Protective effect of extracorporeal membrane pulmonary oxygenation combined with cardiopulmonary resuscitation on post-resuscitation lung injury
|
Protective effect of extracorporeal membrane pulmonary oxygenation combined with cardiopulmonary resuscitation on post-resuscitation lung injury |
| Ji-yang Ling, Chun-sheng Li, Yun Zhang, Xiao-li Yuan, Bo Liu, Yong Liang, Qiang Zhang |
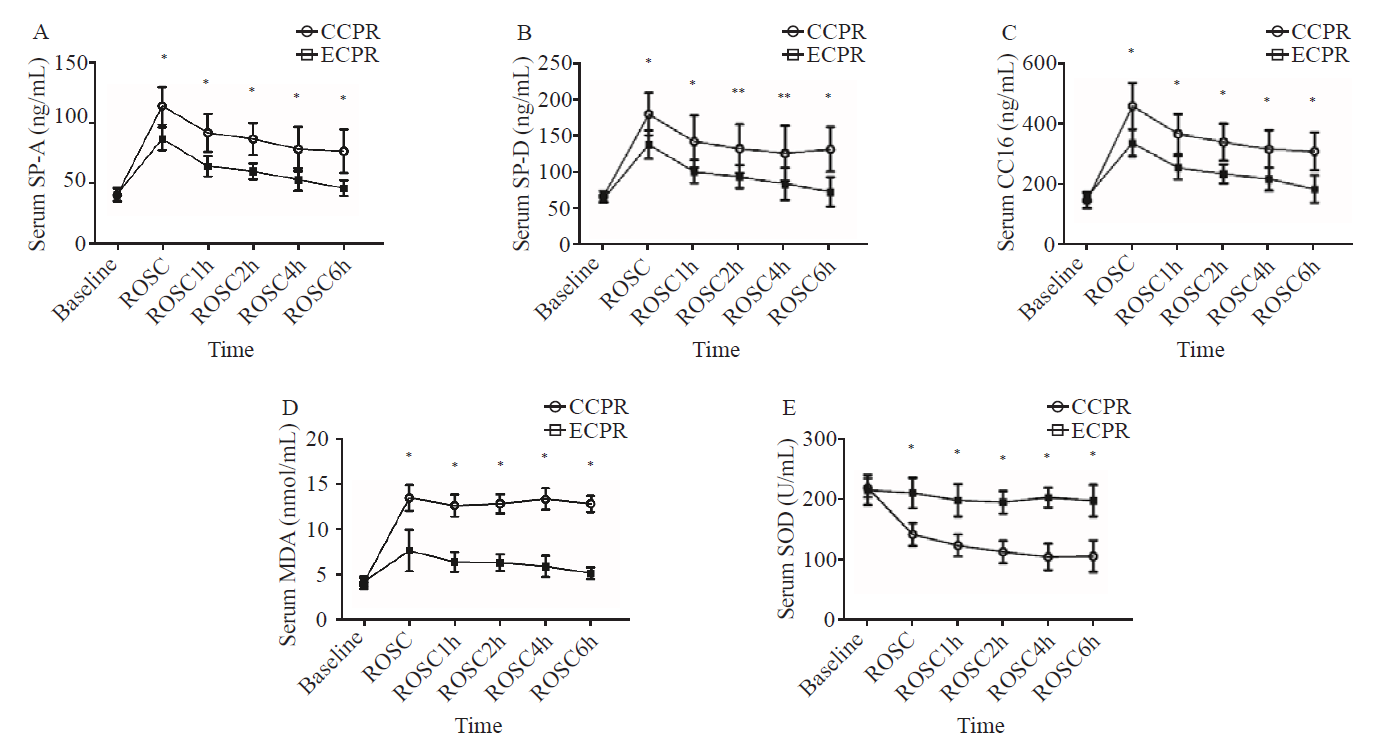
| Figure 1. Comparison of serum markers at each time point between the two groups. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation (n=8); CCPR: conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation; ECPR: extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation; SP-A: surfactant protein A; SP-D: surfactant protein D; CC16: Clara cell protein 16; MDA: malondialdehyde; SOD: superoxide dismutase; ROSC: return of spontaneous circulation; ROSC1h/2h/4h/6h: 1, 2, 4, and 6 hours after ROSC; compared with baseline, *P<0.01, **P <0.05. |

|