World Journal of Emergency Medicine ›› 2014, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (4): 291-297.doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.04.009
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hui Fu1, Qiao-sheng Wang1( ), Qiong Luo1, Si Tan2, Hua Su1, Shi-lin Tang1, Zheng-liang Zhao1, Li-ping Huang1
), Qiong Luo1, Si Tan2, Hua Su1, Shi-lin Tang1, Zheng-liang Zhao1, Li-ping Huang1
Received:2014-04-10
Accepted:2014-10-06
Online:2014-12-15
Published:2014-12-15
Contact:
Qiao-sheng Wang
E-mail:docwqs@163.com
Hui Fu, Qiao-sheng Wang, Qiong Luo, Si Tan, Hua Su, Shi-lin Tang, Zheng-liang Zhao, Li-ping Huang. Simvastatin inhibits apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by sepsis through upregulating the expression of Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax[J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(4): 291-297.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://wjem.com.cn//EN/10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2014.04.009
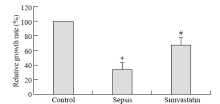
Figure 1.
The relative growth rate of HUVECs in each group was detected by MTT assay. The relative growth rate of HUVECs in both sepsis and simvastatin groups decreased significantly compared with the control group #P<0.05, *P<0.05). However, the relative growth rate of HUVECs increased in the simvastain group compared with the sepsis group (#P<0.05).

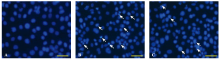
Figure 2.
Apoptosis was detected by staining with Hoechst 33342. The apoptosis of HUVECs showed that intensely condensed chromatin and/or fragmented nuclei in the cells were detected by fluorescence microscopy. The apoptosis increased significantly in the sepsis group (B) compared with the control group (A); however, the apoptosis in the simvastatin group (C) decreased significantly compared with the sepsis group. Scale bars: A-C, 20 μm.
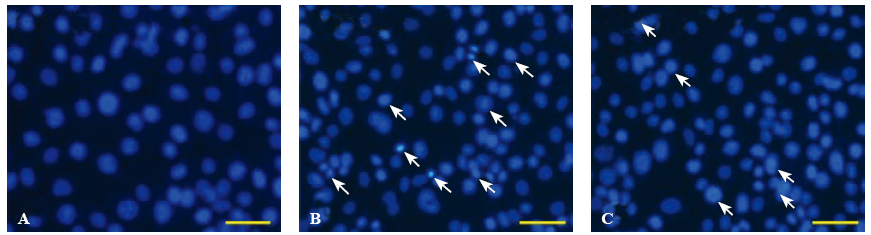
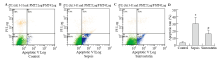
Figure 3.
Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry.The apoptosis of HUVECs increased significantly in the sepsis and simvastatin groups (B) compared with the control group (A); however, the apoptosis in the simvastatin group decreased significantly compared with the sepsis group (C). The apoptotic rate of HUVECs in both sepsis and simvastatin groups significantly increased compared with the control group (#P<0.05, *P<0.05). However, the apoptotic rate decreased in the simvastain group (#P<0.05) (D) compared with the sepsis group.
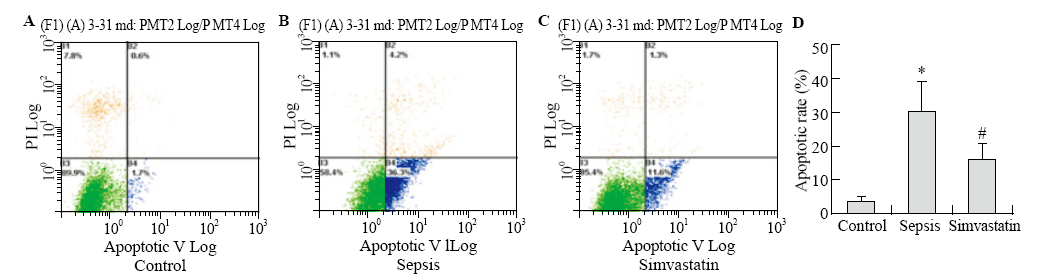

Figure 4.
Bcl-2 mRNA and Bax mRNA were detected respectively by RT-PCR in the two groups (A-D). A showed that the changes of density of Bcl-2 mRNA in the control group (band 1), the sepsis group (band 2) and the simvastatin group (band 3), respectively. The bar grah (C) showed that the optical density of Bcl-2 mRNA decreased in the sepsis group compared with the control group (*P<0.05) and the optical density of Bcl-2 Mrna increased in the simvastatin group compared with the sepsis group (#P<0.05). However, B showed that the changes of density of Bax mRNA in the control group (band 1), the sepsis group (band 2) and the simvastatin group (band 3), respectively. The bar grah (D) showed that the optical density of Bcl-2 mRNA increased in the sepsis group compared with the control group (*P<0.05) and that the opical density of Bcl-2 mRNA decreased in the simvastatin group compared with the sepsis group (#P<0.05).

| 1 |
Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Osuchowski MF, Valentine C, Kurosawa S, Remick DG. The pathogenesis of sepsis. Annu Rev Pathol 2011; 6:19-48.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130327 pmid: 20887193 |
| 2 |
Henneke P, Golenbock DT. Innate immune recognition of lipopolysaccharide by endothelial cells. Crit Care Med 2002; 30:S207-S213.
doi: 10.1097/00003246-200205001-00006 pmid: 12004237 |
| 3 |
Zhang FX, Kirschning CJ, Mancinelli R, Xu XP, Jin Y, Faure E, et al. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide activates nuclear factor-kappaB through interleukin-1 signaling mediators in cultured human dermal endothelial cells and mononuclear phagocytes. J Biol Chem 1999; 274:7611-7614.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.12.7611 pmid: 10075645 |
| 4 |
Aird WC. The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood 2003; 101:3765-3777.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1887 pmid: 12543869 |
| 5 |
Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE, Karl IE. Endothelial cell apoptosis in sepsis. Crit Care Med 2002; 30:S225-S228.
doi: 10.1097/00003246-200205001-00009 pmid: 12004240 |
| 6 |
Lindner H, Holler E, Ertl B, Multhoff G, Schreglmann M, Klauke I, et al. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells induce programmed cell death in human endothelial cells and may prevent repair: role of cytokines. Blood 1997; 89:1931-1938.
pmid: 9058713 |
| 7 |
Bombeli T, Karsan A, Tait JF, Harlan JM. Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells become procoagulant. Blood 1997; 89:2429-2442.
pmid: 9116287 |
| 8 |
Stefanec T. Endothelial apoptosis: could it have a role in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease? Chest 2000; 117:841-854.
doi: 10.1378/chest.117.3.841 pmid: 10713015 |
| 9 |
Weitz-Schmidt G, Welzenbach K, Brinkmann V, Kamata T, Kallen J, Bruns C, et al. Statins selectively inhibit leukocyte function antigen-1 by binding to a novel regulatory integrin site. Nat Med 2001; 7:687-692.
doi: 10.1038/89058 pmid: 11385505 |
| 10 |
Pruefer D, Makowski J, Dahm M, Guth S, Oelert H, Darius H, et al. Aprotinin inhibits leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions after hemorrhage and reperfusion. Ann Thorac Surg 2003; 75, 210-215, 215-216.
doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(02)04315-1 |
| 11 | Souza Neto JL, Araújo Filho I, Rego AC, Dominici VA, Azevedo IM, Egito ES, et al. Effects of simvastatin in abdominal sepsis in rats. Acta Cir Bras 2006; 21 Suppl 4: 8-12. |
| 12 |
Boyd AR, Hinojosa CA, Rodriguez PJ, Orihuela CJ. Impact of oral simvastatin therapy on acute lung injury in mice during pneumococcal pneumonia. BMC Microbiol 2012; 12:73.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-73 pmid: 22587610 |
| 13 |
Kono Y, Inomata M, Hagiwara S, Shiraishi N, Noguchi T, Kitano S. A newly synthetic vitamin E derivative, E-Ant-S-GS, attenuates lung injury caused by cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis in rats. Surgery 2012; 151:420-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.08.003 pmid: 22000829 |
| 14 |
Lee JG, Kay EP. Common and distinct pathways for cellular activities in FGF-2 signaling induced by IL-1beta in corneal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009; 50:2067-2076.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-3135 pmid: 19136710 |
| 15 |
Raju J, Bird RP. Energy restriction reduces the number of advanced aberrant crypt foci and attenuates the expression of colonic transforming growth factor beta and cyclooxygenase isoforms in Zucker obese (fa/fa) rats. Cancer Res 2003; 63:6595-6601.
pmid: 14583451 |
| 16 |
Darwish I, Liles WC. Emerging therapeutic strategies to prevent infection-related microvascular endothelial activation and dysfunction. Virulence 2013; 4:572-582.
doi: 10.4161/viru.25740 pmid: 23863603 |
| 17 |
Semeraro N, Ammollo CT, Semeraro F, Colucci M. Sepsis, thrombosis and organ dysfunction. Thromb Res 2012; 129:290-295.
doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.10.013 |
| 18 |
Calderari B, Liaudet L. Pathophysiological mechanisms of organ dysfunction in sepsis. Rev Med Suisse 2010; 6:2406-2409.
pmid: 21268420 |
| 19 |
Schouten M, Wiersinga WJ, Levi M, van der Poll T. Inflammation, endothelium, and coagulation in sepsis. J Leukoc Biol 2008; 83:536-545.
doi: 10.1189/jlb.0607373 pmid: 18032692 |
| 20 |
Matsuda N, Yamamoto S, Hatakeyama N, Hattori Y. Vascular endothelial dysfunction in septic shock. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi 2008; 131:96-100.
doi: 10.1254/fpj.131.96 pmid: 18277008 |
| 21 |
Boos CJ, Goon PK, Lip GY. The endothelium, inflammation, and coagulation in sepsis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2006; 79:20-22.
doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.10.004 pmid: 16413238 |
| 22 |
Meziani F, Delabranche X, Asfar P, Toti F. Bench-to-bedside review: circulating microparticles—a new player in sepsis? Crit Care 2010; 14:236.
doi: 10.1186/cc9231 pmid: 21067540 |
| 23 |
Walenta KL, Link A, Friedrich EB, Böhm M. Circulating microparticles in septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009; 180: 100, 100-101.
doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.180.1.100a pmid: 19535667 |
| 24 |
Wu ZH, Ji CL, Li H, Qiu GX, Gao CJ, Weng XS. Membrane microparticles and diseases. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2013; 17:2420-2427.
pmid: 24089218 |
| 25 |
Mason JC. The statins—therapeutic diversity in renal disease? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2005; 14:17-24.
doi: 10.1097/00041552-200501000-00004 pmid: 15586011 |
| 26 |
Epstein M, Campese VM. Pleiotropic effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors on renal function. Am J Kidney Dis 2005; 45:2-14.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2004.08.040 |
| 27 |
Khanal S, Attallah N, Smith DE, Kline-Rogers E, Share D, O'Donnell MJ, et al. Statin therapy reduces contrast-induced nephropathy: an analysis of contemporary percutaneous interventions. Am J Med 2005; 118:843-849.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.03.031 pmid: 16084176 |
| 28 |
Pierre-Paul D, Gahtan V. Noncholesterol-lowering effects of statins. Vasc Endovascular Surg 2003; 37:301-313.
doi: 10.1177/153857440303700501 pmid: 14528375 |
| 29 |
Ridker PM, Cannon CP, Morrow D, Rifai N, Rose LM, McCabe CH, et al. C-reactive protein levels and outcomes after statin therapy. N Engl J Med 2005; 352:20-28.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa042378 pmid: 15635109 |
| 30 |
Liappis AP, Kan VL, Rochester CG, Simon GL. The effect of statins on mortality in patients with bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 33:1352-1357.
doi: 10.1086/323334 pmid: 11565076 |
| 31 |
Kruger P, Fitzsimmons K, Cook D, Jones M, Nimmo G. Statin therapy is associated with fewer deaths in patients with bacteraemia. Intensive Care Med 2006; 32:75-79.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-005-2859-y pmid: 16283159 |
| 32 |
Almog Y, Shefer A, Novack V, Maimon N, Barski L, Eizinger M, et al. Prior statin therapy is associated with a decreased rate of severe sepsis. Circulation 2004; 110:880-885.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000138932.17956.F1 pmid: 15289367 |
| 33 |
Merx MW, Liehn EA, Graf J, van de Sandt A, Schaltenbrand M, Schrader J, et al. Statin treatment after onset of sepsis in a murine model improves survival. Circulation 2005; 112:117-124.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.502195 pmid: 15998696 |
| 34 |
Grommes J, Vijayan S, Drechsler M, Hartwig H, Mörgelin M, Dembinski R, et al. Simvastatin reduces endotoxin-induced acute lung injury by decreasing neutrophil recruitment and radical formation. PLoS One 2012; 7:e38917.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038917 pmid: 22701728 |
| 35 |
Yasuda H, Yuen PS, Hu X, Zhou H, Star RA. Simvastatin improves sepsis-induced mortality and acute kidney injury via renal vascular effects. Kidney Int 2006; 69:1535-1542.
doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000300 pmid: 16557230 |
| 36 |
La Mura V, Pasarín M, Meireles CZ, Miquel R, Rodríguez-Vilarrupla A, Hide D, et al. Effects of simvastatin administration on rodents with lipopolysaccharide-induced liver microvascular dysfunction. Hepatology 2013; 57:1172-1181.
doi: 10.1002/hep.26127 pmid: 23184571 |
| 37 |
Buerke U, Carter JM, Schlitt A, Russ M, Schmidt H, Sibelius U, et al. Apoptosis contributes to septic cardiomyopathy and is improved by simvastatin therapy. Shock 2008; 29:497-503.
doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e318142c434 pmid: 18598004 |
| 38 |
Pinheiro da Silva F, Nizet V. Cell death during sepsis: integration of disintegration in the inflammatory response to overwhelming infection. Apoptosis 2009; 14:509-521.
doi: 10.1007/s10495-009-0320-3 pmid: 19199035 |
| 39 |
Chittenden T, Harrington EA, O'Connor R, Flemington C, Lutz RJ, Evan GI, et al. Induction of apoptosis by the Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature 1995; 374:733-736.
doi: 10.1038/374733a0 pmid: 7715730 |
| 40 |
Schulz JB, Weller M, Moskowitz MA. Caspases as treatment targets in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Ann Neurol 1999; 45:421-429.
doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199904)45:4<421::aid-ana2>3.0.co;2-q pmid: 10211465 |
| 41 |
Du G, Song Y, Zhang T, Ma L, Bian N, Chen X, et al. Simvastatin attenuates TNFalpha induced apoptosis in endothelial progenitor cells via the upregulation of SIRT1. Int J Mol Med 2014; 34:177-182.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1740 |
| 42 |
Kim YC, Song SB, Lee SK, Park SM, Kim YS. The Nuclear Orphan Receptor NR4A1 is Involved in the Apoptotic Pathway Induced by LPS and Simvastatin in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Immune Netw 2014; 14:116-122.
doi: 10.4110/in.2014.14.2.116 pmid: 24851101 |
| [1] | Li-wei Duan, Jin-long Qu, Jian Wan, Yong-hua Xu, Yi Shan, Li-xue Wu, Jin-hao Zheng, Wei-wei Jiang, Qi-tong Chen, Yan Zhu, Jian Zhou, Wen-bo Yu, Lei Pei, Xi Song, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Effects of viral infection and microbial diversity on patients with sepsis: A retrospective study based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 12(1): 29-35. |
| [2] | Hai-jiang Zhou, Tian-fei Lan, Shu-bin Guo. Outcome prediction value of National Early Warning Score in septic patients with community-acquired pneumonia in emergency department: A single-center retrospective cohort study [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 206-215. |
| [3] | Yu-ming Wang, Yan-jun Zheng, Ying Chen, Yun-chuan Huang, Wei-wei Chen, Ran Ji, Li-li Xu, Zhi-tao Yang, Hui-qiu Sheng, Hong-ping Qu, En-qiang Mao, Er-zhen Chen. Effects of fluid balance on prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients secondary to sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 216-222. |
| [4] | Miao Yuan, Ding-yi Yan, Fang-shi Xu, Yi-di Zhao, Yang Zhou, Long-fei Pan. Effects of sepsis on hippocampal volume and memory function [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(4): 223-230. |
| [5] | Wen-peng Yin, Jia-bao Li, Xiao-fang Zheng, Le An, Huan Shao, Chun-sheng Li. Effect of neutrophil CD64 for diagnosing sepsis in emergency department [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 79-86. |
| [6] | Shao-hua Liu, Huo-yan Liang, Hong-yi Li, Xian-fei Ding, Tong-wen Sun, Jing Wang. Effect of low high-density lipoprotein levels on mortality of septic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(2): 109-116. |
| [7] | Yi-wen Fan, Shao-wei Jiang, Jia-meng Chen, Hui-qi Wang, Dan Liu, Shu-ming Pan, Cheng-jin Gao. A pulmonary source of infection in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury leads to a worse outcome and poor recovery of kidney function [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020, 11(1): 18-26. |
| [8] | Kimberly A. Chambers, Adam Y. Park, Rosa C. Banuelos, Bryan F. Darger, Bindu H. Akkanti, Annamaria Macaluso, Manoj Thangam, Pratik B. Doshi. Outcomes of severe sepsis and septic shock patients after stratification by initial lactate value [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 9(2): 113-117. |
| [9] | Yun Ge, Man Huang, Yue-feng Ma. The effects of microRNA-34a regulating Notch-1/NF-κB signaling pathway on lipopolysaccharide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(4): 292-296. |
| [10] | Muhammad Akbar Baig, Hira Shahzad, Erfan Hussain, Asad Mian. Validating a point of care lactate meter in adult patients with sepsis presenting to the emergency department of a tertiary care hospital of a low- to middle-income country [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2017, 8(3): 184-189. |
| [11] | Chao Cao, Tao Ma, Yan-fen Chai, Song-tao Shou. The role of regulatory T cells in immune dysfunction during sepsis [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 5-9. |
| [12] | Kun Chen, Qiu-xiang Zhou, Hong-wei Shan, Wen-fang Li, Zhao-fen Lin. Prognostic value of CD4+CD25+ Tregs as a valuable biomarker for patients with sepsis in ICU [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2015, 6(1): 40-43. |
| [13] | Guo-ming Zhang, Yu Wang, Tian-de Li, Xiao-yan Li, Shao-ping Su, Yuan-yuan Sun, Xiu-hua Liu. Post-conditioning with gradually increased reperfusion provides better cardioprotection in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 128-134. |
| [14] | Pei-ren Shan, Wei-wei Xu, Zhou-qing Huang, Jun Pu, Wei-jian Huang. Protective role of retinoid X receptor in H9c2 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in rats [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(2): 122-127. |
| [15] | Qi Zou, Wei Wen, Xin-chao Zhang. Presepsin as a novel sepsis biomarker [J]. World Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 5(1): 16-19. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
