. |
| [13] | Gan-nan Wang, Xu-feng Chen, Li Qiao, Yong Mei, Jin-ru Lv, Xi-hua Huang, Bin Shen, Jin-song Zhang. Comparison of extracorporeal and conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation: A meta-analysis of 2 260 patients with cardiac arrest [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(1): 5-11. |
| [14] | Marion Leary, David G. Buckler, Daniel J. Ikeda, Daiane A. Saraiva, Robert A. Berg, Vinay M. Nadkarni, Audrey L. Blewer, Benjamin S. Abella. The association of layperson characteristics with the quality of simulated cardiopulmonary resuscitation performance [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(1): 12-18. |
| [15] | Sarah A. Alkandari, Lolwa Alyahya, Mohammed Abdulwahab. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation knowledge and attitude among general dentists in Kuwait [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(1): 19-24. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
