Mutual promotion of mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress contributes to mitochondrial-DNA-mediated inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis
|
Mutual promotion of mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress contributes to mitochondrial-DNA-mediated inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis |
| Jie Zhang, Wen-jing Li, Shi-qiang Chen, Ze Chen, Chen Zhang, Ran Ying, Hong-bing Liu, Long-wang Chen, Ya-hui Tang, Zhong-qiu Lu, Guang-ju Zhao |
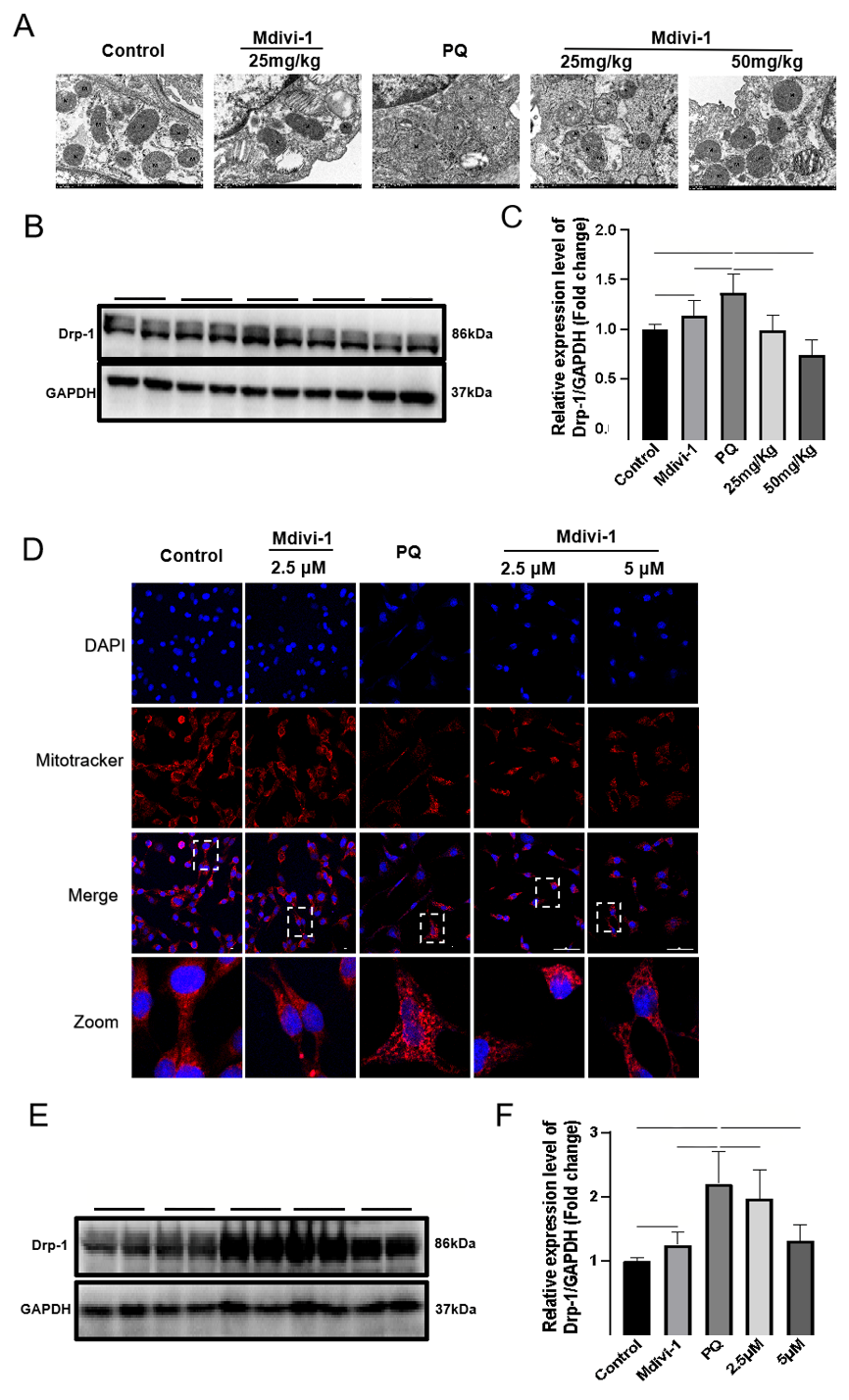
| Figure 1. Effects of Midivi-1 treatment on mitochondrial morphology and Drp1 expression in PQ-induced PF. A: morphological changes in mitochondria in lung tissues observed by transmission electron microscopy (original magnification, ×200); B, C: representative immunoblots and quantitative histogram of Drp1 in lung tissues from mice (n=6); D: MitoTracker? Deep Red FM and DAPI used to stain mitochondria and nuclei, and mitochondrial morphology determined using confocal laser microscopy (original magnification, ×200); E, F: representative immunoblots and quantitative histogram of Drp1 in MLE-12 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. All values are denoted as the mean±SD. PQ: paraquat; Drp-1: dynamin-related protein 1; Midivi-1: mitochondrial division inhibitor-1; PF: pulmonary fibrosis; 25 mg/kg: PQ+Mdivi-1 (25 mg/kg); 50 mg/kg: PQ+Mdivi-1 (50 mg/kg); 2.5 μmol/L: PQ+Mdivi-1 (2.5 μmol/L); 5.0 μmol/L: PQ+Mdivi-1 (5.0 μmol/L); GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ns: not significant. |

|