World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2020, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (1): 18-26.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2020.01.003
Special Issue: Sepsis
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yi-wen Fan, Shao-wei Jiang, Jia-meng Chen, Hui-qi Wang, Dan Liu, Shu-ming Pan( ), Cheng-jin Gao(
), Cheng-jin Gao( )
)
Online:2020-01-01
Published:2020-01-01
Contact:
Shu-ming Pan,Cheng-jin Gao
E-mail:panshuming@xinhuamed.com.cn;gaochengjin@xinhuamed.com.cn
Yi-wen Fan, Shao-wei Jiang, Jia-meng Chen, Hui-qi Wang, Dan Liu, Shu-ming Pan, Cheng-jin Gao. A pulmonary source of infection in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury leads to a worse outcome and poor recovery of kidney function[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(1): 18-26.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2020.01.003
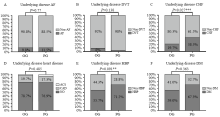
Figure 1.
Comparisons between the OG and PG groups with respect to underlying diseases. OG: other sources infection group; PG: pulmonary infection group; AF: atrial fibrillation; DVT: deep-vein thrombosis; CHF: chronic heart failure; ACS: acute coronary syndrome; CAD: coronary atherosclerotic heart disease; HBP: high blood pressure; DM: diabetes mellitus; CKD: chronic kidney disease; **: using χ2 test, means P<0.1; ***: using χ2 test, means P<0.05.

Table 1
Baseline data
| Variables | Counts | Mean±SD | Median | Percentage in total patients (n=113) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(year) | 72.49±12.25 | 74.00 | ||
| Age group (n) | ||||
| ≤60 | 15 | 13.3 | ||
| >60, <80 | 60 | 53.1 | ||
| ≥80 | 38 | 33.6 | ||
| Gender (n) | ||||
| Male | 63 | 55.8 | ||
| Female | 50 | 44.2 | ||
| Blood routine tests | ||||
| WBC (×109) | 15.49±7.91 | 15.30 | ||
| Percent of the lymphocytes (%) | 6.46±5.09 | 5.10 | ||
| Percent of the neutrophil (%) | 87.60±8.22 | 89.80 | ||
| NLR | 24.07±20.57 | 18.00 | ||
| PLT (×109) | 128.11±75.49 | 123.5 | ||
| APACHE II on admission | 19.96±7.10 | 20 | ||
| SOFA on admission | 7.14±3.75 | 6 | ||
| KDIGO (n) | ||||
| KDIGO 2 | 50 | 44.2 | ||
| KDIGO 3 | 63 | 55.8 | ||
| RRT | 38 | 33.6 | ||
| Death (n) | 44 | 38.9 | ||
| Death time (n=44) | 15.11±18.03 | 9.5 | ||
| Renal recovery at 90 days from ICU admission (n) | ||||
| Full recovery | 52 | 46 | ||
| Partial recovery | 35 | 31 | ||
| Non-recovery | 26 | 23 |
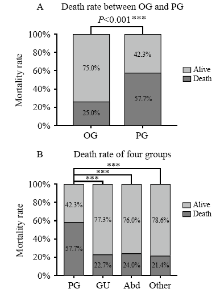
Figure 2.
Comparison of the mortality rate between the OG and PG groups and across the four groups. PG: pulmonary infection group; GU: genitourinary infection group; Abd: abdominal infection; Other: other sources of infection including blooding, etc. ***: using χ2 test, means P<0.05 (A); ***: one way ANOVA analysis post hoc, using LSD method, means P<0.05 (B).
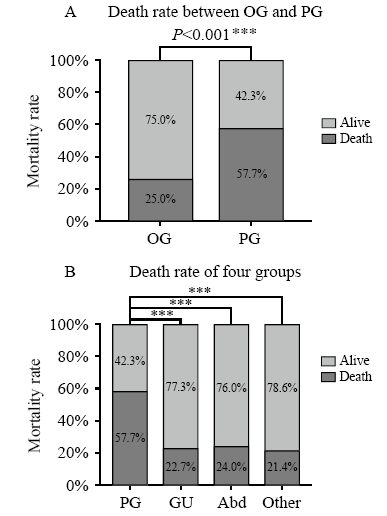
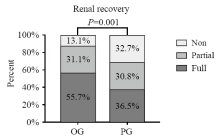
Figure 5.
Comparison of renal recovery between OG and PG groups. Non: non-recovery patients; partial: partial renal recovery patients; full: full renal recovery patients. The P value was the result of Wilcoxon rank sum test, and we assigned “full” as a value of 1,“partial” a value of 2, and “non” a value of 3.
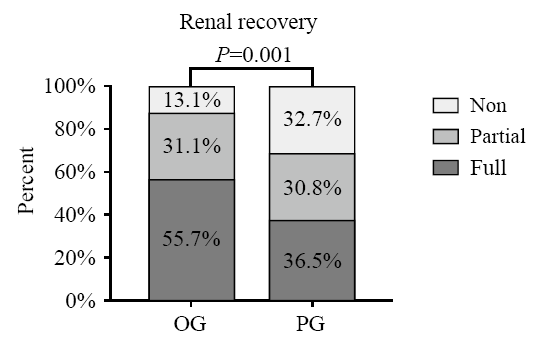
Table 3
The comparison of baseline for OG and PG
| Variables | OG (n=61) | PG (n=52) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (n) | 0.057 | ||
| Male | 29 | 34 | |
| Female | 32 | 18 | |
| Age(±SD) | 70.75±12.85 | 74.52±11.28 | 0.104 |
| Urea on admission (mmol/L) | 22.48±13.65 | 20.39±10.23 | 0.365 |
| Creatinine on admission (μmol/L) | 341.53±227.83 | 271.07±155.08 | 0.062 |
| APACHE II on admission | 19.10±6.85 | 20.96±7.32 | 0.166 |
| SOFA on admission | 7.16±3.49 | 7.12±4.06 | 0.946 |
| Blood routine tests | |||
| WBC (×109) | 16.85±8.18 | 13.88±7.32 | 0.046 |
| Percent of the lymphocytes (%) | 6.36±5.84 | 6.59±4.10 | 0.806 |
| Percent of the neutrophil (%) | 87.94±8.71 | 87.20±7.66 | 0.637 |
| NLR | 28.50±24.7 | 18.85±12 | 0.01 |
| PLT (×109) | 116.72±72.73 | 141.25±77.16 | 0.086 |
| Shock (n) | 0.037 | ||
| No | 33 | 38 | |
| Yes | 28 | 14 |
| 1 |
Siew ED, Deger SM. Recent advances in acute kidney injury epidemiology. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012; 21(3):309-17.
doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283521d95 pmid: 22449946 |
| 2 |
Poukkanen M, Vaara ST, Pettila V, Kaukonen KM, Korhonen AM, Hovilehto S, et al. Acute kidney injury in patients with severe sepsis in Finnish Intensive Care Units. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2013; 57(7):863-872.
doi: 10.1111/aas.12133 pmid: 23713703 |
| 3 |
Koyner JL. Assessment and diagnosis of renal dysfunction in the ICU. Chest. 2012; 141(6):1584-94.
doi: 10.1378/chest.11-1513 |
| 4 |
Fan PC, Chang CH, Tsai MH, Lin SM, Jenq CC, Hsu HH, et al. Predictive value of acute kidney injury in medical intensive care patients with sepsis originating from different infection sites. Am J Med Sci. 2012; 344(2):83-9.
doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3182373d36 |
| 5 |
Sood M, Mandelzweig K, Rigatto C, Tangri N, Komenda P, Martinka G, et al. Non-pulmonary infections but not specific pathogens are associated with increased risk of AKI in septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2014; 40(8):1080-8.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3361-1 pmid: 24981956 |
| 6 |
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315(8):801-10.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 pmid: 26903338 |
| 7 |
Brower RG, Matthay MA, Morris A, Schoenfeld D, Thompson BT, Wheeler A. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342(18):1301-8.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM200005043421801 pmid: 10793162 |
| 8 |
Zahar JR, Timsit JF, Garrouste-Orgeas M, Francais A, Vesin A, Descorps-Declere A, et al. Outcomes in severe sepsis and patients with septic shock: pathogen species and infection sites are not associated with mortality. Crit Care Med. 2011; 39(8):1886-95.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821b827c pmid: 21516036 |
| 9 |
Chambers KA, Park AY, Banuelos RC, Darger BF, Akkanti BH, Macaluso A, et al. Outcomes of severe sepsis and septic shock patients after stratification by initial lactate value. World J Emerg Med. 2018; 9(2):113-7.
pmid: 29576823 |
| 10 |
Ferrer R, Artigas A, Suarez D, Palencia E, Levy MM, Arenzana A, et al. Effectiveness of treatments for severe sepsis: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180(9):861-6.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.200812-1912OC pmid: 19696442 |
| 11 |
Yoshida J, Furugaki K, Oyama M. Perioperative antimicrobials in chest surgery patients positive for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 58(12):657-9.
doi: 10.1007/s11748-009-0582-2 pmid: 21170640 |
| 12 |
Shorr AF, Bernard GR, Dhainaut JF, Russell JR, Macias WL, Nelson DR, et al. Protein C concentrations in severe sepsis: an early directional change in plasma levels predicts outcome. Crit Care. 2006; 10(3):R92.
doi: 10.1186/cc4946 pmid: 16780598 |
| 13 |
Ahuja N, Andres-Hernando A, Altmann C, Bhargava R, Bacalja J, Webb RG, et al. Circulating IL-6 mediates lung injury via CXCL1 production after acute kidney injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012; 303(6):F864-F872.
doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00025.2012 |
| 14 |
Bhargava R, Janssen W, Altmann C, Andres-Hernando A, Okamura K, Vandivier RW, et al. Intratracheal IL-6 protects against lung inflammation in direct, but not indirect, causes of acute lung injury in mice. PLoS One. 2013; 8(5):e61405.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061405 pmid: 23667439 |
| 15 |
Leligdowicz A, Dodek PM, Norena M, Wong H, Kumar A, Kumar A, et al. Association between source of infection and hospital mortality in patients who have septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 189(10):1204-13.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201310-1875OC pmid: 24635548 |
| 16 |
Volakli E, Spies C, Michalopoulos A, Groeneveld AB, Sakr Y, Vincent JL. Infections of respiratory or abdominal origin in ICU patients: what are the differences? Crit Care. 2010; 14(2):R32.
doi: 10.1186/cc8909 pmid: 20230620 |
| 17 |
Nielsen SL, Roder B, Magnussen P, Engquist A, Frimodt-Moller N. Nosocomial pneumonia in an intensive care unit in a Danish university hospital: incidence, mortality and etiology. Scand J Infect Dis. 1992; 24(1):65-70.
doi: 10.3109/00365549209048402 pmid: 1589727 |
| 18 |
Arumugam SK, Mudali I, Strandvik G, El-Menyar A, Al-Hassani A, Al-Thani H. Risk factors for ventilator-associated pneumonia in trauma patients: A descriptive analysis. World J Emerg Med. 2018; 9(3):203-10.
pmid: 29796145 |
| 19 |
Rello J, Jubert P, Valles J, Artigas A, Rue M, Niederman MS. Evaluation of outcome for intubated patients with pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 23(5):973-98.
doi: 10.1093/clinids/23.5.973 pmid: 8922788 |
| 20 |
Stevens RM, Teres D, Skillman JJ, Feingold DS. Pneumonia in an intensive care unit. A 30-month experience. Arch Intern Med. 1974; 134(1):106-11.
pmid: 4365670 |
| 21 |
Palevsky PM, Liu KD, Brophy PD, Chawla LS, Parikh CR, Thakar CV, et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013; 61(5):649-72.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.02.349 |
| 22 |
Chawla LS, Bellomo R, Bihorac A, Goldstein SL, Siew ED, Bagshaw SM, et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery:consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 workgroup. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2017; 13(4):241-57.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.2 pmid: 28239173 |
| 23 |
Esper AM, Moss M, Lewis CA, Nisbet R, Mannino DM, Martin GS. The role of infection and comorbidity: Factors that influence disparities in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34(10):2576-82.
doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000239114.50519.0E pmid: 16915108 |
| 24 |
Vincent JL, Rello J, Marshall J, Silva E, Anzueto A, Martin CD, et al. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA. 2009; 302(21):2323-9.
pmid: 19952319 |
| 25 |
Awad AS, Okusa MD. Distant organ injury following acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007; 293(1):F28-F29.
doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00159.2007 pmid: 17429033 |
| 26 |
Darmon M, Clec'h C, Adrie C, Argaud L, Allaouchiche B, Azoulay E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and risk of AKI among critically ill patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014; 9(8):1347-53.
doi: 10.2215/CJN.08300813 pmid: 24875195 |
| 27 | Peng Q, Zhang L, Ai Y, Zhang L. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in intensive care septic patients based on the KDIGO guidelines. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014; 127(10):1820-26. |
| 28 |
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care Med. 2008; 34(1):17-60.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0934-2 pmid: 18058085 |
| 29 |
Carrigan SD, Scott G, Tabrizian M. Toward resolving the challenges of sepsis diagnosis. Clin Chem. 2004; 50(8):1301-14.
doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2004.032144 pmid: 15166107 |
| 30 |
Van Amersfoort ES, Van Berkel TJ, Kuiper J. Receptors, mediators, and mechanisms involved in bacterial sepsis and septic shock. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003; 16(3):379-414.
doi: 10.1128/cmr.16.3.379-414.2003 pmid: 12857774 |
| 31 |
Barbar SD, Binquet C, Monchi M, Bruyere R, Quenot JP. Impact on mortality of the timing of renal replacement therapy in patients with severe acute kidney injury in septic shock: the IDEAL-ICU study (initiation of dialysis early versus delayed in the intensive care unit): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2014; 15:270.
doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-270 pmid: 24998258 |
| 32 |
Kuiper JW, Groeneveld AB, Slutsky AS, Plotz FB. Mechanical ventilation and acute renal failure. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33(6):1408-15.
doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000165808.30416.ef pmid: 15942363 |
| 33 |
Parra ER, Kairalla RA, Ribeiro de Carvalho CR, Eher E, Capelozzi VL. Inflammatory cell phenotyping of the pulmonary interstitium in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Respiration. 2007; 74(2):159-69.
doi: 10.1159/000097133 |
| 34 |
Liu YC, Qi YM, Zhang H, Walline J, Zhu HD. A survey of ventilation strategies during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. World J Emerg Med. 2019; 10(4):222-7.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2019.04.005 pmid: 31534596 |
| 35 |
Ranieri VM, Suter PM, Tortorella C, De Tullio R, Dayer JM, Brienza A, et al. Effect of mechanical ventilation on inflammatory mediators in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999; 282:54-61.
doi: 10.1001/jama.282.1.54 pmid: 10404912 |
| 36 |
Liu KD, Glidden DV, Eisner MD, Parsons PE, Ware LB, Wheeler A, et al. Predictive and pathogenetic value of plasma biomarkers for acute kidney injury in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2007; 35(12):2755-61.
pmid: 18074478 |
| [1] | Li-wei Duan, Jin-long Qu, Jian Wan, Yong-hua Xu, Yi Shan, Li-xue Wu, Jin-hao Zheng, Wei-wei Jiang, Qi-tong Chen, Yan Zhu, Jian Zhou, Wen-bo Yu, Lei Pei, Xi Song, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Effects of viral infection and microbial diversity on patients with sepsis: A retrospective study based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(1): 29-35. |
| [2] | Hai-jiang Zhou, Tian-fei Lan, Shu-bin Guo. Outcome prediction value of National Early Warning Score in septic patients with community-acquired pneumonia in emergency department: A single-center retrospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 206-215. |
| [3] | Yu-ming Wang, Yan-jun Zheng, Ying Chen, Yun-chuan Huang, Wei-wei Chen, Ran Ji, Li-li Xu, Zhi-tao Yang, Hui-qiu Sheng, Hong-ping Qu, En-qiang Mao, Er-zhen Chen. Effects of fluid balance on prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients secondary to sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 216-222. |
| [4] | Miao Yuan, Ding-yi Yan, Fang-shi Xu, Yi-di Zhao, Yang Zhou, Long-fei Pan. Effects of sepsis on hippocampal volume and memory function [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 223-230. |
| [5] | Wen-peng Yin, Jia-bao Li, Xiao-fang Zheng, Le An, Huan Shao, Chun-sheng Li. Effect of neutrophil CD64 for diagnosing sepsis in emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 79-86. |
| [6] | Shao-hua Liu, Huo-yan Liang, Hong-yi Li, Xian-fei Ding, Tong-wen Sun, Jing Wang. Effect of low high-density lipoprotein levels on mortality of septic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 109-116. |
| [7] | Kimberly A. Chambers, Adam Y. Park, Rosa C. Banuelos, Bryan F. Darger, Bindu H. Akkanti, Annamaria Macaluso, Manoj Thangam, Pratik B. Doshi. Outcomes of severe sepsis and septic shock patients after stratification by initial lactate value [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(2): 113-117. |
| [8] | Muhammad Akbar Baig, Hira Shahzad, Erfan Hussain, Asad Mian. Validating a point of care lactate meter in adult patients with sepsis presenting to the emergency department of a tertiary care hospital of a low- to middle-income country [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(3): 184-189. |
| [9] | Ming Wei, Yan-jie Gong, Ling Tu, Jia Li, Ying-hong Liang, Yi-hua Zhang. Expression of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and effects of inhibitor Wortmannin on expression of tumor necrosis factor-α in severe acute pancreatitis associated with acute lung injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(4): 299-304. |
| [10] | Chao Cao, Tao Ma, Yan-fen Chai, Song-tao Shou. The role of regulatory T cells in immune dysfunction during sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 5-9. |
| [11] | Zhi-wei Liu, Hai-ying Wang, Lan Guan, Bin Zhao. Regulatory effects of hydrogen sulfide on alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with acute lung injury [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 67-73. |
| [12] | Kun Chen, Qiu-xiang Zhou, Hong-wei Shan, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Prognostic value of CD4+CD25+ Tregs as a valuable biomarker for patients with sepsis in ICU [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 40-43. |
| [13] | Hui Fu, Qiao-sheng Wang, Qiong Luo, Si Tan, Hua Su, Shi-lin Tang, Zheng-liang Zhao, Li-ping Huang. Simvastatin inhibits apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by sepsis through upregulating the expression of Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(4): 291-297. |
| [14] | Qi Zou, Wei Wen, Xin-chao Zhang. Presepsin as a novel sepsis biomarker [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(1): 16-19. |
| [15] | Nishant Raj Pandey, Yu-yao Bian, Song-tao Shou. Significance of blood pressure variability in patients with sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(1): 42-47. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
