Protective effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal treatment of hippocampal neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced injury
|
Protective effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal treatment of hippocampal neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced injury |
| Xiao-fang Guo, Shuang-shuang Gu, Jun Wang, Hao Sun, Yu-juan Zhang, Peng-fei Yu, Jin-song Zhang, Lei Jiang |
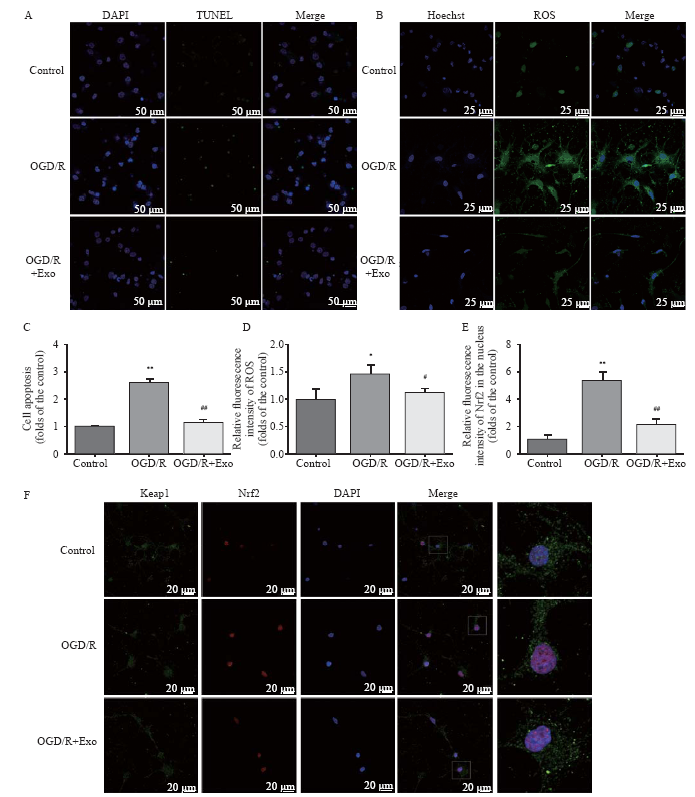
| Figure 2. Protective effects of MSC-Exo against OGD/R-induced injury in rat hippocampal neurons. A, C: the antiapoptotic activity of exosomes based on TUNEL staining; the apoptosis in hippocampal neurons was assessed as the ratio of TUNEL-positive cells to the total number of cells counted within five randomly chosen fields; B, D: intracellular ROS generation; the data were shown as the mean intensities in the entire fields of view in five random graphs and were expressed as the fold intensity relative to the intensity in the control group; E, F: representative images and quantitative analysis indicating the nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with the OGD/R group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01. MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells; MSC-Exo: MSC-derived exosomes; OGD/R: oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion; ROS: reactive oxygen species. |

|