World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (4): 263-272.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.033
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuhan Sun1, Baoqing Sun2, Zhigang Ren3, Mingshan Xue2, Changju Zhu4( ), Qi Liu1(
), Qi Liu1( )
)
Received:2023-05-29
Accepted:2023-11-20
Online:2024-07-15
Published:2024-07-01
Contact:
Qi Liu, Email: qi.liu@vip.163.com; Changju Zhu, Email: zhuchangju98@163.com
Yuhan Sun, Baoqing Sun, Zhigang Ren, Mingshan Xue, Changju Zhu, Qi Liu. Heparin-binding protein as a predictor of mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus and community-acquired pneumonia in intensive care unit : a propensity score matched study[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2024, 15(4): 263-272.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn/EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.033
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics before propensity score match
| Characteristics | DM group (n=68) | Non-DM group (n=84) | χ2/Z value | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demography | ||||
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 68 (55-74) | 57 (44-71) | -2.421 | 0.015 |
| Male, n (%) | 46 (67.6) | 60 (71.4) | 0.255 | 0.614 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 39 (57.4) | 20 (23.8) | 17.804 | <0.001 |
| COPD | 8 (11.8) | 17 (20.2) | 1.963 | 0.161 |
| ACD | 13 (19.1) | 9 (10.7) | 2.144 | 0.143 |
| Cor pulmonale | 6 (8.8) | 7 (8.3) | 0.012 | 0.914 |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 7 (10.3) | 9 (10.7) | 0.007 | 0.933 |
| Remote cerebral infarction | 14 (20.6) | 8 (9.5) | 3.716 | 0.054 |
| CKD | 7 (10.3) | 3 (3.6) | 2.763 | 0.096 |
| Others | 6 (8.8) | 9 (10.7) | 0.151 | 0.698 |
| Laboratory tests, median (IQR) | ||||
| HBP, ng/mL | 67.55 (37.87-115.27) | 54.04 (28.07-109.57) | -1.162 | 0.245 |
| PO2/FiO2, mmHg | 162.4 (118.2-216.9) | 204.1 (129.2-261.95) | -2.162 | 0.031 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 10.42 (7.93-14.15) | 6.40 (5.53-7.70) | -8.148 | <0.001 |
| WBC,×109/L | 9.73 (6.97-12.88) | 7.47 (5.05-11.5) | -2.412 | 0.016 |
| NEUT, % | 7.74 (5.98-11.03) | 5.62 (3.70-9.89) | -2.548 | 0.011 |
| CRP, mg/L | 75.11 (39.25-124.28) | 59.46 (16.82-98.48) | -2.212 | 0.027 |
| PCT, ng/L | 0.47 (0.140-1.076) | 0.27 (0.071-0.783) | -1.595 | 0.111 |
| ESR, mm/h | 54 (30-77) | 31 (14-66) | -2.539 | 0.011 |
| Clinical evaluation, median (IQR) | ||||
| APACHE II | 13 (8-18) | 8 (6-12) | -4.425 | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 4 (3-6) | 3 (2-4) | -4.498 | 0.008 |
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes after propensity score match
| Characteristics | DM group (n=60) | Non-DM group (n=60) | χ2/Z value | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristic | ||||
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 64 (54-74) | 64 (55-74) | -0.200 | 0.842 |
| Male, n (%) | 41 (68.3) | 41(68.3) | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 33 (55.0) | 17 (28.3) | 8.777 | 0.003 |
| COPD | 6 (10.0) | 17 (28.3) | 6.508 | 0.011 |
| ACD | 9 (15.0) | 9 (15.0) | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Cor pulmonale | 5 (8.3) | 7 (11.7) | 0.370 | 0.543 |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 5 (8.3) | 7 (11.7) | 0.370 | 0.543 |
| Remote cerebral infarction | 10 (16.7) | 8 (13.3) | 0.261 | 0.609 |
| CKD | 7 (11.7) | 1 (1.7) | 4.821 | 0.061 |
| Others | 6 (10.0) | 9 (15.0) | 0.686 | 0.408 |
| Laboratory tests, median (IQR) | ||||
| HBP, ng/mL | 69.71 (34.57-134.35) | 54.93 (27.05-91.86) | -1.220 | 0.222 |
| PO2/FiO2, mmHg | 160.1 (113.35-202.7) | 209.4 (171.8-263.6) | -3.727 | <0.001 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 11.34 (8.50-15.22) | 6.30 (5.43-7.20) | -8.021 | <0.001 |
| WBC,×109/L | 9.73 (7.07-13.28) | 7.58 (5.23-11.17) | -2.181 | 0.029 |
| NEUT, % | 84.95 (77.40-91.78) | 83.80 (74.50-89.73) | -0.562 | 0.574 |
| CRP, mg/L | 75.11 (39.25-127.17) | 49.78 (12.98-88.35) | -2.590 | 0.010 |
| PCT, ng/L | 0.46 (0.11-0.99) | 0.17 (0.07-0.56) | -2.000 | 0.046 |
| ESR, mm/h | 53 (26.2-77) | 34 (14.3-68.5) | -1.913 | 0.056 |
| Clinical evaluation and clinical outcomes | ||||
| APACHE II, median (IQR) | 12 (8-17) | 9 (6-12) | -3.127 | 0.002 |
| SOFA, median (IQR) | 4 (3-6.75) | 3 (2-4) | -4.627 | <0.001 |
| SRF, n (%) | 19 (31.7) | 5 (8.3) | 10.208 | 0.001 |
| ARDS, n (%) | 36 (60.0) | 19 (31.7) | 9.701 | 0.002 |
| Severe pneumonia, n (%) | 43 (71.7) | 30 (50.0) | 5.911 | 0.015 |
| Invasive ventilation, n (%) | 19 (31.7) | 6 (10.0) | 8.539 | 0.003 |
| Length of ICU stay, d, median (IQR) | 5 (3-11) | 3 (2-6) | -3.073 | 0.002 |
| 10-day mortality, n (%) | 9 (15.0) | 4 (6.7) | 2.157 | 0.142 |
| 28-day mortality, n (%) | 14 (23.3) | 5 (8.3) | 5.065 | 0.024 |
| 90-day mortality, n (%) | 16 (26.7) | 5 (8.3) | 6.984 | 0.008 |
Table 3.
HBP and infection biomarkers in the prediction of mortality by ROC curves
| Indicators | Maximum Youden index | Cut-off value | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel A: CAP patients with DM | |||||||
| 10-day mortality | |||||||
| HBP | 0.569 | 160.6 ng/mL | 0.667 | 0.902 | 0.747 | 0.54-0.96 | |
| PCT | 0.477 | 1.805 ng/L | 0.556 | 0.921 | 0.732 | 0.56-0.91 | |
| ESR | 0.301 | 63.5 mm/h | 0.889 | 0.412 | 0.614 | 0.41-0.82 | |
| CRP | 0.216 | 74.97 mg/L | 0.667 | 0.549 | 0.536 | 0.35-0.72 | |
| 28-day mortality | |||||||
| HBP | 0.320 | 160.6 ng/mL | 0.429 | 0.891 | 0.576 | 0.38-0.77 | |
| PCT | 0.354 | 0.8085 ng/L | 0.571 | 0.783 | 0.683 | 0.53-0.83 | |
| ESR | 0.161 | 76.5 mm/h | 0.857 | 0.304 | 0.549 | 0.37-0.73 | |
| CRP | 0.214 | 85.8 mg/L | 0.714 | 0.500 | 0.545 | 0.38-0.71 | |
| 90-day mortality | |||||||
| HBP | 0.347 | 160.6 ng/mL | 0.436 | 0.909 | 0.624 | 0.44-0.81 | |
| PCT | 0.358 | 0.8085 ng/L | 0.563 | 0.796 | 0.675 | 0.52-0.83 | |
| ESR | 0.119 | 36.2 mm/h | 0.438 | 0.682 | 0.523 | 0.35-0.70 | |
| CRP | 0.188 | 85.8 mg/L | 0.688 | 0.500 | 0.551 | 0.39-0.72 | |
| Panel B: CAP patients without DM | |||||||
| 10-day mortality | |||||||
| HBP | 0.429 | 83.48 ng/mL | 0.750 | 0.679 | 0.714 | 0.46-0.97 | |
| PCT | 0.536 | 0.542 ng/L | 0.750 | 0.786 | 0.690 | 0.38-1.0 | |
| ESR | 0.232 | 2.5 mm/h | 0.250 | 0.982 | 0.540 | 0.22-0.87 | |
| CRP | 0.714 | 162.7 mg/L | 0.750 | 0.964 | 0.763 | 0.40-1.00 | |
| 28-day and 90-day mortality﹡ | |||||||
| HBP | 0.436 | 73.66 ng/mL | 0.800 | 0.636 | 0.698 | 0.49-0.92 | |
| PCT | 0.546 | 0.397 ng/L | 0.800 | 0.746 | 0.700 | 0.45-0.95 | |
| ESR | 0.327 | 6.2 mm/h | 0.400 | 0.927 | 0.622 | 0.33-0.91 | |
| CRP | 0.564 | 162.7 mg/L | 0.600 | 0.964 | 0.687 | 0.37-1.00 | |
Figure 2.
The survival probability analyzed by Kaplan-Meier analysis according to the cut-off values of HBP and PCT. HBP for predicting survival probability within 10 d (A), 28 d (B), and 90 d (C) follow-up in patients with DM. PCT for predicting survival probability within 10 d (D), 28 d (E), and 90 d (F) follow-up in patients with DM. HBP for predicting survival probability within 10 d (G), 28 d (H), and 90 d (I) follow-up in patients without DM. PCT for predicting survival probability within 10 d (J), 28 d (K), and 90 d (L) follow-up in patients without DM. HBP: heparin-binding protein; PCT: procalcitonin; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-reactive protein; ns: no significance; DM: diabetes mellitus.
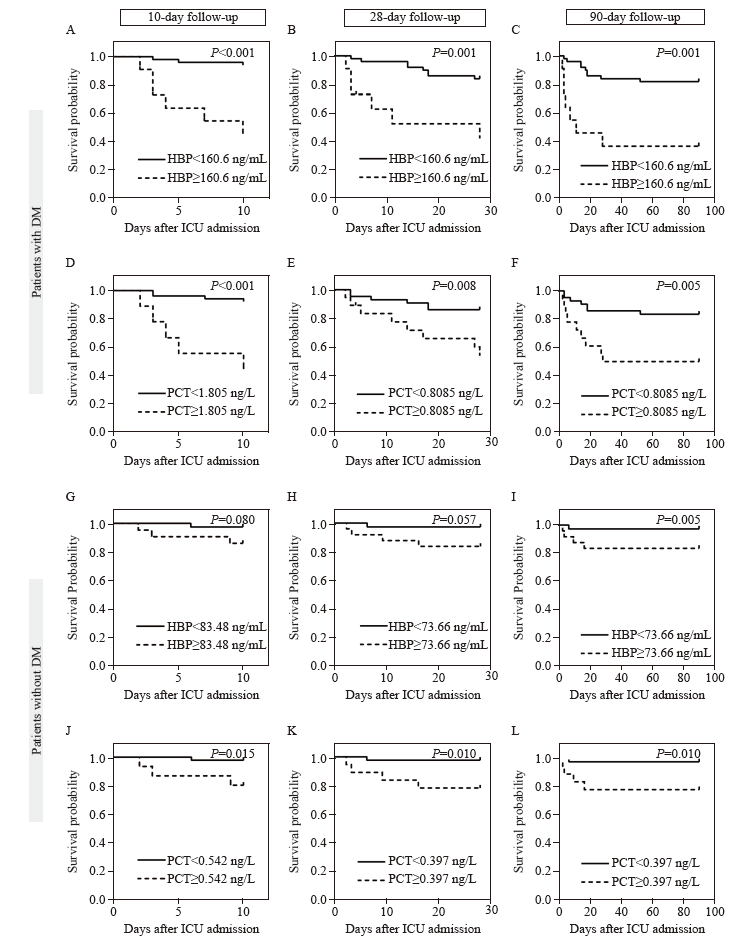
Table 4.
Univariate and multivariate COX regression analysis of related factors of mortality in patients with DM and CAP
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | P-value | HR (95%CI) | P-value | ||
| 10-day mortality | |||||
| HBP>160.6 ng/mL | 11.917 (2.961-47.961) | 0.000 | 7.196 (1.596-32.455) | 0.010 | |
| PCT>1.805 ng/L | 9.405 (2.509-135.254) | 0.001 | 4.231 (0.865-20.699) | 0.075 | |
| SRF | 4.877 (1.217-19.552) | 0.025 | 2.015 (0.380-10.680) | 0.410 | |
| CRP>74.97 mg/L | 0.458 (0.115-1.833) | 0.458 | |||
| ESR>63.5 mm/h | 0.202 (0.025-1.614) | 0.202 | |||
| Age | 0.998 (0.953-1.044) | 0.917 | |||
| Male | 0.558 (0.150-2.078) | 0.384 | |||
| Diabetes duration | 0.979 (0.895-1.072) | 0.646 | |||
| HbA1c | 1.051 (0.754-1.465) | 0.768 | |||
| Hypertension | 1.654 (0.414-6.614) | 0.477 | |||
| COPD | 1.048 (0.131-8.384) | 0.965 | |||
| 28-day mortality | |||||
| HBP>160.6 ng/mL | 5.291 (1.819-15.393) | 0.002 | 4.381 (1.449-13.245) | 0.009 | |
| PCT>0.809 ng/L | 3.873 (1.341-11.191) | 0.012 | 2.791 (0.944-8.253) | 0.063 | |
| SRF | 5.188 (1.728-15.576) | 0.003 | 4.754 (1.546-14.619) | 0.007 | |
| CRP>85.8 mg/L | 0.477 (0.150-1.521) | 0.211 | |||
| ESR>76.5 mm/h | 0.471 (0.106-2.107) | 0.325 | |||
| Age | 1.013 (0.975-1.052) | 0.515 | |||
| Male | 0.792 (0.265-2.365) | 0.677 | |||
| Diabetes duration | 0.948 (0.865-1.039) | 0.258 | |||
| HbA1c | 0.907 (0.673-1.222) | 0.520 | |||
| Hypertension | 1.544 (0.517-4.609) | 0.436 | |||
| COPD | 1.467 (0.328-6.559) | 0.616 | |||
| 90-day mortality | |||||
| HBP>160.6 ng/mL | 5.560 (2.052-15.062) | 0.001 | 4.581 (1.637-12.819) | 0.004 | |
| PCT>0.809 ng/L | 3.776 (1.402-10.169) | 0.009 | 2.719 (0.985-7.504) | 0.054 | |
| SRF | 4.861 (1.756-13.455) | 0.002 | 4.405 (1.557-12.461) | 0.005 | |
| CRP>85.8 mg/L | 0.539 (0.187-1.551) | 0.252 | |||
| ESR>36.2 mm/h | 0.786 (0.286-2.163) | 0.641 | |||
| Age | 0.998 (0.964-1.033) | 0.920 | |||
| Male | 0.730 (0.265-2.008) | 0.542 | |||
| Diabetes duration | 0.949 (0.872-1.033) | 0.230 | |||
| HbA1c | 0.947 (0.725-1.237) | 0.690 | |||
| Hypertension | 1.894 (0.658-5.452) | 0.237 | |||
| COPD | 1.265 (0.287-5.567) | 0.756 | |||
| [1] | Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183: 109119. |
| [2] | Daryabor G, Atashzar MR, Kabelitz D, Meri S, Kalantar K. The effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus on organ metabolism and the immune system. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 1582. |
| [3] |
Carey IM, Critchley JA, DeWilde S, Harris T, Hosking FJ, Cook DG. Risk of infection in type 1 and type 2 diabetes compared with the general population: a matched cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41(3): 513-21.
doi: 10.2337/dc17-2131 pmid: 29330152 |
| [4] | McDonald HI, Nitsch D, Millett ERC, Sinclair A, Thomas SL. New estimates of the burden of acute community-acquired infections among older people with diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cohort study using linked electronic health records. Diabet Med. 2014; 31(5): 606-14. |
| [5] |
Torres A, Blasi F, Dartois N, Akova M. Which individuals are at increased risk of pneumococcal disease and why? Impact of COPD, asthma, smoking, diabetes, and/or chronic heart disease on community-acquired pneumonia and invasive pneumococcal disease. Thorax. 2015; 70(10): 984-9.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-206780 pmid: 26219979 |
| [6] | López-de-Andrés A, Perez-Farinos N, de Miguel-Díez J, Hernández-Barrera V, Jiménez-Trujillo I, Méndez-Bailón M, et al. Type 2 diabetes and postoperative pneumonia: an observational, population-based study using the Spanish Hospital Discharge Database, 2001-2015. PLoS One,. 2019;14(2): e0211230. |
| [7] | Martins M, Boavida JM, Raposo JF, Froes F, Nunes B, Ribeiro RT, et al. Diabetes hinders community-acquired pneumonia outcomes in hospitalized patients. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2016; 4(1): e000181. |
| [8] |
Falguera M, Pifarre R, Martin A, Sheikh A, Moreno A. Etiology and outcome of community-acquired pneumonia in patients with diabetes mellitus. Chest. 2005; 128(5): 3233-9.
pmid: 16304267 |
| [9] |
Kornum JB, Thomsen RW, Riis A, Lervang HH, Schønheyder HC, Sørensen HT. Type 2 diabetes and pneumonia outcomes: a population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30(9): 2251-7.
doi: 10.2337/dc06-2417 pmid: 17595354 |
| [10] | Koskela HO, Salonen PH, Romppanen J, Niskanen L. Long-term mortality after community-acquired pneumonia—impacts of diabetes and newly discovered hyperglycaemia: a prospective, observational cohort study. BMJ Open. 2014; 4(8): e005715. |
| [11] |
Lim S, Bae JH, Kwon HS, Nauck MA. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021; 17(1): 11-30.
doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4 pmid: 33188364 |
| [12] | Bader MS, Abouchehade KA, Yi Y, Haroon B, Bishop LD, Hawboldt J. Antibiotic administration longer than eight hours after triage and mortality of community-acquired pneumonia in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 30(7): 881-6. |
| [13] |
Bader MS, Yi YQ, Abouchehade K, Haroon B, Bishop LD, Hawboldt J. Community-acquired pneumonia in patients with diabetes mellitus: predictors of complications and length of hospital stay. Am J Med Sci. 2016; 352(1): 30-5.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2016.02.032 pmid: 27432032 |
| [14] | Karakioulaki M, Stolz D. Biomarkers in pneumonia-beyond procalcitonin. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(8): 2004. |
| [15] |
Linder A, Christensson B, Herwald H, Björck L, Akesson P. Heparin-binding protein: an early marker of circulatory failure in sepsis. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 49(7): 1044-50.
doi: 10.1086/605563 pmid: 19725785 |
| [16] |
Linder A, Soehnlein O, Akesson P. Roles of heparin-binding protein in bacterial infections. J Innate Immun. 2010; 2(5): 431-8.
doi: 10.1159/000314853 pmid: 20505311 |
| [17] |
Bentzer P, Fisher J, Kong HJ, Mörgelin M, Boyd JH, Walley KR, et al. Heparin-binding protein is important for vascular leak in sepsis. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2016; 4(1):33.
doi: 10.1186/s40635-016-0104-3 pmid: 27704481 |
| [18] |
Chew MS, Linder A, Santen S, Ersson A, Herwald H, Thorlacius H. Increased plasma levels of heparin-binding protein in patients with shock: a prospective, cohort study. Inflamm Res. 2012; 61(4): 375-9.
doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0422-6 pmid: 22207392 |
| [19] |
Dankiewicz J, Linder A, Annborn M, Rundgren M, Friberg H. Heparin-binding protein: an early indicator of critical illness and predictor of outcome in cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2013; 84(7): 935-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2013.01.006 pmid: 23318914 |
| [20] | Kahn F, Tverring J, Mellhammar L, Wetterberg N, Bläckberg A, Studahl E, et al. Heparin-binding protein as a prognostic biomarker of sepsis and disease severity at the emergency department. Shock. 2019; 52(6): e135-e145. |
| [21] | Fisher J, Linder A, Bentzer P, Boyd J, Kong HJ, Lee T, et al. Is heparin-binding protein inhibition a mechanism of albumin’s efficacy in human septic shock? Crit Care Med. 2018; 46(5): e364-e374. |
| [22] | Lin QH, Shen J, Shen LH, Zhang ZW, Fu FM. Increased plasma levels of heparin-binding protein in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care. 2013; 17(4): R155. |
| [23] | Saridaki M, Metallidis S, Grigoropoulou S, Vrentzos E, Lada M, Argyraki K, et al. Integration of heparin-binding protein and interleukin-6 in the early prediction of respiratory failure and mortality in pneumonia by SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021; 40(7): 1405-12. |
| [24] |
Olson G, Davis AM. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. JAMA. 2020; 323(9): 885-6.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.21118 pmid: 32027358 |
| [25] |
American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44(Suppl 1): S15-S33.
doi: 10.2337/dc21-S002 pmid: 33298413 |
| [26] |
Salih W, Schembri S, Chalmers JD. Simplification of the IDSA/ATS criteria for severe CAP using meta-analysis and observational data. Eur Respir J. 2014; 43(3): 842-51.
doi: 10.1183/09031936.00089513 pmid: 24114960 |
| [27] |
Definition Task Force ARDS, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA. 2012; 307(23): 2526-33.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.5669 pmid: 22797452 |
| [28] |
Di Yacovo S, Garcia-Vidal C, Viasus D, Adamuz J, Oriol I, Gili F, et al. Clinical features, etiology, and outcomes of community-acquired pneumonia in patients with diabetes mellitus. Medicine. 2013; 92(1): 42-50.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e31827f602a pmid: 23263718 |
| [29] | Zhang QR, Chen H, Liu B, Zhou M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in diabetics: a single-center, retrospective analysis. Chin Med J. 2019; 132(12): 1429-34. |
| [30] |
Shen Y, Fan XH, Zhang L, Wang YX, Li C, Lu JY, et al. Thresholds of glycemia and the outcomes of COVID-19 complicated with diabetes: a retrospective exploratory study using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44(4): 976-82.
doi: 10.2337/dc20-1448 pmid: 33574126 |
| [31] |
Gautam N, Olofsson AM, Herwald H, Iversen LF, Lundgren-Akerlund E, Hedqvist P, et al. Heparin-binding protein (HBP/CAP37): a missing link in neutrophil-evoked alteration of vascular permeability. Nat Med. 2001; 7(10): 1123-7.
doi: 10.1038/nm1001-1123 pmid: 11590435 |
| [32] |
Linder A, Arnold R, Boyd JH, Zindovic M, Zindovic I, Lange AN, et al. Heparin-binding protein measurement improves the prediction of severe infection with organ dysfunction in the emergency department. Crit Care Med. 2015; 43(11): 2378-86.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001265 pmid: 26468696 |
| [33] | Linder A, Åkesson P, Inghammar M, Treutiger CJ, Linnér A, Sundén-Cullberg J. Elevated plasma levels of heparin-binding protein in intensive care unit patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care. 2012; 16(3): R90. |
| [34] | Paulsson M, Thelaus L, Riesbeck K, Qvarfordt I, Smith ME, Lindén A, et al. Heparin-binding protein in lower airway samples as a biomarker for pneumonia. Respir Res. 2021; 22(1): 174. |
| [35] | Dowey R, Iqbal A, Heller SR, Sabroe I, Prince LR. A bittersweet response to infection in diabetes; targeting neutrophils to modify inflammation and improve host immunity. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 678771. |
| [36] |
Caseiro A, Ferreira R, Quintaneiro C, Pereira A, Marinheiro R, Vitorino R, et al. Protease profiling of different biofluids in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45(18): 1613-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.08.027 pmid: 22975642 |
| [37] |
Soongsathitanon J, Umsa-Ard W, Thongboonkerd V. Proteomic analysis of peripheral blood polymorphonuclear cells (PBMCs) reveals alteration of neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) components in uncontrolled diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019; 461(1-2): 1-14.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03583-y pmid: 31273604 |
| [38] | Cai RT, Li HH, Tao Z. Heparin-binding protein and procalcitonin in the diagnosis of pathogens causing community-acquired pneumonia in adult patients: a retrospective study. PeerJ. 2021;9: e11056. |
| [39] | Fritzsching B, Zhou-Suckow Z, Trojanek JB, Schubert SC, Schatterny J, Hirtz S, et al. Hypoxic epithelial necrosis triggers neutrophilic inflammation via IL-1 receptor signaling in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 191(8): 902-13. |
| [40] |
Hoenderdos K, Lodge KM, Hirst RA, Chen C, Palazzo SGC, Emerenciana A, et al. Hypoxia upregulates neutrophil degranulation and potential for tissue injury. Thorax. 2016; 71(11): 1030-8.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207604 pmid: 27581620 |
| [41] | Lodge KM, Vassallo A, Liu B, Long M, Tong Z, Newby PR, et al. Hypoxia increases the potential for neutrophil-mediated endothelial damage in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022; 205(8): 903-16. |
| [42] | Montgomery ST, Mall MA, Kicic A, Stick SM, AREST CF. Hypoxia and sterile inflammation in cystic fibrosis airways: mechanisms and potential therapies. Eur Respir J. 2017; 49(1): 1600903. |
| [43] | Huang CZ, Zhang C, Zhang J, Zhang L, Mo Y, Mo LY. Heparin-binding protein in critically ill children with severe community-acquired pneumonia. Front Pediatr. 2021;9: 759535. |
| [44] |
Hatanaka E, Monteagudo PT, Marrocos MS, Campa A. Neutrophils and monocytes as potentially important sources of proinflammatory cytokines in diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006; 146(3): 443-7.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03229.x pmid: 17100763 |
| [45] | Sjöbeck M, Sternby H, Herwald H, Thorlacius H, Regnér S. Heparin-binding protein is significantly increased in acute pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021; 21(1): 337. |
| [46] | 46 Ristagno G, Masson S, Tiainen M, Bendel S, Bernasconi R, Varpula T, et al. Elevated plasma heparin-binding protein is associated with early death after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 2016; 20(1): 251. |
| [47] | Tverring J, Nielsen N, Dankiewicz J, Linder A, Kahn F, Åkesson P. Repeated measures of heparin-binding protein (HBP) and procalcitonin during septic shock: biomarker kinetics and association with cardiovascular organ dysfunction. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020; 8(1): 51. |
| [48] | Kaukonen KM, Linko R, Herwald H, Lindbom L, Ruokonen E, Ala-Kokko T, et al. Heparin-binding protein (HBP) in critically ill patients with influenza a (H1N1) infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013; 19(12): 1122-8. |
| [1] | Rebekah Shaw, Erica Popovsky, Alyssa Abo, Marni Jacobs, Nicole Herrera, James Chamberlain, Andrea Hahn. Improving antibiotic prescribing in the emergency department for uncomplicated community-acquired pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 199-205. |
| [2] | Hai-jiang Zhou, Tian-fei Lan, Shu-bin Guo. Outcome prediction value of National Early Warning Score in septic patients with community-acquired pneumonia in emergency department: A single-center retrospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 206-215. |
| [3] | Zhong-shu Kuang, Yi-lin Yang, Wei Wei, Jian-li Wang, Xiang-yu Long, Ke-yong Li, Chao-yang Tong, Zhan Sun, Zhen-ju Song. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of community-acquired pneumonia in autoimmune disease-induced immunocompromised host: A retrospective observational study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(3): 145-151. |
| [4] | Li-ping Chen, Jun-hui Chen, Ying Chen, Chao Wu, Xiao-hong Yang. Efficacy and safety of glucocorticoids in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(3): 172-178. |
| [5] | Jing Li, Huan Ye, Li Zhao. B-type natriuretic peptide in predicting the severity of community-acquired pneumonia [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(2): 131-136. |
| [6] | Hai-yan Zhang, Cai-jun Wu, Chun-sheng Li. Glycated hemoglobin A1C and diabetes mellitus in critically ill patients [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2013, 4(3): 201-204. |
| [7] | Samuel George Campbell, R. Andrew McIvor, Vincent Joanis, David Graydon Urquhart. Can we predict which patients with community-acquired pneumonia are likely to have positive blood cultures? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(4): 272-278. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
