World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2020, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (4): 223-230.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2020.04.004
Special Issue: Sepsis
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Miao Yuan1, Ding-yi Yan2, Fang-shi Xu1, Yi-di Zhao1, Yang Zhou1, Long-fei Pan1( )
)
Received:2019-08-06
Accepted:2020-04-02
Online:2020-10-01
Published:2020-10-01
Contact:
Long-fei Pan
E-mail:longfei_pan123@163.com
Miao Yuan, Ding-yi Yan, Fang-shi Xu, Yi-di Zhao, Yang Zhou, Long-fei Pan. Effects of sepsis on hippocampal volume and memory function[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 223-230.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2020.04.004
Table 1
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with sepsis and healthy controls
| Parameters | Sepsis patients (n=20) | Healthy people (n=20) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F:M) | 8:12 | 9:11 | 0.749 |
| Age (years) | 57.60±3.46 | 55.80±4.41 | 0.159 |
| Education (years) | 13.50±5.12 | 12.70±4.87 | 0.616 |
| LVEF | 0.52±0.27 | 0.58±0.32 | 0.525 |
| Hypertersion (Y:N) | 9:11 | 10:10 | 0.752 |
| DM (Y:N) | 12:8 | 10:10 | 0.525 |
| CHD (Y:N) | 4:16 | 5:15 | 0.705 |
| Smoking (Y:N) | 12:8 | 16:4 | 0.168 |
| NSAID use (Y:N) | 3:17 | 1:19 | 0.292 |
| APACHE II score | 11.85 | 0 | - |
Figure 1.
Results of clinical neuropsychological tests of different cognitive region functions between the two groups. WAIS-III: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-III; HVOT: Hooper Visual Organization Test; CVLT: California Verbal Learning Test; WCST: Wisconsin Card Sorting Test; PASAT: Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test; PDP: process dissociation procedure.
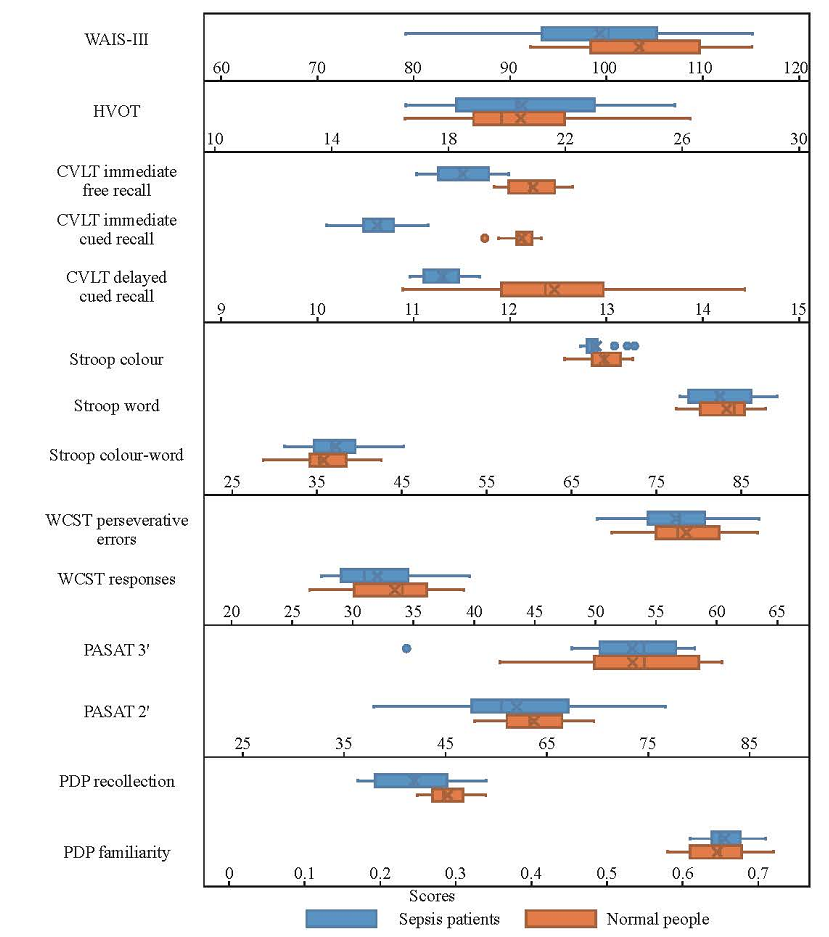
Table 2
The volume of different brain regions (mm3)
| Parameters | Sepsis patients (n=20) | Healthy people (n=20) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left hippocampal subfields | |||
| Whole hippocampus | 3,259.72±330.42 | 3,476.74±292.90 | 0.034 |
| Subiculum | 432.18±108.56 | 428.61±119.28 | 0.921 |
| CA1 | 605.17±98.76 | 629.19±91.67 | 0.430 |
| Presubiculum | 254.18±61.79 | 308.78±79.61 | 0.020 |
| Parasubiculum | 72.89±14.72 | 76.54±19.61 | 0.510 |
| CA3 | 241.65±58.67 | 274.63±62.31 | 0.093 |
| CA4 | 286.19±72.06 | 291.03±68.47 | 0.829 |
| Hippo-amyg transitional area | 65.23±31.76 | 67.21±24.89 | 0.827 |
| Molecular layer | 576.87±101.27 | 591.72±98.16 | 0.640 |
| Granule dentate gyrus cell layer | 309.72±65.43 | 321.58±71.86 | 0.588 |
| Right hippocampal subfields | |||
| Whole hippocampus | 3,090.40±347.39 | 3,367.58±301.87 | 0.010 |
| Subiculum | 418.76±108.53 | 461.72±107.65 | 0.216 |
| CA1 | 654.92±103.68 | 701.75±115.48 | 0.185 |
| Presubiculum | 308.72±95.46 | 392.87±86.78 | 0.005 |
| Parasubiculum | 61.65±31.76 | 67.82±29.74 | 0.530 |
| CA3 | 239.74±81.65 | 261.76±76.49 | 0.384 |
| CA4 | 254.82±107.83 | 286.65±132.74 | 0.410 |
| Hippo-amyg transitional area | 74.73±42.69 | 78.64±34.73 | 0.752 |
| Molecular layer | 599.78±98.67 | 621.76±107.64 | 0.505 |
| Granule dentate gyrus cell layer | 317.95±98.65 | 348.69±87.69 | 0.304 |
| Left subcortical segmentation | |||
| Thalamus | 7,243.76±498.57 | 6,935.64±512.87 | 0.061 |
| Caudate | 3,395.46±329.58 | 3,492.76±312.75 | 0.344 |
| Putamen | 5,349.82±806.63 | 5,437.65±798.67 | 0.731 |
| Pallidum | 1,498.47±419.54 | 1,529.03±452.93 | 0.826 |
| Amygdala | 1,743.67±489.73 | 1,728.44±521.64 | 0.925 |
| Ventral diencephalon | 3,598.43±112.54 | 3,655.64±101.65 | 0.100 |
| Right subcortical segmentation | |||
| Thalamus | 6,291.64±776.84 | 5,921.56±881.42 | 0.167 |
| Caudate | 3,154.87±89.76 | 3,345.26±92.65 | 0.089 |
| Putamen | 5,083.46±119.47 | 5,143.65±121.65 | 0.123 |
| Pallidum | 1,327.65±64.53 | 1,293.64±72.47 | 0.125 |
| Amygdala | 1,873.45±175.94 | 1,908.82±216.72 | 0.574 |
| Ventral diencephalon | 3,728.59±433.29 | 3,892.39±397.28 | 0.220 |
| 1 |
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017; 43(3):1-74.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-016-4523-0 |
| 2 |
Sprung CL, Peduzzi PN, Shatney CH, Schein RM, Wilson MF, Sheagren JN, et al. Impact of encephalopathy on mortality in the sepsis syndrome. The Veterans Administration Systemic Sepsis Cooperative Study Group. Crit Care Med. 1990; 18(8):801-6.
doi: 10.1097/00003246-199008000-00001 pmid: 2379391 |
| 3 |
Young GB, Bolton CF, Austin TW, Archibald YM, Gonder J, Wells GA. The encephalopathy associated with septic illness. Clin Invest Med. 1990; 13(6):297-304.
pmid: 2078909 |
| 4 | Chaudhry N, Duggal AK. Sepsis associated encephalopathy. Adv Med. 2014; 2014(3):195-204. |
| 5 |
Papadopoulos MC, Davies DC, Moss RF, Tighe D, Bennett ED. Pathophysiology of septic encephalopathy: a review. Crit Care Med. 2000; 28(8):3019-24.
doi: 10.1097/00003246-200008000-00057 pmid: 10966289 |
| 6 | Schramm P, Klein KU, Falkenberg L, Berres M, Closhen D, Werhahn KJ, et al. Impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation in patients with severe sepsis and sepsis-associated delirium. Crit Care. 2012; 16(5):1-8. |
| 7 | Polito A, Eischwald F, Maho AL, Polito A, Azabou E, Annane D, et al. Pattern of brain injury in the acute setting of human septic shock. Crit Care. 2013; 17(5):1-9. |
| 8 |
Sutter R, Kaplan PW. Clinical and imaging correlates of EEG patterns in hospitalized patients with encephalopathy. J Neurol. 2013; 260(4):1087-98.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-012-6766-1 |
| 9 |
Pandharipande PP, Sanders RD, Girard TD, McGrane S, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on outcome in sepsis patients: an a priori-designed analysis of the MENDS randomized controlled trial. Crit Care. 2010; 14(2):R38.
doi: 10.1186/cc8916 pmid: 20233428 |
| 10 |
De Backer D, Donadello K, Sakr Y, Ospina-Tascon G, Salgado D, Scolletta S, et al. Microcirculatory alterations in patients with severe sepsis: impact of time of assessment and relationship with outcome. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41(3):791-9.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182742e8b pmid: 23318492 |
| 11 |
Taccone FS, Castanares-Zapatero D, Peres-Bota D, Vincent JL, Berre J, Melot C. Cerebral autoregulation is influenced by carbon dioxide levels in patients with septic shock. Neurocrit Care. 2010; 12(1):35.
doi: 10.1007/s12028-009-9289-6 |
| 12 |
Terborg C, Schummer W, Albrecht M, Reinhart K, Weiller C, Röther J. Dysfunction of vasomotor reactivity in severe sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2001; 27(7):1231-4.
doi: 10.1007/s001340101005 pmid: 11534574 |
| 13 |
Pfister D, Siegemund M, Dell-Kuster S, Smielewski P, Rüegg S, Strebel SP, et al. Cerebral perfusion in sepsis-associated delirium. Crit Care. 2008; 12(3):R63.
doi: 10.1186/cc6891 pmid: 18457586 |
| 14 |
Schmidt-Kastner R, Freund TF. Selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia. Neuroscience. 2015; 309(3):259-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.034 |
| 15 |
Girard TD, Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Delirium as a predictor of long-term cognitive impairment in survivors of critical illness. Crit Care Med. 2016; 38(7):1513.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181e47be1 pmid: 20473145 |
| 16 |
Chou CH, Lee JT, Lin CC, Sung YF, Lin CC, Muo CH, et al. Septicemia is associated with increased risk for dementia: a population-based longitudinal study. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(48):84300-8.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20899 pmid: 29137424 |
| 17 |
Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM, Langa KM. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA. 2010; 304(16):1787.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1553 pmid: 20978258 |
| 18 |
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985; 13(10):818-29.
pmid: 3928249 |
| 19 |
Keilp JG, Corbera K, Slavov I, Taylor MJ, Sackeim HA, Fallon BA. WAIS-III and WMS-III performance in chronic Lyme disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2006; 12(1):119-29.
doi: 10.1017/S1355617706060231 pmid: 16433951 |
| 20 |
Su CY, Lin YH, Wu YY, Wuang YP. Development of the Chinese version of the Hooper Visual Organization Test: normative data. Int J Rehabil Res. 2013; 36(1):56-67.
doi: 10.1097/MRR.0b013e3283588b95 |
| 21 |
Woods SP, Delis DC, Scott JC, Kramer JH, Holdnack JA. The California Verbal Learning Test-second edition: test-retest reliability, practice effects, and reliable change indices for the standard and alternate forms. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2006; 21(5):413-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.acn.2006.06.002 pmid: 16843636 |
| 22 |
Stroop JR. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J Exp Psychol. 1935; 18(6):643.
doi: 10.1037/h0054651 |
| 23 |
MacAllister WS, Maiman M, Marsh M, Whitman L, Vasserman M, Cohen RJ, et al. Sensitivity of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (64-Card Version) versus the Tower of London (Drexel Version) for detecting executive dysfunction in children with epilepsy. Child Neuropsychol. 2018; 24(3):354-69.
doi: 10.1080/09297049.2016.1265101 pmid: 28049367 |
| 24 |
Diehr MC, Cherner M, Wolfson TJ, Miller SW, Grant I, Heaton RK, et al. The 50- and 100-item short forms of the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Task (PASAT): demographically corrected norms and comparisons with the full PASAT in normal and clinical samples. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2003; 25(4):571-85.
doi: 10.1076/jcen.25.4.571.13876 pmid: 12911108 |
| 25 |
Jacoby LL. A process dissociation framework: separating automatic from intentional uses of memory. J Mem Lang. 1991; 30(5):513-41.
doi: 10.1016/0749-596X(91)90025-F |
| 26 |
Fischl B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage. 2012; 62(2):774-81.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.021 |
| 27 |
Yaffe K, Fox P, Newcomer R, Sands L, Lindquist K, Dane K, et al. Patient and caregiver characteristics and nursing home placement in patients with dementia. JAMA. 2002; 287(16):2090.
doi: 10.1001/jama.287.16.2090 pmid: 11966383 |
| 28 |
Azabou E, Magalhaes E, Braconnier A, Yahiaoui L, Moneger G, Heming N, et al. Early standard electroencephalogram abnormalities predict mortality in septic intensive care unit patients. PLoS One. 2015; 10(10):e0139969.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139969 pmid: 26447697 |
| 29 |
Dunn N, Mullee M, Perry VH, Holmes C. Association between dementia and infectious disease: evidence from a case-control study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2005; 19(2):91.
doi: 10.1097/01.wad.0000165511.52746.1f pmid: 15942327 |
| 30 |
Winters BD, Eberlein M, Leung J, Needham DM, Pronovost PJ, Sevransky JE. Long-term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care Med. 2010; 38(5):1276.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181d8cc1d pmid: 20308885 |
| 31 |
Duncan K, Ketz N, Inati SJ, Davachi L. Evidence for area CA1 as a match/mismatch detector: a high-resolution fMRI study of the human hippocampus. Hippocampus. 2012; 22(3):389-98.
doi: 10.1002/hipo.20933 |
| 32 |
Yende S, Angus DC. Long-term outcomes from sepsis. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2007; 9(5):382.
doi: 10.1007/s11908-007-0059-3 |
| 33 |
Huang Y, Chen J, Zhong S, Yuan J. Role of APACHE II scoring system in the prediction of severity and outcome of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Int J Neurosci. 2016; 126(11):1020-4.
doi: 10.3109/00207454.2015.1099099 pmid: 26393395 |
| 34 |
Wixted JT, Squire LR. The role of the human hippocampus in familiarity-based and recollection-based recognition memory. Behav Brain Res. 2010; 215(2):197-208.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.04.020 pmid: 20412819 |
| 35 |
Kafkas A, Montaldi D. Familiarity and recollection produce distinct eye movement, pupil and medial temporal lobe responses when memory strength is matched. Neuropsychologia. 2012; 50(13):3080-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.08.001 |
| [1] | Ji Yong Jung, Ji Ung Na, Sang Kuk Han, Pil Cho Choi, Jang Hee LEE, Dong Hyuk Shin. Differential diagnoses of magnetic resonance imaging for suspected acute appendicitis in pregnant patients [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(1): 26-32. |
| [2] | Jian-min Li, Pan Zhang, Ya-ning Zhao, Chang-xiang Chen, Shu-xing Li. Protective effects of edaravone on diffuse brain injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011, 2(3): 222-227. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
