World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2018, Vol. 9 ›› Issue (1): 33-40.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2018.01.005
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Sean P. Denny1, William B. Minteer1, Reece T.H. Fenning1, Sahil Aggarwal1, Debora H. Lee1, Shella K. Raja1, Kaavya R. Raman1, Allison O. Farfel1, Priya A. Patel1, MarkLieber1, Megan E. Bernstein1, Shadi Lahham2( ), John C. Fox2
), John C. Fox2
Received:2017-03-28
Accepted:2017-09-06
Online:2018-03-15
Published:2018-03-15
Contact:
Shadi Lahham
E-mail:slahham@uci.edu
Sean P. Denny, William B. Minteer, Reece T.H. Fenning, Sahil Aggarwal, Debora H. Lee, Shella K. Raja, Kaavya R. Raman, Allison O. Farfel, Priya A. Patel, MarkLieber, Megan E. Bernstein, Shadi Lahham, John C. Fox. Ultrasound curriculum taught by first-year medical students: A four-year experience in Tanzania[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(1): 33-40.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2018.01.005
Table 1
Ultrasound topic covered by program year
| Year | Topic covered by program year |
|---|---|
| 2013 | Ultrasound physics and instrumentation, abdominal, cardiac, pelvis, FAST/pulmonary, musculoskeletal |
| 2014 | Ultrasound physics and instrumentation, abdominal, cardiac, pelvis, FAST/pulmonary, musculoskeletal |
| 2015 | Ultrasound physics and instrumentation, abdominal, cardiac, pelvis, FAST/pulmonary, basic pathology |
| 2016 | Ultrasound physics and instrumentation, abdominal, cardiac, pelvis, FAST/pulmonary, basic pathology |
Table 2
Participants in ultrasound curriculum
| Participant type | n=354 | % of participants who completed course |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical officer student | 309 | 87.29 |
| Laboratory technician student | 26 | 7.34 |
| Health information technician student | 7 | 1.98 |
| Practicing physician | 5 | 1.41 |
| Practicing nurse | 4 | 1.13 |
| TIHEST employee | 2 | 0.56 |
| Practicing radiographer | 1 | 0.28 |

Figure 4.
Clinical officer students vs. non-clinical health students in 2016. Non-clinical health student and clinical officer student pre-course and post-course exam scores are plotted on the X-axis, respectively. Percent correct is shown on the Y-axis. Both non-clinical officer students and clinical officer students scored significantly higher on the post-course exam than the pre-course exam (P<0.01). In addition, the clinical officer students had significantly higher post-course exam scores than non-clinical officer students (P<0.01). Outliers are shown.Usefulness of resource
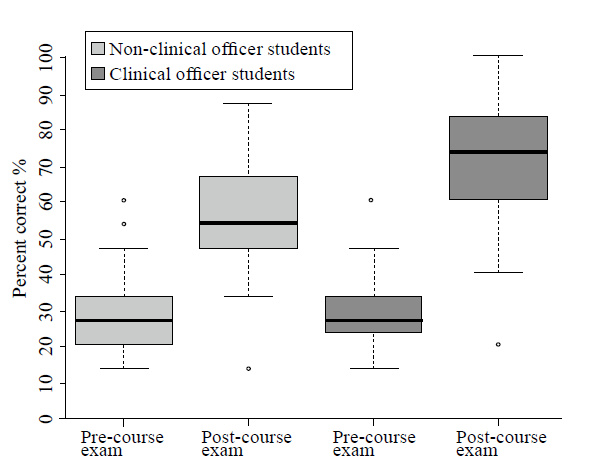
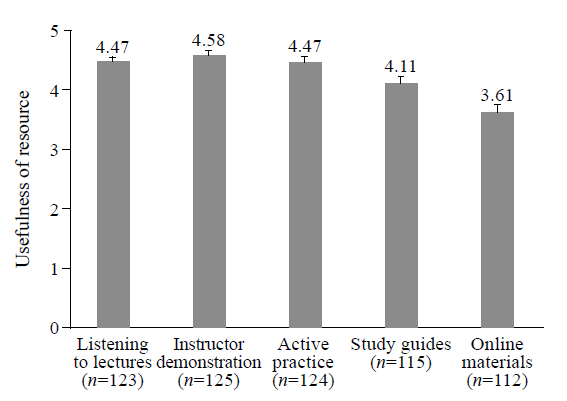
Figure 5.
Post-course evaluation of various resources. After course completion, participants from 2015-2016 rated the usefulness of various resources from 0 to 5 for learning ultrasound (with 0 corresponding to not useful at all, and 5 corresponding to very useful). Instructor demonstration was found to be the most useful, and online materials the least useful (P<0.01). Resources and number of respondents (n) lie on the X-axis. Mean scores for each resource type lie above the standard error bars.
| 1 | WHO. The World Health Report 2006 - Working Together for Health. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2006. |
| 2 |
Physicians (per 1,000 people) | Data. Dataworldbankorg. 2017. Available at: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.MED.PHYS.ZS?locations=TZ. Accessed December 5, 2016.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09220-4 pmid: 32652971 |
| 3 |
Nurses and midwives (per 1,000 people) | Data. Dataworldbankorg. 2017. Available at: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.MED.NUMW.P3?locations=TZ. Accessed December 5, 2016.
doi: 10.1186/s12960-017-0190-7 pmid: 28202047 |
| 4 |
Ostensen H. Developing countries. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2000;26:S159-S161.
doi: 10.1016/s0301-5629(00)00194-0 pmid: 10794906 |
| 5 | Global Atlas of Medical Devices - Tanzania, United Republic of. 2014. Available at: http://www.who.int/medical_devices/countries/tza.pdf. Accessed December 5, 2016. |
| 6 |
Mindel S. Role of imager in developing world. The Lancet. 1997;350(9075):426-429.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)03340-0 |
| 7 | Hoyer PF, Weber M. Ultrasound in developing world. The Lancet. 1997;350(9087):1330. |
| 8 |
Steinmetz JP, Berger JP. Ultrasonography as an aid to diagnosis and treatment in a rural African hospital: a prospective study of 1 119 cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60(1):119-123.
doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1999.60.119 pmid: 9988334 |
| 9 |
Sippel S, Muruganandan K, Levine A, Shah S. Use of ultrasound in the developing world. Int J Emerg Med. 2011;4:72.
doi: 10.1186/1865-1380-4-72 pmid: 22152055 |
| 10 |
Felkel S. Ultrasound safety. J Diagn Med Sonogr. 1999;15(2):77-80.
doi: 10.1177/875647939901500206 |
| 11 |
Shah SP, Epino H, Bukhman G, Umulisa I, Dushimiyimana JM, Reichman A, et al. Impact of the introduction of ultrasound services in a limited resource setting: rural Rwanda 2008. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2009;9:4.
doi: 10.1186/1472-698X-9-4 pmid: 19327157 |
| 12 |
Kotlyar S, Moore CL. Assessing the utility of ultrasound in Liberia. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2008;1(1):10-4
doi: 10.4103/0974-2700.41785 pmid: 19561936 |
| 13 |
Blaivas M, Kuhn W, Reynolds B, Brannam L. Change in differential diagnosis and patient management with the use of portable ultrasound in a remote setting. Wilderness Environ Med. 2005;16(1):38-41.
doi: 10.1580/1080-6032(2005)16[38:ciddap]2.0.co;2 pmid: 15813146 |
| 14 |
Spencer J, Adler R. Utility of portable ultrasound in a community in Ghana. J Ultrasound Med. 2008;27(12):1735-43.
doi: 10.7863/jum.2008.27.12.1735 pmid: 19022999 |
| 15 | Henwood PC, Mackenzie DC, Rempell JS, Murray AF, Leo MM, Dean AJ, et al. A practical guide to self-sustaining point-of-care ultrasounz education programs in resource-limited settings. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;64(3):277-285.e2. |
| 16 |
Nelson B, Melnick E, Li J. Portable ultrasound for remote environments, Part I: Feasibility of field deployment. J Emerg Med. 2011;40(2):190-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2009.09.006 |
| 17 |
LaGrone L, Sadasivam V, Kushner A, Groen RS. A review of training opportunities for ultrasonography in low and middle income countries. Trop Med Int Health. 2012;17(7):808-819.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2012.03014.x |
| 18 |
Shah S, Bellows B, Adedipe A, Totten JE, Backlund BH, Sajed D. Perceived barriers in the use of ultrasound in developing countries. Crit Ultrasound J. 2015;7(1):28.
doi: 10.1186/s13089-015-0028-2 pmid: 26123609 |
| 19 |
Ferraioli G, Meloni M. Sonographic Training program at a district hospital in a developing country: work in progress. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189(3):W119-W122.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.2202 |
| 20 |
Adler D, Mgalula K, Price D, Taylor O. Introduction of a portable ultrasound unit into the health services of the Lugufu refugee camp, Kigoma District, Tanzania. Int J Emerg Med. 2008;1(4):261-6.
doi: 10.1007/s12245-008-0074-7 |
| 21 |
Shaffer M, Brown H, McCoy C, Bashaka P. Evaluation of a short-term training program in bedside emergency ultrasound in southwestern Tanzania. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36(3):515-521.
doi: 10.7863/ultra.16.04006 pmid: 28088840 |
| 22 |
Lee JB, Tse C, Keown T, Louthan M, Gabriel C, Anshus A, et al. Evaluation of a point of care ultrasound curriculum for Indonesian physicians taught by first-year medical students. World J Emerg Med. 2017;8(4):281-6.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2017.04.006 pmid: 29123606 |
| 23 |
Collins J, Riebe JD, Albanese MA, Dobos N, Heiserman K, Primack SL, et al. Medical students and radiology residents: Can they learn as effectively with the same educational materials? Acad Radiol. 1999;6(11):691-5.
doi: 10.1016/S1076-6332(99)80119-6 pmid: 10894073 |
| 24 |
Zaidman C, Wu JS, Wilder S, Darras BT, Rutkove SB. Minimal training is required to reliably perform quantitative ultrasound of muscle. Muscle Nerve. 2014;50(1):124-8.
doi: 10.1002/mus.24117 |
| 25 |
Bahner D, Adkins EJ, Hughes D, Barrie M, Boulger CT, Royall NA. Integrated medical school ultrasound: development of an ultrasound vertical curriculum. Crit Ultrasound J. 2013;5(1):6.
doi: 10.1186/2036-7902-5-6 pmid: 23819896 |
| 26 | R: A Language And Environment For Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Development Core Team; 2016. |
| 27 |
Baltarowich O, Goldberg BB, Wilkes AN, Anane-Firempong A, Veloski JJ. Effectiveness of “teaching the teachers” initiative for ultrasound training in Africa1. Acad Radiol. 2009;16(6):758-62.
doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2008.12.023 |
| 28 |
Kawooya M. Training for rural radiology and imaging in sub-saharan africa: addressing the mismatch between services and population. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2012;2:37.
doi: 10.4103/2156-7514.97747 pmid: 22919551 |
| [1] | Sagar Shah, Steven Tohmasi, Emily Frisch, Amanda Anderson, Roy Almog, Shadi Lahham, Roland Bingisser, John C. Fox. A comparison of simulation versus didactics for teaching ultrasound to Swiss medical students [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(3): 169-176. |
| [2] | Alexander S. Kwon, Shadi Lahham, John C. Fox. Can an 8th grade student learn point of care ultrasound? [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2019, 10(2): 109-113. |
| [3] | Annasha Vyas, Katherine Moran, Joshua Livingston, Savannah Gonzales, Marlene Torres, Ali Duffens, Carina Mireles Romo, Genevieve Mazza, Briana Livingston, Shadi Lahham, John Christian Fox. Feasibility study of minimally trained medical students using the Rural Obstetrical Ultrasound Triage Exam (ROUTE) in rural Panama [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(3): 216-222. |
| [4] | Jonathan B. Lee, Christina Tse, Thomas Keown, Michael Louthan, Christopher Gabriel, Alexander Anshus, Bima Hasjim, Katrina Lee, Esther Kim, Luke Yu, Allen Yu, Shadi Lahham, Steven Bunch, Maili Alvarado, Abdulatif Gari, John C. Fox. Evaluation of a point of care ultrasound curriculum for Indonesian physicians taught by first-year medical students [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(4): 281-286. |
| [5] | Allen R. Yu, Bima Hasjim, Luke E. Yu, Christopher Gabriel, Alexander Anshus, Jonathan B. Lee, Michael J. Louthan, Esther C. Kim, Katrina Lee, Christina Tse, Thomas Keown, Shadi Lahham, Maili Alvarado, Steven Bunch, Abdulatif Gari, J. Christian Fox. Comparison of ultrasound-measured properties of the common carotid artery to tobacco smoke exposure in a cohort of Indonesian patients [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(3): 177-183. |
| [6] | Maria Barsky, Lauren Kushner, MeganAnsbro, Kate Bowman, Michael Sassounian, Kevin Gustafson, Shadi Lahham, Linda Joseph, John C Fox. A feasibility study to determine if minimally trained medical students can identify markers of chronic parasitic infection using bedside ultrasound in rural Tanzania [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(4): 293-298. |
| [7] | Yuanting Zha, Michelle Zhou, Anjali Hari, Bradley Jacobsen, Neha Mitragotri, Bianca Rivas, Olga Gabriela Ventura, Janice Boughton, John Christian Fox. Ultrasound diagnosis of malaria: examination of the spleen, liver, and optic nerve sheath diameter [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 10-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
