Xuebijing improves intestinal microcirculation dysfunction in septic rats by regulating the VEGF-A/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
|
Xuebijing improves intestinal microcirculation dysfunction in septic rats by regulating the VEGF-A/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway |
| A-ling Tang, Yan Li, Li-chao Sun, Xiao-yu Liu, Nan Gao, Sheng-tao Yan, Guo-qiang Zhang |
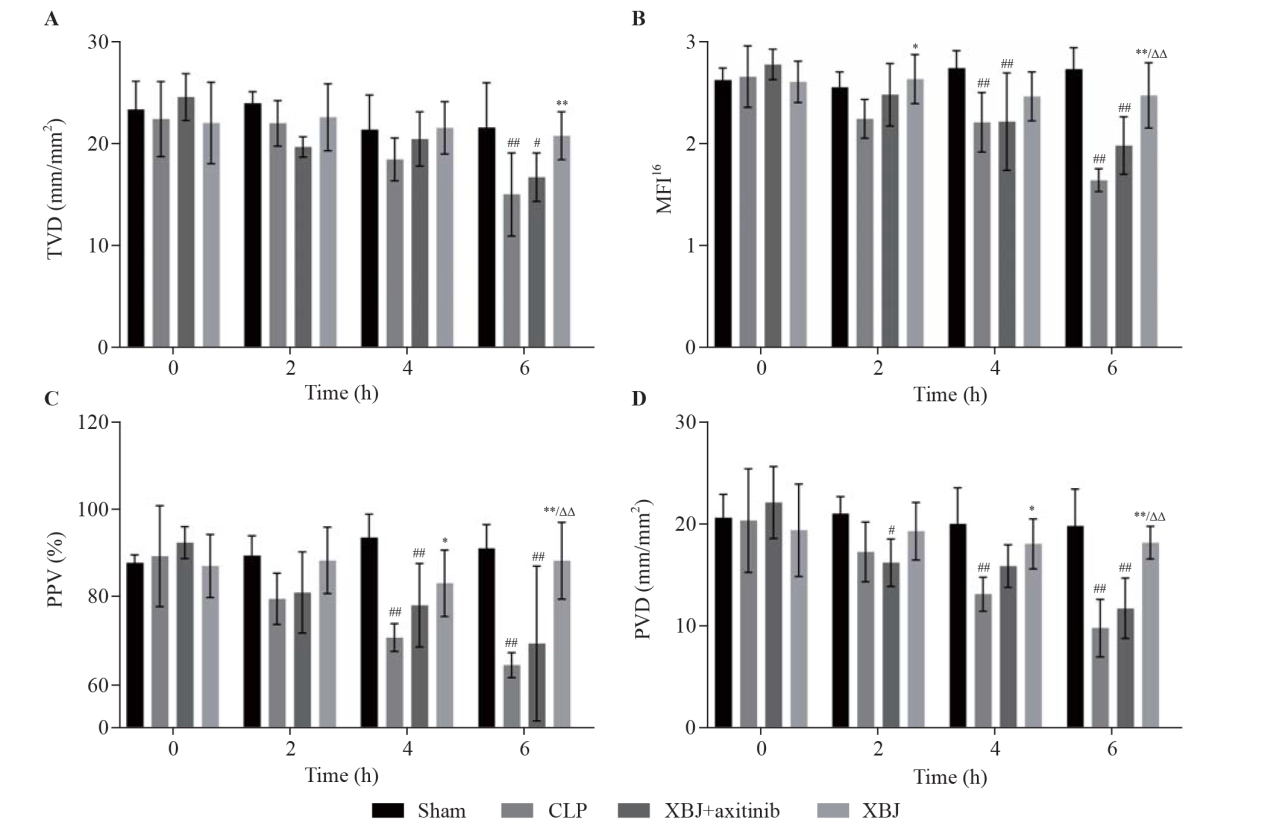
| Figure 1. Effects of XBJ on sepsis-induced disruption of intestinal microcirculation dysfunction (sample size for each group=6). A: total vessel density (TVD); B: microvascular flow index 16 (MFI16); C: proportion of perfused vessels (PPV); D: perfusion vessel density (PVD). XBJ: Xuebijing; CLP: cecal ligation and puncture. Compared with the sham group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01; compared with the CLP group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with the XBJ + axitinib group, ΔΔ P<0.01. |

|